Boren Hu
SEER: Self-Aligned Evidence Extraction for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Oct 15, 2024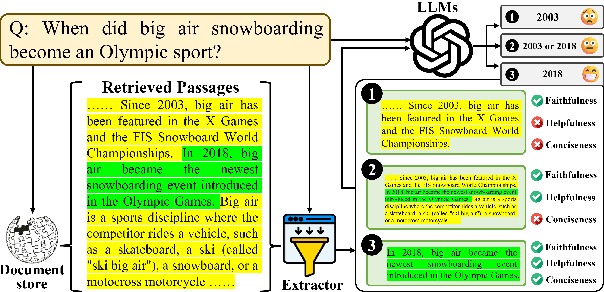
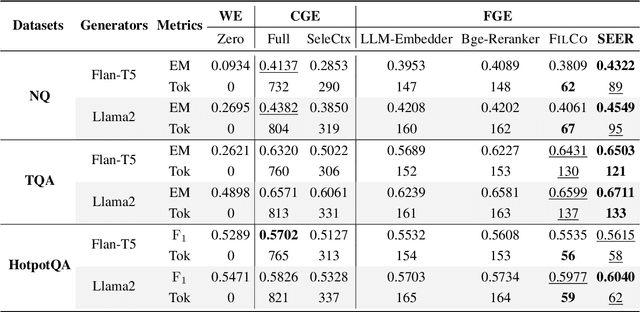
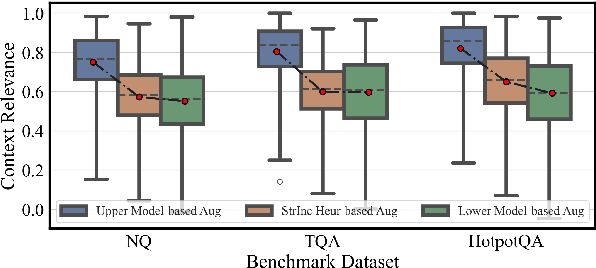
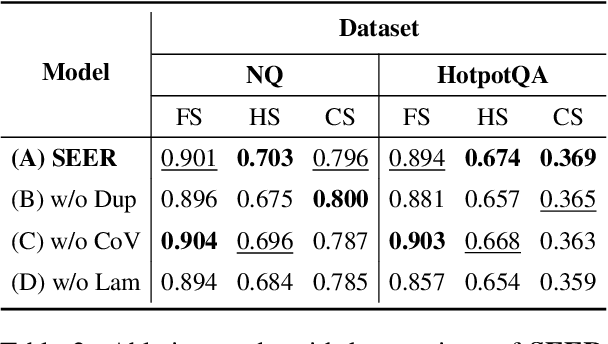
Abstract:Recent studies in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) have investigated extracting evidence from retrieved passages to reduce computational costs and enhance the final RAG performance, yet it remains challenging. Existing methods heavily rely on heuristic-based augmentation, encountering several issues: (1) Poor generalization due to hand-crafted context filtering; (2) Semantics deficiency due to rule-based context chunking; (3) Skewed length due to sentence-wise filter learning. To address these issues, we propose a model-based evidence extraction learning framework, SEER, optimizing a vanilla model as an evidence extractor with desired properties through self-aligned learning. Extensive experiments show that our method largely improves the final RAG performance, enhances the faithfulness, helpfulness, and conciseness of the extracted evidence, and reduces the evidence length by 9.25 times. The code will be available at https://github.com/HITsz-TMG/SEER.
LLaSA: Large Language and E-Commerce Shopping Assistant
Aug 04, 2024Abstract:The e-commerce platform has evolved rapidly due to its widespread popularity and convenience. Developing an e-commerce shopping assistant for customers is crucial to aiding them in quickly finding desired products and recommending precisely what they need. However, most previous shopping assistants face two main problems: (1) task-specificity, which necessitates the development of different models for various tasks, thereby increasing development costs and limiting effectiveness; and (2) poor generalization, where the trained model performs inadequately on up-to-date products. To resolve these issues, we employ Large Language Models (LLMs) to construct an omnipotent assistant, leveraging their adeptness at handling multiple tasks and their superior generalization capability. Nonetheless, LLMs lack inherent knowledge of e-commerce concepts. To address this, we create an instruction dataset comprising 65,000 samples and diverse tasks, termed as EshopInstruct. Through instruction tuning on our dataset, the assistant, named LLaSA, demonstrates the potential to function as an omnipotent assistant. Additionally, we propose various inference optimization strategies to enhance performance with limited inference resources. In the Amazon KDD Cup 2024 Challenge, our proposed method, LLaSA, achieved an overall ranking of 3rd place on ShopBench, including 57 tasks and approximately 20,000 questions, and we secured top-5 rankings in each track, especially in track4, where we achieved the best performance result among all student teams. Our extensive practices fully demonstrate that LLMs possess the great potential to be competent e-commerce shopping assistants.
MMNeuron: Discovering Neuron-Level Domain-Specific Interpretation in Multimodal Large Language Model
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Projecting visual features into word embedding space has become a significant fusion strategy adopted by Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). However, its internal mechanisms have yet to be explored. Inspired by multilingual research, we identify domain-specific neurons in multimodal large language models. Specifically, we investigate the distribution of domain-specific neurons and the mechanism of how MLLMs process features from diverse domains. Furthermore, we propose a three-stage framework for language model modules in MLLMs when handling projected image features, and verify this hypothesis using logit lens. Extensive experiments indicate that while current MLLMs exhibit Visual Question Answering (VQA) capability, they may not fully utilize domain-specific information. Manipulating domain-specific neurons properly will result in a 10\% change of accuracy at most, shedding light on the development of cross-domain, all-encompassing MLLMs in the future. Our code will be released upon paper notification.
SmartBERT: A Promotion of Dynamic Early Exiting Mechanism for Accelerating BERT Inference
Mar 16, 2023Abstract:Dynamic early exiting has been proven to improve the inference speed of the pre-trained language model like BERT. However, all samples must go through all consecutive layers before early exiting and more complex samples usually go through more layers, which still exists redundant computation. In this paper, we propose a novel dynamic early exiting combined with layer skipping for BERT inference named SmartBERT, which adds a skipping gate and an exiting operator into each layer of BERT. SmartBERT can adaptively skip some layers and adaptively choose whether to exit. Besides, we propose cross-layer contrastive learning and combine it into our training phases to boost the intermediate layers and classifiers which would be beneficial for early exiting. To keep the consistent usage of skipping gates between training and inference phases, we propose a hard weight mechanism during training phase. We conduct experiments on eight classification datasets of the GLUE benchmark. Experimental results show that SmartBERT achieves 2-3x computation reduction with minimal accuracy drops compared with BERT and our method outperforms previous methods in both efficiency and accuracy. Moreover, in some complex datasets like RTE and WNLI, we prove that the early exiting based on entropy hardly works, and the skipping mechanism is essential for reducing computation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge