Xiangyu Shi
STEP-LLM: Generating CAD STEP Models from Natural Language with Large Language Models
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Computer-aided design (CAD) is vital to modern manufacturing, yet model creation remains labor-intensive and expertise-heavy. To enable non-experts to translate intuitive design intent into manufacturable artifacts, recent large language models-based text-to-CAD efforts focus on command sequences or script-based formats like CadQuery. However, these formats are kernel-dependent and lack universality for manufacturing. In contrast, the Standard for the Exchange of Product Data (STEP, ISO 10303) file is a widely adopted, neutral boundary representation (B-rep) format directly compatible with manufacturing, but its graph-structured, cross-referenced nature poses unique challenges for auto-regressive LLMs. To address this, we curate a dataset of ~40K STEP-caption pairs and introduce novel preprocessing tailored for the graph-structured format of STEP, including a depth-first search-based reserialization that linearizes cross-references while preserving locality and chain-of-thought(CoT)-style structural annotations that guide global coherence. We integrate retrieval-augmented generation to ground predictions in relevant examples for supervised fine-tuning, and refine generation quality through reinforcement learning with a specific Chamfer Distance-based geometric reward. Experiments demonstrate consistent gains of our STEP-LLM in geometric fidelity over the Text2CAD baseline, with improvements arising from multiple stages of our framework: the RAG module substantially enhances completeness and renderability, the DFS-based reserialization strengthens overall accuracy, and the RL further reduces geometric discrepancy. Both metrics and visual comparisons confirm that STEP-LLM generates shapes with higher fidelity than Text2CAD. These results show the feasibility of LLM-driven STEP model generation from natural language, showing its potential to democratize CAD design for manufacturing.
SpatialNav: Leveraging Spatial Scene Graphs for Zero-Shot Vision-and-Language Navigation
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Although learning-based vision-and-language navigation (VLN) agents can learn spatial knowledge implicitly from large-scale training data, zero-shot VLN agents lack this process, relying primarily on local observations for navigation, which leads to inefficient exploration and a significant performance gap. To deal with the problem, we consider a zero-shot VLN setting that agents are allowed to fully explore the environment before task execution. Then, we construct the Spatial Scene Graph (SSG) to explicitly capture global spatial structure and semantics in the explored environment. Based on the SSG, we introduce SpatialNav, a zero-shot VLN agent that integrates an agent-centric spatial map, a compass-aligned visual representation, and a remote object localization strategy for efficient navigation. Comprehensive experiments in both discrete and continuous environments demonstrate that SpatialNav significantly outperforms existing zero-shot agents and clearly narrows the gap with state-of-the-art learning-based methods. Such results highlight the importance of global spatial representations for generalizable navigation.
When Helpers Become Hazards: A Benchmark for Analyzing Multimodal LLM-Powered Safety in Daily Life
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:As Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) become an indispensable assistant in human life, the unsafe content generated by MLLMs poses a danger to human behavior, perpetually overhanging human society like a sword of Damocles. To investigate and evaluate the safety impact of MLLMs responses on human behavior in daily life, we introduce SaLAD, a multimodal safety benchmark which contains 2,013 real-world image-text samples across 10 common categories, with a balanced design covering both unsafe scenarios and cases of oversensitivity. It emphasizes realistic risk exposure, authentic visual inputs, and fine-grained cross-modal reasoning, ensuring that safety risks cannot be inferred from text alone. We further propose a safety-warning-based evaluation framework that encourages models to provide clear and informative safety warnings, rather than generic refusals. Results on 18 MLLMs demonstrate that the top-performing models achieve a safe response rate of only 57.2% on unsafe queries. Moreover, even popular safety alignment methods limit effectiveness of the models in our scenario, revealing the vulnerabilities of current MLLMs in identifying dangerous behaviors in daily life. Our dataset is available at https://github.com/xinyuelou/SaLAD.
DS-ProGen: A Dual-Structure Deep Language Model for Functional Protein Design
May 18, 2025Abstract:Inverse Protein Folding (IPF) is a critical subtask in the field of protein design, aiming to engineer amino acid sequences capable of folding correctly into a specified three-dimensional (3D) conformation. Although substantial progress has been achieved in recent years, existing methods generally rely on either backbone coordinates or molecular surface features alone, which restricts their ability to fully capture the complex chemical and geometric constraints necessary for precise sequence prediction. To address this limitation, we present DS-ProGen, a dual-structure deep language model for functional protein design, which integrates both backbone geometry and surface-level representations. By incorporating backbone coordinates as well as surface chemical and geometric descriptors into a next-amino-acid prediction paradigm, DS-ProGen is able to generate functionally relevant and structurally stable sequences while satisfying both global and local conformational constraints. On the PRIDE dataset, DS-ProGen attains the current state-of-the-art recovery rate of 61.47%, demonstrating the synergistic advantage of multi-modal structural encoding in protein design. Furthermore, DS-ProGen excels in predicting interactions with a variety of biological partners, including ligands, ions, and RNA, confirming its robust functional retention capabilities.
Think in Safety: Unveiling and Mitigating Safety Alignment Collapse in Multimodal Large Reasoning Model
May 10, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of multimodal large reasoning models (MLRMs) has demonstrated broad application potential, yet their safety and reliability remain critical concerns that require systematic exploration. To address this gap, we conduct a comprehensive and systematic safety evaluation of 11 MLRMs across 5 benchmarks and unveil prevalent safety degradation phenomena in most advanced models. Moreover, our analysis reveals distinct safety patterns across different benchmarks: significant safety degradation is observed across jailbreak robustness benchmarks, whereas safety-awareness benchmarks demonstrate less pronounced degradation. In particular, a long thought process in some scenarios even enhances safety performance. Therefore, it is a potential approach to addressing safety issues in MLRMs by leveraging the intrinsic reasoning capabilities of the model to detect unsafe intent. To operationalize this insight, we construct a multimodal tuning dataset that incorporates a safety-oriented thought process. Experimental results from fine-tuning existing MLRMs with this dataset effectively enhances the safety on both jailbreak robustness and safety-awareness benchmarks. This study provides a new perspective for developing safe MLRMs. Our dataset is available at https://github.com/xinyuelou/Think-in-Safety.
SmartWay: Enhanced Waypoint Prediction and Backtracking for Zero-Shot Vision-and-Language Navigation
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) in continuous environments requires agents to interpret natural language instructions while navigating unconstrained 3D spaces. Existing VLN-CE frameworks rely on a two-stage approach: a waypoint predictor to generate waypoints and a navigator to execute movements. However, current waypoint predictors struggle with spatial awareness, while navigators lack historical reasoning and backtracking capabilities, limiting adaptability. We propose a zero-shot VLN-CE framework integrating an enhanced waypoint predictor with a Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM)-based navigator. Our predictor employs a stronger vision encoder, masked cross-attention fusion, and an occupancy-aware loss for better waypoint quality. The navigator incorporates history-aware reasoning and adaptive path planning with backtracking, improving robustness. Experiments on R2R-CE and MP3D benchmarks show our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in zero-shot settings, demonstrating competitive results compared to fully supervised methods. Real-world validation on Turtlebot 4 further highlights its adaptability.
Large Language Models in Bioinformatics: A Survey
Mar 06, 2025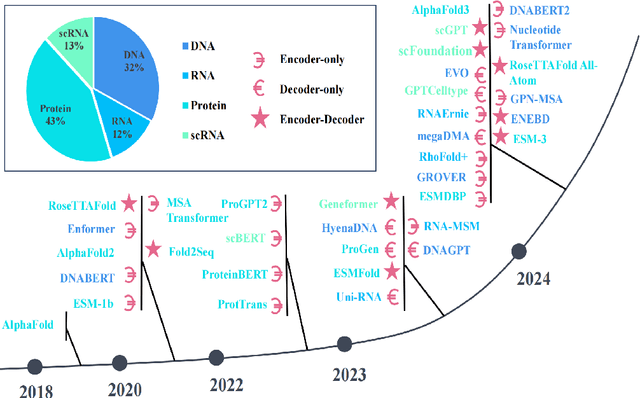
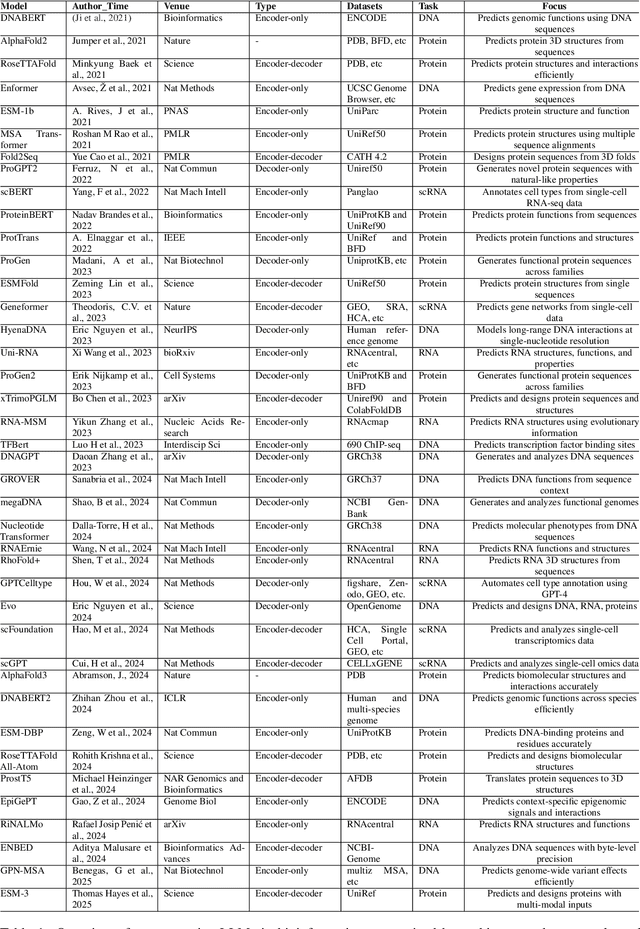
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are revolutionizing bioinformatics, enabling advanced analysis of DNA, RNA, proteins, and single-cell data. This survey provides a systematic review of recent advancements, focusing on genomic sequence modeling, RNA structure prediction, protein function inference, and single-cell transcriptomics. Meanwhile, we also discuss several key challenges, including data scarcity, computational complexity, and cross-omics integration, and explore future directions such as multimodal learning, hybrid AI models, and clinical applications. By offering a comprehensive perspective, this paper underscores the transformative potential of LLMs in driving innovations in bioinformatics and precision medicine.
EUR/USD Exchange Rate Forecasting incorporating Text Mining Based on Pre-trained Language Models and Deep Learning Methods
Nov 12, 2024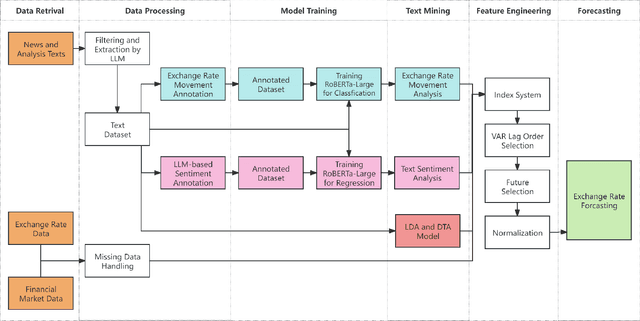
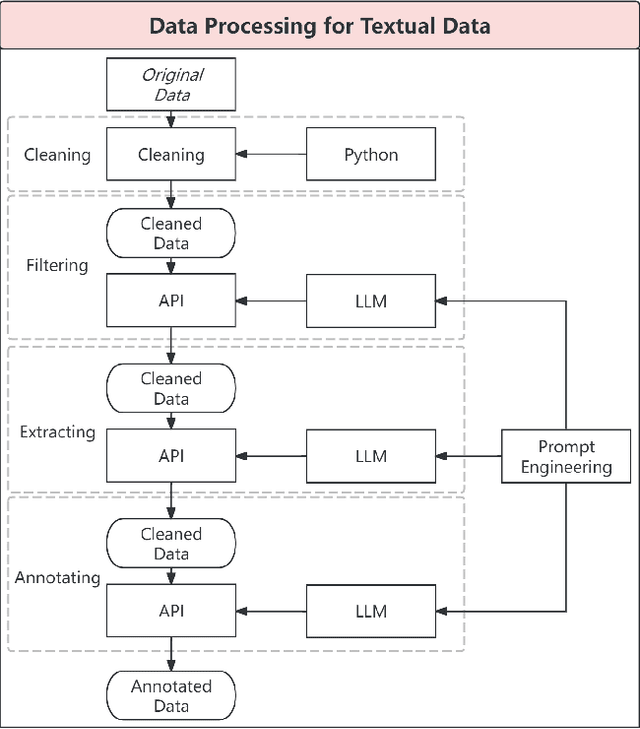
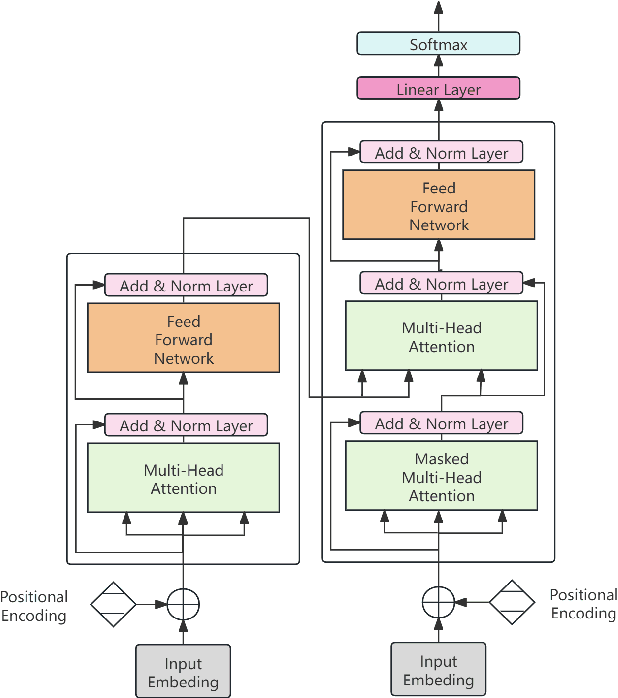
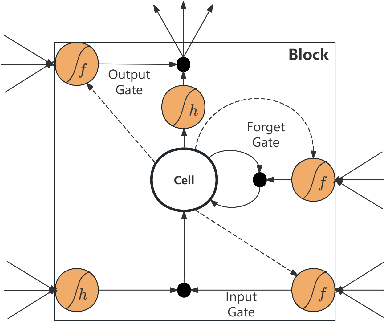
Abstract:This study introduces a novel approach for EUR/USD exchange rate forecasting that integrates deep learning, textual analysis, and particle swarm optimization (PSO). By incorporating online news and analysis texts as qualitative data, the proposed PSO-LSTM model demonstrates superior performance compared to traditional econometric and machine learning models. The research employs advanced text mining techniques, including sentiment analysis using the RoBERTa-Large model and topic modeling with LDA. Empirical findings underscore the significant advantage of incorporating textual data, with the PSO-LSTM model outperforming benchmark models such as SVM, SVR, ARIMA, and GARCH. Ablation experiments reveal the contribution of each textual data category to the overall forecasting performance. The study highlights the transformative potential of artificial intelligence in finance and paves the way for future research in real-time forecasting and the integration of alternative data sources.
TransportationGames: Benchmarking Transportation Knowledge of (Multimodal) Large Language Models
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) and multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown excellent general capabilities, even exhibiting adaptability in many professional domains such as law, economics, transportation, and medicine. Currently, many domain-specific benchmarks have been proposed to verify the performance of (M)LLMs in specific fields. Among various domains, transportation plays a crucial role in modern society as it impacts the economy, the environment, and the quality of life for billions of people. However, it is unclear how much traffic knowledge (M)LLMs possess and whether they can reliably perform transportation-related tasks. To address this gap, we propose TransportationGames, a carefully designed and thorough evaluation benchmark for assessing (M)LLMs in the transportation domain. By comprehensively considering the applications in real-world scenarios and referring to the first three levels in Bloom's Taxonomy, we test the performance of various (M)LLMs in memorizing, understanding, and applying transportation knowledge by the selected tasks. The experimental results show that although some models perform well in some tasks, there is still much room for improvement overall. We hope the release of TransportationGames can serve as a foundation for future research, thereby accelerating the implementation and application of (M)LLMs in the transportation domain.
Towards Faster k-Nearest-Neighbor Machine Translation
Dec 12, 2023



Abstract:Recent works have proven the effectiveness of k-nearest-neighbor machine translation(a.k.a kNN-MT) approaches to produce remarkable improvement in cross-domain translations. However, these models suffer from heavy retrieve overhead on the entire datastore when decoding each token. We observe that during the decoding phase, about 67% to 84% of tokens are unvaried after searching over the corpus datastore, which means most of the tokens cause futile retrievals and introduce unnecessary computational costs by initiating k-nearest-neighbor searches. We consider this phenomenon is explainable in linguistics and propose a simple yet effective multi-layer perceptron (MLP) network to predict whether a token should be translated jointly by the neural machine translation model and probabilities produced by the kNN or just by the neural model. The results show that our method succeeds in reducing redundant retrieval operations and significantly reduces the overhead of kNN retrievals by up to 53% at the expense of a slight decline in translation quality. Moreover, our method could work together with all existing kNN-MT systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge