You Li
NRCIEA
Imagination Helps Visual Reasoning, But Not Yet in Latent Space
Feb 26, 2026Abstract:Latent visual reasoning aims to mimic human's imagination process by meditating through hidden states of Multimodal Large Language Models. While recognized as a promising paradigm for visual reasoning, the underlying mechanisms driving its effectiveness remain unclear. Motivated to demystify the true source of its efficacy, we investigate the validity of latent reasoning using Causal Mediation Analysis. We model the process as a causal chain: the input as the treatment, the latent tokens as the mediator, and the final answer as the outcome. Our findings uncover two critical disconnections: (a) Input-Latent Disconnect: dramatic perturbations on the input result in negligible changes to the latent tokens, suggesting that latent tokens do not effectively attend to the input sequence. (b) Latent-Answer Disconnect: perturbations on the latent tokens yield minimal impact on the final answer, indicating the limited causal effect latent tokens imposing on the outcome. Furthermore, extensive probing analysis reveals that latent tokens encode limited visual information and exhibit high similarity. Consequently, we challenge the necessity of latent reasoning and propose a straightforward alternative named CapImagine, which teaches the model to explicitly imagine using text. Experiments on vision-centric benchmarks show that CapImagine significantly outperforms complex latent-space baselines, highlighting the superior potential of visual reasoning through explicit imagination.
LLA: Enhancing Security and Privacy for Generative Models with Logic-Locked Accelerators
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce LLA, an effective intellectual property (IP) protection scheme for generative AI models. LLA leverages the synergy between hardware and software to defend against various supply chain threats, including model theft, model corruption, and information leakage. On the software side, it embeds key bits into neurons that can trigger outliers to degrade performance and applies invariance transformations to obscure the key values. On the hardware side, it integrates a lightweight locking module into the AI accelerator while maintaining compatibility with various dataflow patterns and toolchains. An accelerator with a pre-stored secret key acts as a license to access the model services provided by the IP owner. The evaluation results show that LLA can withstand a broad range of oracle-guided key optimization attacks, while incurring a minimal computational overhead of less than 0.1% for 7,168 key bits.
Simultaneous Enhancement and Noise Suppression under Complex Illumination Conditions
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Under challenging light conditions, captured images often suffer from various degradations, leading to a decline in the performance of vision-based applications. Although numerous methods have been proposed to enhance image quality, they either significantly amplify inherent noise or are only effective under specific illumination conditions. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework for simultaneous enhancement and noise suppression under complex illumination conditions. Firstly, a gradient-domain weighted guided filter (GDWGIF) is employed to accurately estimate illumination and improve image quality. Next, the Retinex model is applied to decompose the captured image into separate illumination and reflection layers. These layers undergo parallel processing, with the illumination layer being corrected to optimize lighting conditions and the reflection layer enhanced to improve image quality. Finally, the dynamic range of the image is optimized through multi-exposure fusion and a linear stretching strategy. The proposed method is evaluated on real-world datasets obtained from practical applications. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method achieves better performance compared to state-of-the-art methods in both contrast enhancement and noise suppression.
One Model for All: Universal Pre-training for EEG based Emotion Recognition across Heterogeneous Datasets and Paradigms
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:EEG-based emotion recognition is hampered by profound dataset heterogeneity (channel/subject variability), hindering generalizable models. Existing approaches struggle to transfer knowledge effectively. We propose 'One Model for All', a universal pre-training framework for EEG analysis across disparate datasets. Our paradigm decouples learning into two stages: (1) Univariate pre-training via self-supervised contrastive learning on individual channels, enabled by a Unified Channel Schema (UCS) that leverages the channel union (e.g., SEED-62ch, DEAP-32ch); (2) Multivariate fine-tuning with a novel 'ART' (Adaptive Resampling Transformer) and 'GAT' (Graph Attention Network) architecture to capture complex spatio-temporal dependencies. Experiments show universal pre-training is an essential stabilizer, preventing collapse on SEED (vs. scratch) and yielding substantial gains on DEAP (+7.65%) and DREAMER (+3.55%). Our framework achieves new SOTA performance on all within-subject benchmarks: SEED (99.27%), DEAP (93.69%), and DREAMER (93.93%). We also show SOTA cross-dataset transfer, achieving 94.08% (intersection) and 93.05% (UCS) on the unseen DREAMER dataset, with the former surpassing the within-domain pre-training benchmark. Ablation studies validate our architecture: the GAT module is critical, yielding a +22.19% gain over GCN on the high-noise DEAP dataset, and its removal causes a catastrophic -16.44% performance drop. This work paves the way for more universal, scalable, and effective pre-trained models for diverse EEG analysis tasks.
Think in Safety: Unveiling and Mitigating Safety Alignment Collapse in Multimodal Large Reasoning Model
May 10, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of multimodal large reasoning models (MLRMs) has demonstrated broad application potential, yet their safety and reliability remain critical concerns that require systematic exploration. To address this gap, we conduct a comprehensive and systematic safety evaluation of 11 MLRMs across 5 benchmarks and unveil prevalent safety degradation phenomena in most advanced models. Moreover, our analysis reveals distinct safety patterns across different benchmarks: significant safety degradation is observed across jailbreak robustness benchmarks, whereas safety-awareness benchmarks demonstrate less pronounced degradation. In particular, a long thought process in some scenarios even enhances safety performance. Therefore, it is a potential approach to addressing safety issues in MLRMs by leveraging the intrinsic reasoning capabilities of the model to detect unsafe intent. To operationalize this insight, we construct a multimodal tuning dataset that incorporates a safety-oriented thought process. Experimental results from fine-tuning existing MLRMs with this dataset effectively enhances the safety on both jailbreak robustness and safety-awareness benchmarks. This study provides a new perspective for developing safe MLRMs. Our dataset is available at https://github.com/xinyuelou/Think-in-Safety.
HSS-IAD: A Heterogeneous Same-Sort Industrial Anomaly Detection Dataset
Apr 17, 2025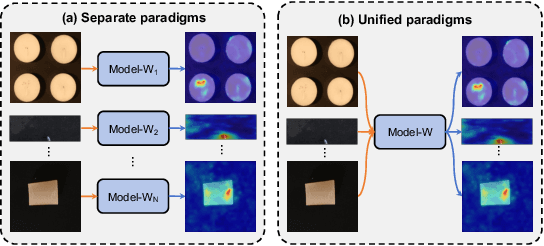
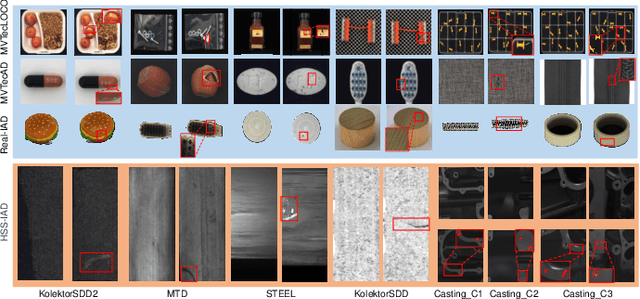
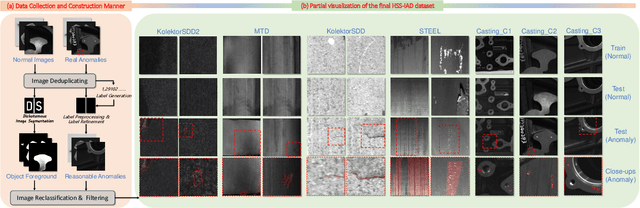
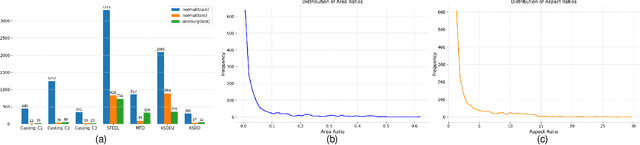
Abstract:Multi-class Unsupervised Anomaly Detection algorithms (MUAD) are receiving increasing attention due to their relatively low deployment costs and improved training efficiency. However, the real-world effectiveness of MUAD methods is questioned due to limitations in current Industrial Anomaly Detection (IAD) datasets. These datasets contain numerous classes that are unlikely to be produced by the same factory and fail to cover multiple structures or appearances. Additionally, the defects do not reflect real-world characteristics. Therefore, we introduce the Heterogeneous Same-Sort Industrial Anomaly Detection (HSS-IAD) dataset, which contains 8,580 images of metallic-like industrial parts and precise anomaly annotations. These parts exhibit variations in structure and appearance, with subtle defects that closely resemble the base materials. We also provide foreground images for synthetic anomaly generation. Finally, we evaluate popular IAD methods on this dataset under multi-class and class-separated settings, demonstrating its potential to bridge the gap between existing datasets and real factory conditions. The dataset is available at https://github.com/Qiqigeww/HSS-IAD-Dataset.
OmniGeo: Towards a Multimodal Large Language Models for Geospatial Artificial Intelligence
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of multimodal large language models (LLMs) has opened new frontiers in artificial intelligence, enabling the integration of diverse large-scale data types such as text, images, and spatial information. In this paper, we explore the potential of multimodal LLMs (MLLM) for geospatial artificial intelligence (GeoAI), a field that leverages spatial data to address challenges in domains including Geospatial Semantics, Health Geography, Urban Geography, Urban Perception, and Remote Sensing. We propose a MLLM (OmniGeo) tailored to geospatial applications, capable of processing and analyzing heterogeneous data sources, including satellite imagery, geospatial metadata, and textual descriptions. By combining the strengths of natural language understanding and spatial reasoning, our model enhances the ability of instruction following and the accuracy of GeoAI systems. Results demonstrate that our model outperforms task-specific models and existing LLMs on diverse geospatial tasks, effectively addressing the multimodality nature while achieving competitive results on the zero-shot geospatial tasks. Our code will be released after publication.
Migician: Revealing the Magic of Free-Form Multi-Image Grounding in Multimodal Large Language Models
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:The recent advancement of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has significantly improved their fine-grained perception of single images and general comprehension across multiple images. However, existing MLLMs still face challenges in achieving precise grounding in complex multi-image scenarios. To address this, we first explore a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) framework that integrates single-image grounding with multi-image comprehension. While partially effective, it remains unstable and struggles to capture abstract visual information due to its non-end-to-end nature. Therefore, we introduce Migician, the first multi-image grounding model capable of performing free-form and accurate grounding across multiple images. To support this, we present the MGrounding-630k dataset, which comprises data for several multi-image grounding tasks derived from existing datasets, along with newly generated free-form grounding instruction-following data. Furthermore, we propose MIG-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark specifically designed for evaluating multi-image grounding capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves significantly superior multi-image grounding capabilities, outperforming the best existing MLLMs by 21.61% and even surpassing much larger 70B models. Our code, model, dataset, and benchmark are fully open-sourced at https://migician-vg.github.io/.
A Real-time Degeneracy Sensing and Compensation Method for Enhanced LiDAR SLAM
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:LiDAR is widely used in Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) and autonomous driving. The LiDAR odometry is of great importance in multi-sensor fusion. However, in some unstructured environments, the point cloud registration cannot constrain the poses of the LiDAR due to its sparse geometric features, which leads to the degeneracy of multi-sensor fusion accuracy. To address this problem, we propose a novel real-time approach to sense and compensate for the degeneracy of LiDAR. Firstly, this paper introduces the degeneracy factor with clear meaning, which can measure the degeneracy of LiDAR. Then, the Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) clustering method adaptively perceives the degeneracy with better environmental generalization. Finally, the degeneracy perception results are utilized to fuse LiDAR and IMU, thus effectively resisting degeneracy effects. Experiments on our dataset show the method's high accuracy and robustness and validate our algorithm's adaptability to different environments and LiDAR scanning modalities.
AC-LIO: Towards Asymptotic and Consistent Convergence in LiDAR-Inertial Odometry
Dec 08, 2024



Abstract:Existing LiDAR-Inertial Odometry (LIO) frameworks typically utilize prior state trajectories derived from IMU integration to compensate for the motion distortion within LiDAR frames, and demonstrate outstanding accuracy and stability in regular low-speed and smooth scenes. However, in high-speed or intense motion scenarios, the residual distortion may increase due to the limitation of IMU's accuracy and frequency, which will degrade the consistency between the LiDAR frame with its represented geometric environment, leading pointcloud registration to fall into local optima and consequently increasing the drift in long-time and large-scale localization. To address the issue, we propose a novel asymptotically and consistently converging LIO framework called AC-LIO. First, during the iterative state estimation, we backwards propagate the update term based on the prior state chain, and asymptotically compensate the residual distortion before next iteration. Second, considering the weak correlation between the initial error and motion distortion of current frame, we propose a convergence criteria based on pointcloud constraints to control the back propagation. The approach of guiding the asymptotic distortion compensation based on convergence criteria can promote the consistent convergence of pointcloud registration and increase the accuracy and robustness of LIO. Experiments show that our AC-LIO framework, compared to other state-of-the-art frameworks, effectively promotes consistent convergence in state estimation and further improves the accuracy of long-time and large-scale localization and mapping.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge