Xiangkun Hu
InnovatorBench: Evaluating Agents' Ability to Conduct Innovative LLM Research
Nov 03, 2025



Abstract:AI agents could accelerate scientific discovery by automating hypothesis formation, experiment design, coding, execution, and analysis, yet existing benchmarks probe narrow skills in simplified settings. To address this gap, we introduce InnovatorBench, a benchmark-platform pair for realistic, end-to-end assessment of agents performing Large Language Model (LLM) research. It comprises 20 tasks spanning Data Construction, Filtering, Augmentation, Loss Design, Reward Design, and Scaffold Construction, which require runnable artifacts and assessment of correctness, performance, output quality, and uncertainty. To support agent operation, we develop ResearchGym, a research environment offering rich action spaces, distributed and long-horizon execution, asynchronous monitoring, and snapshot saving. We also implement a lightweight ReAct agent that couples explicit reasoning with executable planning using frontier models such as Claude-4, GPT-5, GLM-4.5, and Kimi-K2. Our experiments demonstrate that while frontier models show promise in code-driven research tasks, they struggle with fragile algorithm-related tasks and long-horizon decision making, such as impatience, poor resource management, and overreliance on template-based reasoning. Furthermore, agents require over 11 hours to achieve their best performance on InnovatorBench, underscoring the benchmark's difficulty and showing the potential of InnovatorBench to be the next generation of code-based research benchmark.
DatasetResearch: Benchmarking Agent Systems for Demand-Driven Dataset Discovery
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models has fundamentally shifted the bottleneck in AI development from computational power to data availability-with countless valuable datasets remaining hidden across specialized repositories, research appendices, and domain platforms. As reasoning capabilities and deep research methodologies continue to evolve, a critical question emerges: can AI agents transcend conventional search to systematically discover any dataset that meets specific user requirements, enabling truly autonomous demand-driven data curation? We introduce DatasetResearch, the first comprehensive benchmark evaluating AI agents' ability to discover and synthesize datasets from 208 real-world demands across knowledge-intensive and reasoning-intensive tasks. Our tri-dimensional evaluation framework reveals a stark reality: even advanced deep research systems achieve only 22% score on our challenging DatasetResearch-pro subset, exposing the vast gap between current capabilities and perfect dataset discovery. Our analysis uncovers a fundamental dichotomy-search agents excel at knowledge tasks through retrieval breadth, while synthesis agents dominate reasoning challenges via structured generation-yet both catastrophically fail on "corner cases" outside existing distributions. These findings establish the first rigorous baseline for dataset discovery agents and illuminate the path toward AI systems capable of finding any dataset in the digital universe. Our benchmark and comprehensive analysis provide the foundation for the next generation of self-improving AI systems and are publicly available at https://github.com/GAIR-NLP/DatasetResearch.
AlphaGo Moment for Model Architecture Discovery
Jul 24, 2025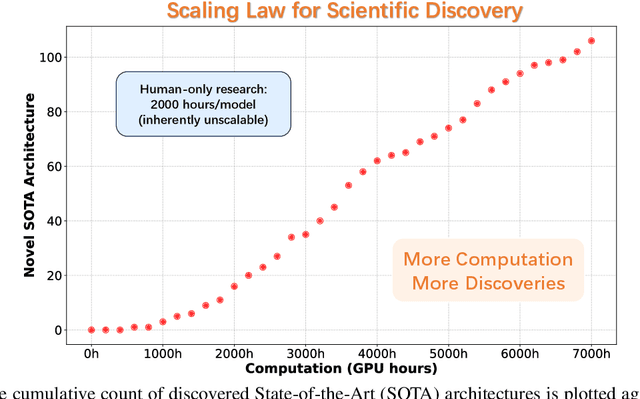
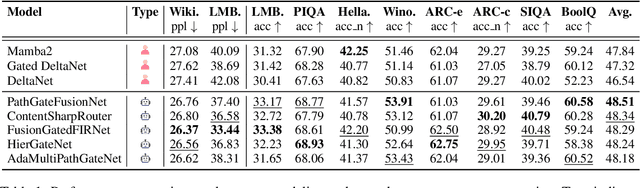
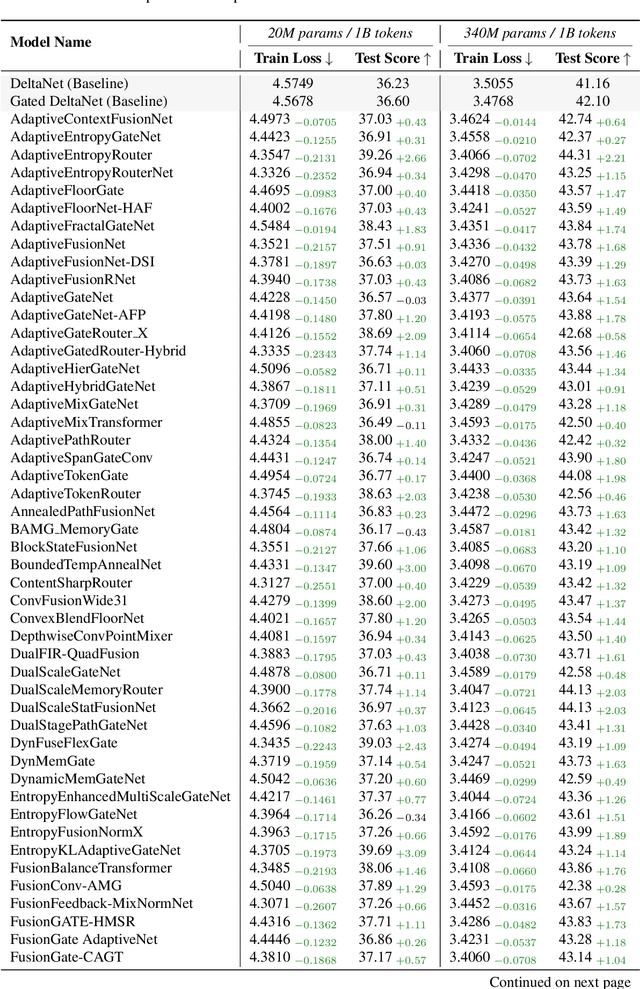
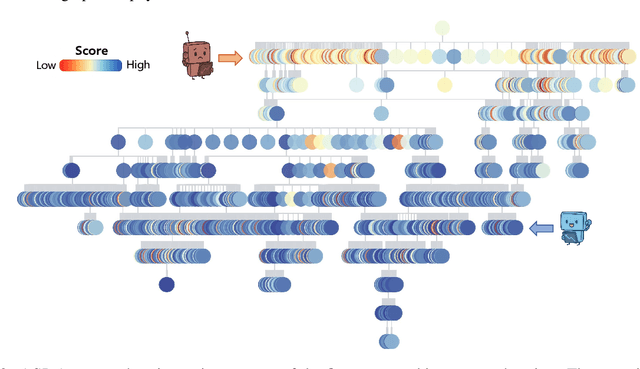
Abstract:While AI systems demonstrate exponentially improving capabilities, the pace of AI research itself remains linearly bounded by human cognitive capacity, creating an increasingly severe development bottleneck. We present ASI-Arch, the first demonstration of Artificial Superintelligence for AI research (ASI4AI) in the critical domain of neural architecture discovery--a fully autonomous system that shatters this fundamental constraint by enabling AI to conduct its own architectural innovation. Moving beyond traditional Neural Architecture Search (NAS), which is fundamentally limited to exploring human-defined spaces, we introduce a paradigm shift from automated optimization to automated innovation. ASI-Arch can conduct end-to-end scientific research in the domain of architecture discovery, autonomously hypothesizing novel architectural concepts, implementing them as executable code, training and empirically validating their performance through rigorous experimentation and past experience. ASI-Arch conducted 1,773 autonomous experiments over 20,000 GPU hours, culminating in the discovery of 106 innovative, state-of-the-art (SOTA) linear attention architectures. Like AlphaGo's Move 37 that revealed unexpected strategic insights invisible to human players, our AI-discovered architectures demonstrate emergent design principles that systematically surpass human-designed baselines and illuminate previously unknown pathways for architectural innovation. Crucially, we establish the first empirical scaling law for scientific discovery itself--demonstrating that architectural breakthroughs can be scaled computationally, transforming research progress from a human-limited to a computation-scalable process. We provide comprehensive analysis of the emergent design patterns and autonomous research capabilities that enabled these breakthroughs, establishing a blueprint for self-accelerating AI systems.
Quantifying Fairness in LLMs Beyond Tokens: A Semantic and Statistical Perspective
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) often generate responses with inherent biases, undermining their reliability in real-world applications. Existing evaluation methods often overlook biases in long-form responses and the intrinsic variability of LLM outputs. To address these challenges, we propose FiSCo(Fine-grained Semantic Computation), a novel statistical framework to evaluate group-level fairness in LLMs by detecting subtle semantic differences in long-form responses across demographic groups. Unlike prior work focusing on sentiment or token-level comparisons, FiSCo goes beyond surface-level analysis by operating at the claim level, leveraging entailment checks to assess the consistency of meaning across responses. We decompose model outputs into semantically distinct claims and apply statistical hypothesis testing to compare inter- and intra-group similarities, enabling robust detection of subtle biases. We formalize a new group counterfactual fairness definition and validate FiSCo on both synthetic and human-annotated datasets spanning gender, race, and age. Experiments show that FiSco more reliably identifies nuanced biases while reducing the impact of stochastic LLM variability, outperforming various evaluation metrics.
Explicit Preference Optimization: No Need for an Implicit Reward Model
Jun 09, 2025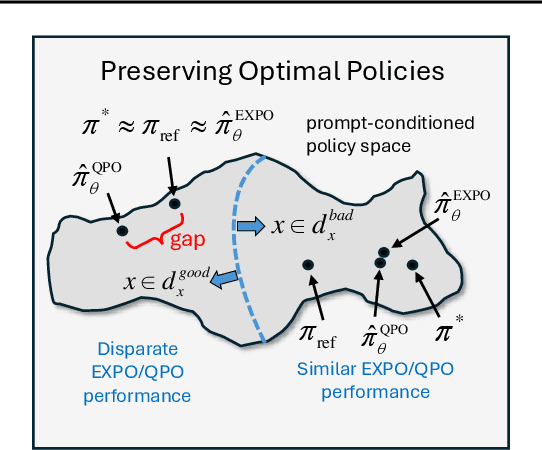
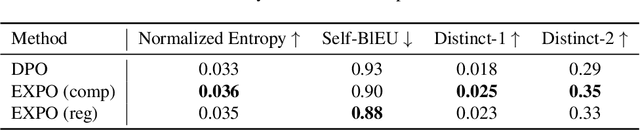
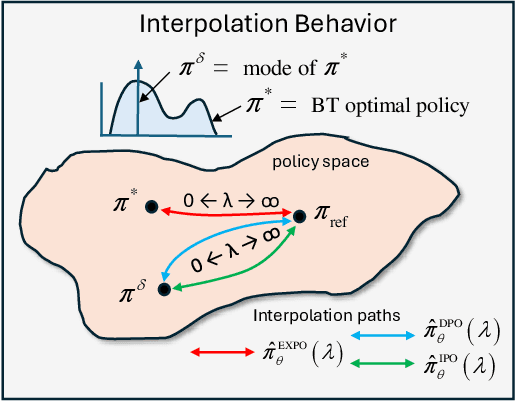
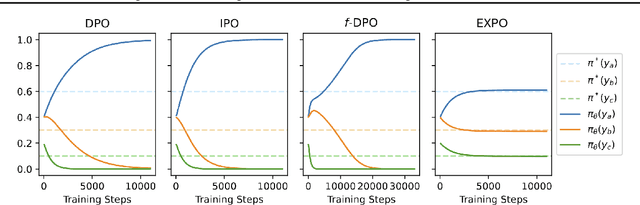
Abstract:The generated responses of large language models (LLMs) are often fine-tuned to human preferences through a process called reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). As RLHF relies on a challenging training sequence, whereby a separate reward model is independently learned and then later applied to LLM policy updates, ongoing research effort has targeted more straightforward alternatives. In this regard, direct preference optimization (DPO) and its many offshoots circumvent the need for a separate reward training step. Instead, through the judicious use of a reparameterization trick that induces an \textit{implicit} reward, DPO and related methods consolidate learning to the minimization of a single loss function. And yet despite demonstrable success in some real-world settings, we prove that DPO-based objectives are nonetheless subject to sub-optimal regularization and counter-intuitive interpolation behaviors, underappreciated artifacts of the reparameterizations upon which they are based. To this end, we introduce an \textit{explicit} preference optimization framework termed EXPO that requires no analogous reparameterization to achieve an implicit reward. Quite differently, we merely posit intuitively-appealing regularization factors from scratch that transparently avoid the potential pitfalls of key DPO variants, provably satisfying regularization desiderata that prior methods do not. Empirical results serve to corroborate our analyses and showcase the efficacy of EXPO.
Generative AI Act II: Test Time Scaling Drives Cognition Engineering
Apr 21, 2025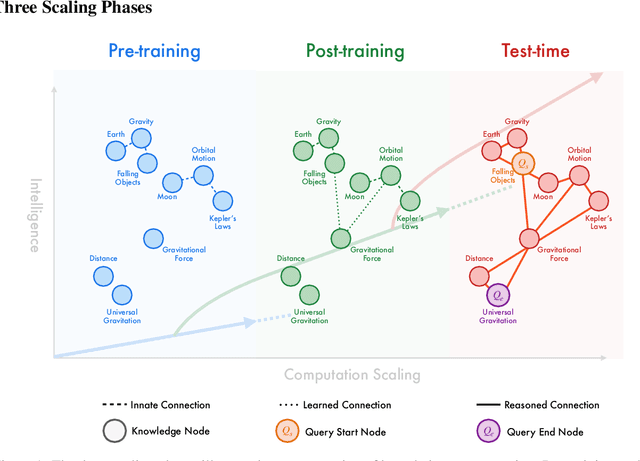
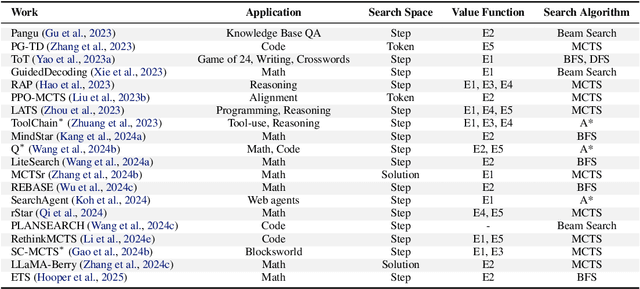
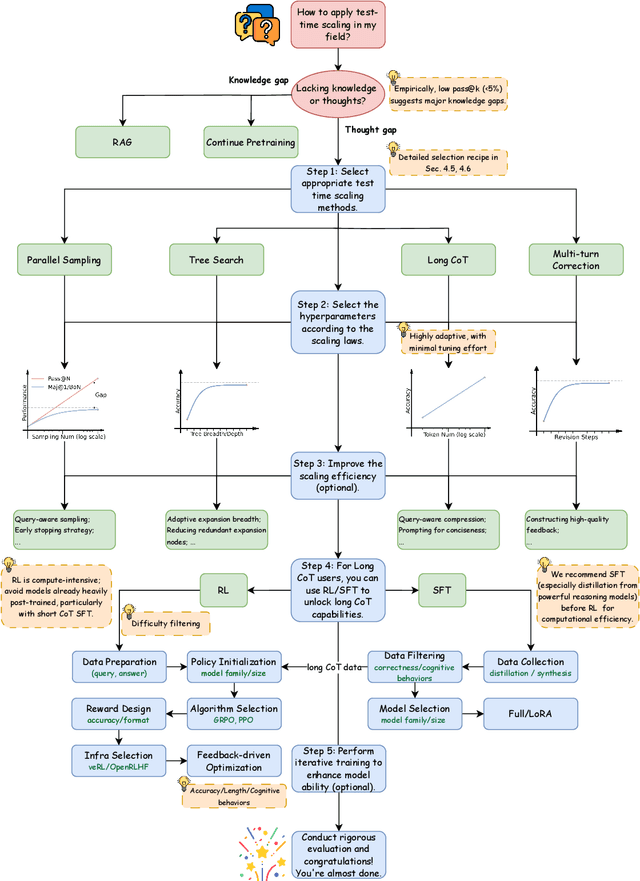
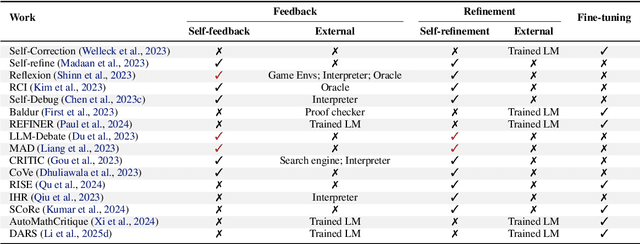
Abstract:The first generation of Large Language Models - what might be called "Act I" of generative AI (2020-2023) - achieved remarkable success through massive parameter and data scaling, yet exhibited fundamental limitations such as knowledge latency, shallow reasoning, and constrained cognitive processes. During this era, prompt engineering emerged as our primary interface with AI, enabling dialogue-level communication through natural language. We now witness the emergence of "Act II" (2024-present), where models are transitioning from knowledge-retrieval systems (in latent space) to thought-construction engines through test-time scaling techniques. This new paradigm establishes a mind-level connection with AI through language-based thoughts. In this paper, we clarify the conceptual foundations of cognition engineering and explain why this moment is critical for its development. We systematically break down these advanced approaches through comprehensive tutorials and optimized implementations, democratizing access to cognition engineering and enabling every practitioner to participate in AI's second act. We provide a regularly updated collection of papers on test-time scaling in the GitHub Repository: https://github.com/GAIR-NLP/cognition-engineering
DeepResearcher: Scaling Deep Research via Reinforcement Learning in Real-world Environments
Apr 07, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) equipped with web search capabilities have demonstrated impressive potential for deep research tasks. However, current approaches predominantly rely on either manually engineered prompts (prompt engineering-based) with brittle performance or reinforcement learning within controlled Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) environments (RAG-based) that fail to capture the complexities of real-world interaction. In this paper, we introduce DeepResearcher, the first comprehensive framework for end-to-end training of LLM-based deep research agents through scaling reinforcement learning (RL) in real-world environments with authentic web search interactions. Unlike RAG-based approaches that assume all necessary information exists within a fixed corpus, our method trains agents to navigate the noisy, unstructured, and dynamic nature of the open web. We implement a specialized multi-agent architecture where browsing agents extract relevant information from various webpage structures and overcoming significant technical challenges. Extensive experiments on open-domain research tasks demonstrate that DeepResearcher achieves substantial improvements of up to 28.9 points over prompt engineering-based baselines and up to 7.2 points over RAG-based RL agents. Our qualitative analysis reveals emergent cognitive behaviors from end-to-end RL training, including the ability to formulate plans, cross-validate information from multiple sources, engage in self-reflection to redirect research, and maintain honesty when unable to find definitive answers. Our results highlight that end-to-end training in real-world web environments is not merely an implementation detail but a fundamental requirement for developing robust research capabilities aligned with real-world applications. We release DeepResearcher at https://github.com/GAIR-NLP/DeepResearcher.
PC Agent: While You Sleep, AI Works -- A Cognitive Journey into Digital World
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Imagine a world where AI can handle your work while you sleep - organizing your research materials, drafting a report, or creating a presentation you need for tomorrow. However, while current digital agents can perform simple tasks, they are far from capable of handling the complex real-world work that humans routinely perform. We present PC Agent, an AI system that demonstrates a crucial step toward this vision through human cognition transfer. Our key insight is that the path from executing simple "tasks" to handling complex "work" lies in efficiently capturing and learning from human cognitive processes during computer use. To validate this hypothesis, we introduce three key innovations: (1) PC Tracker, a lightweight infrastructure that efficiently collects high-quality human-computer interaction trajectories with complete cognitive context; (2) a two-stage cognition completion pipeline that transforms raw interaction data into rich cognitive trajectories by completing action semantics and thought processes; and (3) a multi-agent system combining a planning agent for decision-making with a grounding agent for robust visual grounding. Our preliminary experiments in PowerPoint presentation creation reveal that complex digital work capabilities can be achieved with a small amount of high-quality cognitive data - PC Agent, trained on just 133 cognitive trajectories, can handle sophisticated work scenarios involving up to 50 steps across multiple applications. This demonstrates the data efficiency of our approach, highlighting that the key to training capable digital agents lies in collecting human cognitive data. By open-sourcing our complete framework, including the data collection infrastructure and cognition completion methods, we aim to lower the barriers for the research community to develop truly capable digital agents.
PerSphere: A Comprehensive Framework for Multi-Faceted Perspective Retrieval and Summarization
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:As online platforms and recommendation algorithms evolve, people are increasingly trapped in echo chambers, leading to biased understandings of various issues. To combat this issue, we have introduced PerSphere, a benchmark designed to facilitate multi-faceted perspective retrieval and summarization, thus breaking free from these information silos. For each query within PerSphere, there are two opposing claims, each supported by distinct, non-overlapping perspectives drawn from one or more documents. Our goal is to accurately summarize these documents, aligning the summaries with the respective claims and their underlying perspectives. This task is structured as a two-step end-to-end pipeline that includes comprehensive document retrieval and multi-faceted summarization. Furthermore, we propose a set of metrics to evaluate the comprehensiveness of the retrieval and summarization content. Experimental results on various counterparts for the pipeline show that recent models struggle with such a complex task. Analysis shows that the main challenge lies in long context and perspective extraction, and we propose a simple but effective multi-agent summarization system, offering a promising solution to enhance performance on PerSphere.
Can Language Models Learn to Skip Steps?
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:Trained on vast corpora of human language, language models demonstrate emergent human-like reasoning abilities. Yet they are still far from true intelligence, which opens up intriguing opportunities to explore the parallels of humans and model behaviors. In this work, we study the ability to skip steps in reasoning - a hallmark of human expertise developed through practice. Unlike humans, who may skip steps to enhance efficiency or to reduce cognitive load, models do not inherently possess such motivations to minimize reasoning steps. To address this, we introduce a controlled framework that stimulates step-skipping behavior by iteratively refining models to generate shorter and accurate reasoning paths. Empirical results indicate that models can develop the step skipping ability under our guidance. Moreover, after fine-tuning on expanded datasets that include both complete and skipped reasoning sequences, the models can not only resolve tasks with increased efficiency without sacrificing accuracy, but also exhibit comparable and even enhanced generalization capabilities in out-of-domain scenarios. Our work presents the first exploration into human-like step-skipping ability and provides fresh perspectives on how such cognitive abilities can benefit AI models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge