Cheng Jiayang
Can Language Models Learn to Skip Steps?
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:Trained on vast corpora of human language, language models demonstrate emergent human-like reasoning abilities. Yet they are still far from true intelligence, which opens up intriguing opportunities to explore the parallels of humans and model behaviors. In this work, we study the ability to skip steps in reasoning - a hallmark of human expertise developed through practice. Unlike humans, who may skip steps to enhance efficiency or to reduce cognitive load, models do not inherently possess such motivations to minimize reasoning steps. To address this, we introduce a controlled framework that stimulates step-skipping behavior by iteratively refining models to generate shorter and accurate reasoning paths. Empirical results indicate that models can develop the step skipping ability under our guidance. Moreover, after fine-tuning on expanded datasets that include both complete and skipped reasoning sequences, the models can not only resolve tasks with increased efficiency without sacrificing accuracy, but also exhibit comparable and even enhanced generalization capabilities in out-of-domain scenarios. Our work presents the first exploration into human-like step-skipping ability and provides fresh perspectives on how such cognitive abilities can benefit AI models.
Persona Knowledge-Aligned Prompt Tuning Method for Online Debate
Oct 05, 2024



Abstract:Debate is the process of exchanging viewpoints or convincing others on a particular issue. Recent research has provided empirical evidence that the persuasiveness of an argument is determined not only by language usage but also by communicator characteristics. Researchers have paid much attention to aspects of languages, such as linguistic features and discourse structures, but combining argument persuasiveness and impact with the social personae of the audience has not been explored due to the difficulty and complexity. We have observed the impressive simulation and personification capability of ChatGPT, indicating a giant pre-trained language model may function as an individual to provide personae and exert unique influences based on diverse background knowledge. Therefore, we propose a persona knowledge-aligned framework for argument quality assessment tasks from the audience side. This is the first work that leverages the emergence of ChatGPT and injects such audience personae knowledge into smaller language models via prompt tuning. The performance of our pipeline demonstrates significant and consistent improvement compared to competitive architectures.
ECon: On the Detection and Resolution of Evidence Conflicts
Oct 05, 2024



Abstract:The rise of large language models (LLMs) has significantly influenced the quality of information in decision-making systems, leading to the prevalence of AI-generated content and challenges in detecting misinformation and managing conflicting information, or "inter-evidence conflicts." This study introduces a method for generating diverse, validated evidence conflicts to simulate real-world misinformation scenarios. We evaluate conflict detection methods, including Natural Language Inference (NLI) models, factual consistency (FC) models, and LLMs, on these conflicts (RQ1) and analyze LLMs' conflict resolution behaviors (RQ2). Our key findings include: (1) NLI and LLM models exhibit high precision in detecting answer conflicts, though weaker models suffer from low recall; (2) FC models struggle with lexically similar answer conflicts, while NLI and LLM models handle these better; and (3) stronger models like GPT-4 show robust performance, especially with nuanced conflicts. For conflict resolution, LLMs often favor one piece of conflicting evidence without justification and rely on internal knowledge if they have prior beliefs.
OpenResearcher: Unleashing AI for Accelerated Scientific Research
Aug 13, 2024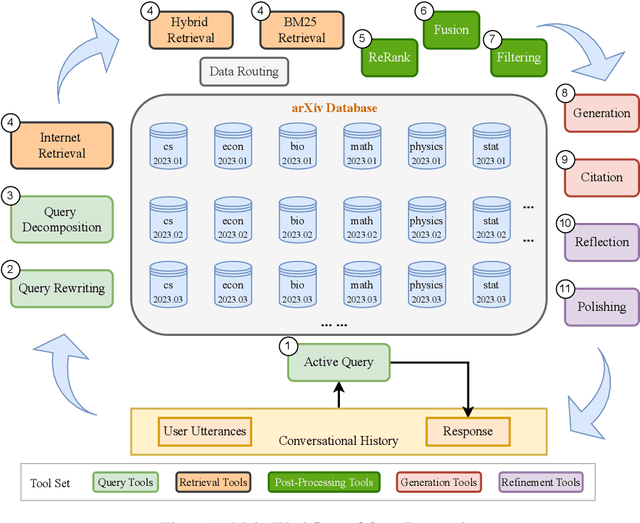
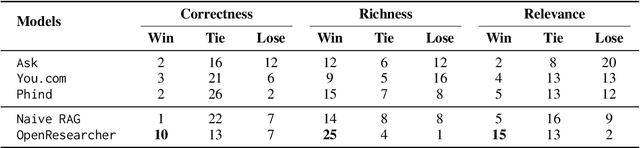
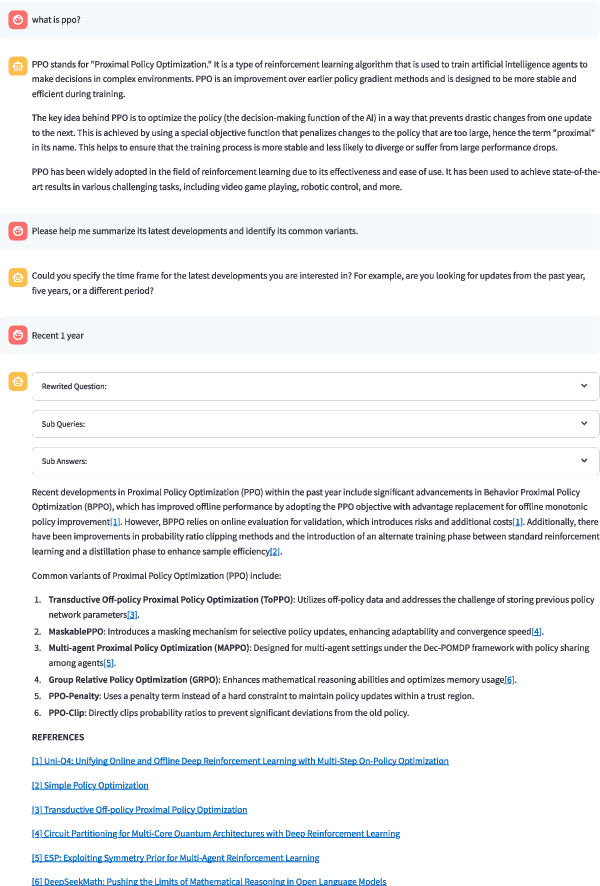
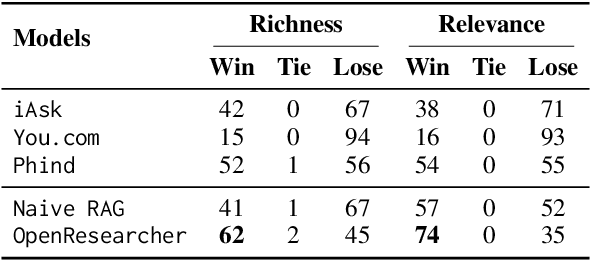
Abstract:The rapid growth of scientific literature imposes significant challenges for researchers endeavoring to stay updated with the latest advancements in their fields and delve into new areas. We introduce OpenResearcher, an innovative platform that leverages Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques to accelerate the research process by answering diverse questions from researchers. OpenResearcher is built based on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) with up-to-date, domain-specific knowledge. Moreover, we develop various tools for OpenResearcher to understand researchers' queries, search from the scientific literature, filter retrieved information, provide accurate and comprehensive answers, and self-refine these answers. OpenResearcher can flexibly use these tools to balance efficiency and effectiveness. As a result, OpenResearcher enables researchers to save time and increase their potential to discover new insights and drive scientific breakthroughs. Demo, video, and code are available at: https://github.com/GAIR-NLP/OpenResearcher.
Boosting Scientific Concepts Understanding: Can Analogy from Teacher Models Empower Student Models?
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Analogical reasoning plays a critical role in human cognition, enabling us to understand new concepts by associating them with familiar ones. Previous research in the AI community has mainly focused on identifying and generating analogies and then examining their quality under human evaluation, which overlooks the practical application of these analogies in real-world settings. Inspired by the human education process, in this paper, we propose to investigate how analogies created by teacher language models (LMs) can assist student LMs in understanding scientific concepts, thereby aligning more closely with practical scenarios. Our results suggest that free-form analogies can indeed aid LMs in understanding concepts. Additionally, analogies generated by student LMs can improve their own performance on scientific question answering, demonstrating their capability to use analogies for self-learning new knowledge. Resources are available at https://github.com/siyuyuan/SCUA.
NegotiationToM: A Benchmark for Stress-testing Machine Theory of Mind on Negotiation Surrounding
Apr 21, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have sparked substantial interest and debate concerning their potential emergence of Theory of Mind (ToM) ability. Theory of mind evaluations currently focuses on testing models using machine-generated data or game settings prone to shortcuts and spurious correlations, which lacks evaluation of machine ToM ability in real-world human interaction scenarios. This poses a pressing demand to develop new real-world scenario benchmarks. We introduce NegotiationToM, a new benchmark designed to stress-test machine ToM in real-world negotiation surrounding covered multi-dimensional mental states (i.e., desires, beliefs, and intentions). Our benchmark builds upon the Belief-Desire-Intention (BDI) agent modeling theory and conducts the necessary empirical experiments to evaluate large language models. Our findings demonstrate that NegotiationToM is challenging for state-of-the-art LLMs, as they consistently perform significantly worse than humans, even when employing the chain-of-thought (CoT) method.
EventGround: Narrative Reasoning by Grounding to Eventuality-centric Knowledge Graphs
Mar 30, 2024Abstract:Narrative reasoning relies on the understanding of eventualities in story contexts, which requires a wealth of background world knowledge. To help machines leverage such knowledge, existing solutions can be categorized into two groups. Some focus on implicitly modeling eventuality knowledge by pretraining language models (LMs) with eventuality-aware objectives. However, this approach breaks down knowledge structures and lacks interpretability. Others explicitly collect world knowledge of eventualities into structured eventuality-centric knowledge graphs (KGs). However, existing research on leveraging these knowledge sources for free-texts is limited. In this work, we propose an initial comprehensive framework called EventGround, which aims to tackle the problem of grounding free-texts to eventuality-centric KGs for contextualized narrative reasoning. We identify two critical problems in this direction: the event representation and sparsity problems. We provide simple yet effective parsing and partial information extraction methods to tackle these problems. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms baseline models when combined with graph neural network (GNN) or large language model (LLM) based graph reasoning models. Our framework, incorporating grounded knowledge, achieves state-of-the-art performance while providing interpretable evidence.
StoryAnalogy: Deriving Story-level Analogies from Large Language Models to Unlock Analogical Understanding
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:Analogy-making between narratives is crucial for human reasoning. In this paper, we evaluate the ability to identify and generate analogies by constructing a first-of-its-kind large-scale story-level analogy corpus, \textsc{StoryAnalogy}, which contains 24K story pairs from diverse domains with human annotations on two similarities from the extended Structure-Mapping Theory. We design a set of tests on \textsc{StoryAnalogy}, presenting the first evaluation of story-level analogy identification and generation. Interestingly, we find that the analogy identification tasks are incredibly difficult not only for sentence embedding models but also for the recent large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and LLaMa. ChatGPT, for example, only achieved around 30% accuracy in multiple-choice questions (compared to over 85% accuracy for humans). Furthermore, we observe that the data in \textsc{StoryAnalogy} can improve the quality of analogy generation in LLMs, where a fine-tuned FlanT5-xxl model achieves comparable performance to zero-shot ChatGPT.
Survey on Factuality in Large Language Models: Knowledge, Retrieval and Domain-Specificity
Oct 18, 2023



Abstract:This survey addresses the crucial issue of factuality in Large Language Models (LLMs). As LLMs find applications across diverse domains, the reliability and accuracy of their outputs become vital. We define the Factuality Issue as the probability of LLMs to produce content inconsistent with established facts. We first delve into the implications of these inaccuracies, highlighting the potential consequences and challenges posed by factual errors in LLM outputs. Subsequently, we analyze the mechanisms through which LLMs store and process facts, seeking the primary causes of factual errors. Our discussion then transitions to methodologies for evaluating LLM factuality, emphasizing key metrics, benchmarks, and studies. We further explore strategies for enhancing LLM factuality, including approaches tailored for specific domains. We focus two primary LLM configurations standalone LLMs and Retrieval-Augmented LLMs that utilizes external data, we detail their unique challenges and potential enhancements. Our survey offers a structured guide for researchers aiming to fortify the factual reliability of LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge