Vikram Voleti
SV4D 2.0: Enhancing Spatio-Temporal Consistency in Multi-View Video Diffusion for High-Quality 4D Generation
Mar 21, 2025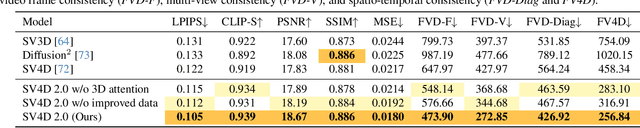
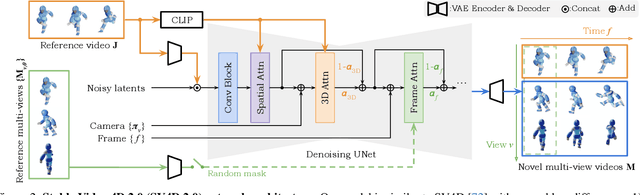
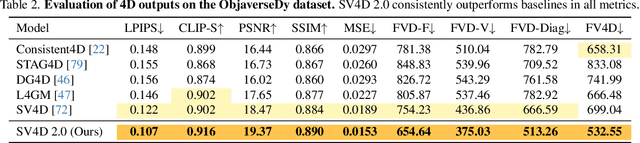
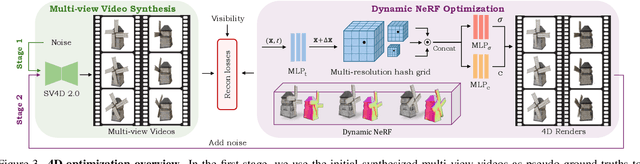
Abstract:We present Stable Video 4D 2.0 (SV4D 2.0), a multi-view video diffusion model for dynamic 3D asset generation. Compared to its predecessor SV4D, SV4D 2.0 is more robust to occlusions and large motion, generalizes better to real-world videos, and produces higher-quality outputs in terms of detail sharpness and spatio-temporal consistency. We achieve this by introducing key improvements in multiple aspects: 1) network architecture: eliminating the dependency of reference multi-views and designing blending mechanism for 3D and frame attention, 2) data: enhancing quality and quantity of training data, 3) training strategy: adopting progressive 3D-4D training for better generalization, and 4) 4D optimization: handling 3D inconsistency and large motion via 2-stage refinement and progressive frame sampling. Extensive experiments demonstrate significant performance gain by SV4D 2.0 both visually and quantitatively, achieving better detail (-14\% LPIPS) and 4D consistency (-44\% FV4D) in novel-view video synthesis and 4D optimization (-12\% LPIPS and -24\% FV4D) compared to SV4D.
Stable Virtual Camera: Generative View Synthesis with Diffusion Models
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:We present Stable Virtual Camera (Seva), a generalist diffusion model that creates novel views of a scene, given any number of input views and target cameras. Existing works struggle to generate either large viewpoint changes or temporally smooth samples, while relying on specific task configurations. Our approach overcomes these limitations through simple model design, optimized training recipe, and flexible sampling strategy that generalize across view synthesis tasks at test time. As a result, our samples maintain high consistency without requiring additional 3D representation-based distillation, thus streamlining view synthesis in the wild. Furthermore, we show that our method can generate high-quality videos lasting up to half a minute with seamless loop closure. Extensive benchmarking demonstrates that Seva outperforms existing methods across different datasets and settings.
SV4D: Dynamic 3D Content Generation with Multi-Frame and Multi-View Consistency
Jul 24, 2024Abstract:We present Stable Video 4D (SV4D), a latent video diffusion model for multi-frame and multi-view consistent dynamic 3D content generation. Unlike previous methods that rely on separately trained generative models for video generation and novel view synthesis, we design a unified diffusion model to generate novel view videos of dynamic 3D objects. Specifically, given a monocular reference video, SV4D generates novel views for each video frame that are temporally consistent. We then use the generated novel view videos to optimize an implicit 4D representation (dynamic NeRF) efficiently, without the need for cumbersome SDS-based optimization used in most prior works. To train our unified novel view video generation model, we curated a dynamic 3D object dataset from the existing Objaverse dataset. Extensive experimental results on multiple datasets and user studies demonstrate SV4D's state-of-the-art performance on novel-view video synthesis as well as 4D generation compared to prior works.
HouseCrafter: Lifting Floorplans to 3D Scenes with 2D Diffusion Model
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:We introduce HouseCrafter, a novel approach that can lift a floorplan into a complete large 3D indoor scene (e.g., a house). Our key insight is to adapt a 2D diffusion model, which is trained on web-scale images, to generate consistent multi-view color (RGB) and depth (D) images across different locations of the scene. Specifically, the RGB-D images are generated autoregressively in a batch-wise manner along sampled locations based on the floorplan, where previously generated images are used as condition to the diffusion model to produce images at nearby locations. The global floorplan and attention design in the diffusion model ensures the consistency of the generated images, from which a 3D scene can be reconstructed. Through extensive evaluation on the 3D-Front dataset, we demonstrate that HouseCraft can generate high-quality house-scale 3D scenes. Ablation studies also validate the effectiveness of different design choices. We will release our code and model weights. Project page: https://neu-vi.github.io/houseCrafter/
SV3D: Novel Multi-view Synthesis and 3D Generation from a Single Image using Latent Video Diffusion
Mar 18, 2024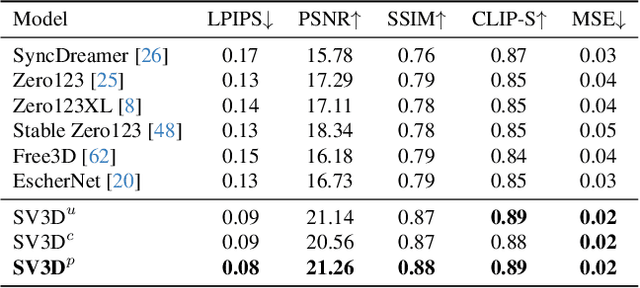
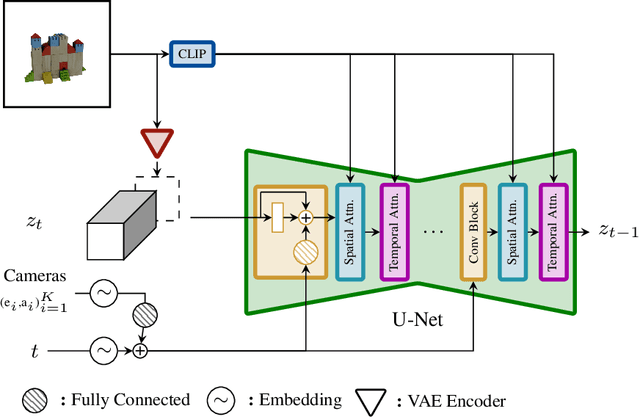
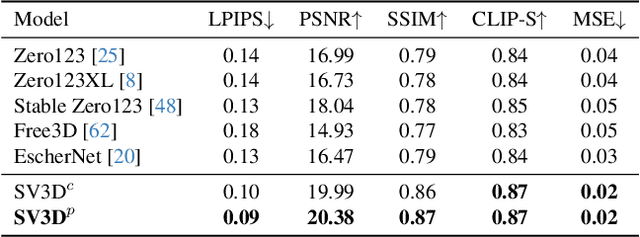
Abstract:We present Stable Video 3D (SV3D) -- a latent video diffusion model for high-resolution, image-to-multi-view generation of orbital videos around a 3D object. Recent work on 3D generation propose techniques to adapt 2D generative models for novel view synthesis (NVS) and 3D optimization. However, these methods have several disadvantages due to either limited views or inconsistent NVS, thereby affecting the performance of 3D object generation. In this work, we propose SV3D that adapts image-to-video diffusion model for novel multi-view synthesis and 3D generation, thereby leveraging the generalization and multi-view consistency of the video models, while further adding explicit camera control for NVS. We also propose improved 3D optimization techniques to use SV3D and its NVS outputs for image-to-3D generation. Extensive experimental results on multiple datasets with 2D and 3D metrics as well as user study demonstrate SV3D's state-of-the-art performance on NVS as well as 3D reconstruction compared to prior works.
Stable Video Diffusion: Scaling Latent Video Diffusion Models to Large Datasets
Nov 25, 2023



Abstract:We present Stable Video Diffusion - a latent video diffusion model for high-resolution, state-of-the-art text-to-video and image-to-video generation. Recently, latent diffusion models trained for 2D image synthesis have been turned into generative video models by inserting temporal layers and finetuning them on small, high-quality video datasets. However, training methods in the literature vary widely, and the field has yet to agree on a unified strategy for curating video data. In this paper, we identify and evaluate three different stages for successful training of video LDMs: text-to-image pretraining, video pretraining, and high-quality video finetuning. Furthermore, we demonstrate the necessity of a well-curated pretraining dataset for generating high-quality videos and present a systematic curation process to train a strong base model, including captioning and filtering strategies. We then explore the impact of finetuning our base model on high-quality data and train a text-to-video model that is competitive with closed-source video generation. We also show that our base model provides a powerful motion representation for downstream tasks such as image-to-video generation and adaptability to camera motion-specific LoRA modules. Finally, we demonstrate that our model provides a strong multi-view 3D-prior and can serve as a base to finetune a multi-view diffusion model that jointly generates multiple views of objects in a feedforward fashion, outperforming image-based methods at a fraction of their compute budget. We release code and model weights at https://github.com/Stability-AI/generative-models .
Conditional Generative Modeling for Images, 3D Animations, and Video
Oct 19, 2023



Abstract:This dissertation attempts to drive innovation in the field of generative modeling for computer vision, by exploring novel formulations of conditional generative models, and innovative applications in images, 3D animations, and video. Our research focuses on architectures that offer reversible transformations of noise and visual data, and the application of encoder-decoder architectures for generative tasks and 3D content manipulation. In all instances, we incorporate conditional information to enhance the synthesis of visual data, improving the efficiency of the generation process as well as the generated content. We introduce the use of Neural ODEs to model video dynamics using an encoder-decoder architecture, demonstrating their ability to predict future video frames despite being trained solely to reconstruct current frames. Next, we propose a conditional variant of continuous normalizing flows that enables higher-resolution image generation based on lower-resolution input, achieving comparable image quality while reducing parameters and training time. Our next contribution presents a pipeline that takes human images as input, automatically aligns a user-specified 3D character with the pose of the human, and facilitates pose editing based on partial inputs. Next, we derive the relevant mathematical details for denoising diffusion models that use non-isotropic Gaussian processes, and show comparable generation quality. Finally, we devise a novel denoising diffusion framework capable of solving all three video tasks of prediction, generation, and interpolation. We perform ablation studies, and show SOTA results on multiple datasets. Our contributions are published articles at peer-reviewed venues. Overall, our research aims to make a meaningful contribution to the pursuit of more efficient and flexible generative models, with the potential to shape the future of computer vision.
Objaverse-XL: A Universe of 10M+ 3D Objects
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:Natural language processing and 2D vision models have attained remarkable proficiency on many tasks primarily by escalating the scale of training data. However, 3D vision tasks have not seen the same progress, in part due to the challenges of acquiring high-quality 3D data. In this work, we present Objaverse-XL, a dataset of over 10 million 3D objects. Our dataset comprises deduplicated 3D objects from a diverse set of sources, including manually designed objects, photogrammetry scans of landmarks and everyday items, and professional scans of historic and antique artifacts. Representing the largest scale and diversity in the realm of 3D datasets, Objaverse-XL enables significant new possibilities for 3D vision. Our experiments demonstrate the improvements enabled with the scale provided by Objaverse-XL. We show that by training Zero123 on novel view synthesis, utilizing over 100 million multi-view rendered images, we achieve strong zero-shot generalization abilities. We hope that releasing Objaverse-XL will enable further innovations in the field of 3D vision at scale.
Are Diffusion Models Vision-And-Language Reasoners?
May 25, 2023Abstract:Text-conditioned image generation models have recently shown immense qualitative success using denoising diffusion processes. However, unlike discriminative vision-and-language models, it is a non-trivial task to subject these diffusion-based generative models to automatic fine-grained quantitative evaluation of high-level phenomena such as compositionality. Towards this goal, we perform two innovations. First, we transform diffusion-based models (in our case, Stable Diffusion) for any image-text matching (ITM) task using a novel method called DiffusionITM. Second, we introduce the Generative-Discriminative Evaluation Benchmark (GDBench) benchmark with 7 complex vision-and-language tasks, bias evaluation and detailed analysis. We find that Stable Diffusion + DiffusionITM is competitive on many tasks and outperforms CLIP on compositional tasks like like CLEVR and Winoground. We further boost its compositional performance with a transfer setup by fine-tuning on MS-COCO while retaining generative capabilities. We also measure the stereotypical bias in diffusion models, and find that Stable Diffusion 2.1 is, for the most part, less biased than Stable Diffusion 1.5. Overall, our results point in an exciting direction bringing discriminative and generative model evaluation closer. We will release code and benchmark setup soon.
Score-based Diffusion Models in Function Space
Feb 14, 2023



Abstract:Diffusion models have recently emerged as a powerful framework for generative modeling. They consist of a forward process that perturbs input data with Gaussian white noise and a reverse process that learns a score function to generate samples by denoising. Despite their tremendous success, they are mostly formulated on finite-dimensional spaces, e.g. Euclidean, limiting their applications to many domains where the data has a functional form such as in scientific computing and 3D geometric data analysis. In this work, we introduce a mathematically rigorous framework called Denoising Diffusion Operators (DDOs) for training diffusion models in function space. In DDOs, the forward process perturbs input functions gradually using a Gaussian process. The generative process is formulated by integrating a function-valued Langevin dynamic. Our approach requires an appropriate notion of the score for the perturbed data distribution, which we obtain by generalizing denoising score matching to function spaces that can be infinite-dimensional. We show that the corresponding discretized algorithm generates accurate samples at a fixed cost that is independent of the data resolution. We theoretically and numerically verify the applicability of our approach on a set of problems, including generating solutions to the Navier-Stokes equation viewed as the push-forward distribution of forcings from a Gaussian Random Field (GRF).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge