Sungjin Ahn
UC Irvine
Loopholing Discrete Diffusion: Deterministic Bypass of the Sampling Wall
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Discrete diffusion models offer a promising alternative to autoregressive generation through parallel decoding, but they suffer from a sampling wall: once categorical sampling occurs, rich distributional information collapses into one-hot vectors and cannot be propagated across steps, forcing subsequent steps to operate with limited information. To mitigate this problem, we introduce Loopholing, a novel and simple mechanism that preserves this information via a deterministic latent pathway, leading to Loopholing Discrete Diffusion Models (LDDMs). Trained efficiently with a self-conditioning strategy, LDDMs achieve substantial gains-reducing generative perplexity by up to 61% over prior baselines, closing (and in some cases surpassing) the gap with autoregressive models, and producing more coherent text. Applied to reasoning tasks, LDDMs also improve performance on arithmetic benchmarks such as Countdown and Game of 24. These results also indicate that loopholing mitigates idle steps and oscillations, providing a scalable path toward high-quality non-autoregressive text generation.
Discrete JEPA: Learning Discrete Token Representations without Reconstruction
Jun 17, 2025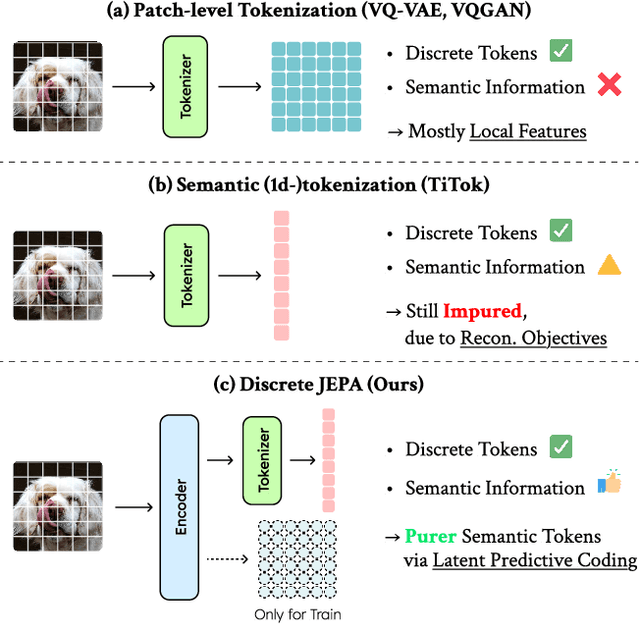
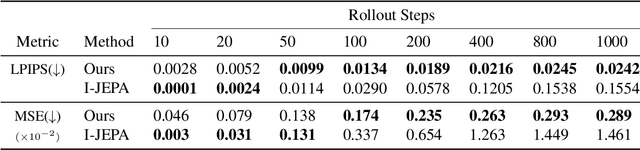
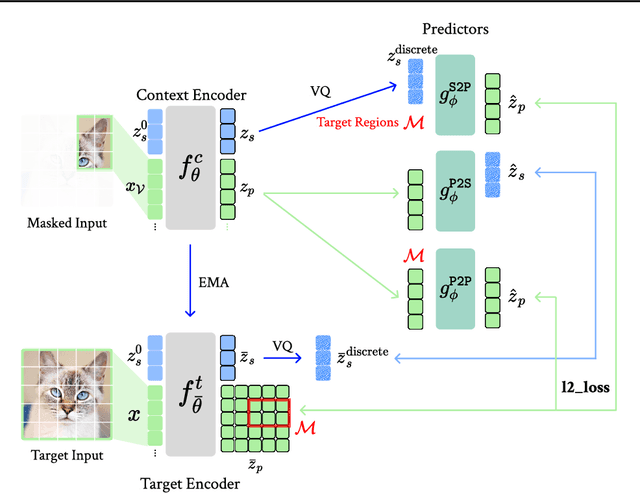
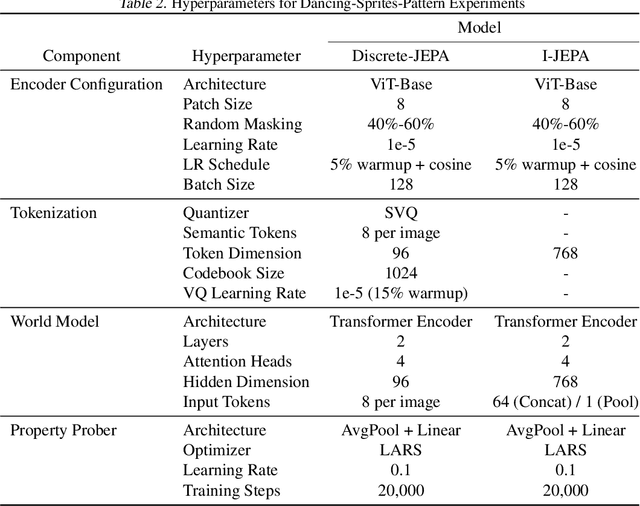
Abstract:The cornerstone of cognitive intelligence lies in extracting hidden patterns from observations and leveraging these principles to systematically predict future outcomes. However, current image tokenization methods demonstrate significant limitations in tasks requiring symbolic abstraction and logical reasoning capabilities essential for systematic inference. To address this challenge, we propose Discrete-JEPA, extending the latent predictive coding framework with semantic tokenization and novel complementary objectives to create robust tokenization for symbolic reasoning tasks. Discrete-JEPA dramatically outperforms baselines on visual symbolic prediction tasks, while striking visual evidence reveals the spontaneous emergence of deliberate systematic patterns within the learned semantic token space. Though an initial model, our approach promises a significant impact for advancing Symbolic world modeling and planning capabilities in artificial intelligence systems.
Fast Monte Carlo Tree Diffusion: 100x Speedup via Parallel Sparse Planning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have recently emerged as a powerful approach for trajectory planning. However, their inherently non-sequential nature limits their effectiveness in long-horizon reasoning tasks at test time. The recently proposed Monte Carlo Tree Diffusion (MCTD) offers a promising solution by combining diffusion with tree-based search, achieving state-of-the-art performance on complex planning problems. Despite its strengths, our analysis shows that MCTD incurs substantial computational overhead due to the sequential nature of tree search and the cost of iterative denoising. To address this, we propose Fast-MCTD, a more efficient variant that preserves the strengths of MCTD while significantly improving its speed and scalability. Fast-MCTD integrates two techniques: Parallel MCTD, which enables parallel rollouts via delayed tree updates and redundancy-aware selection; and Sparse MCTD, which reduces rollout length through trajectory coarsening. Experiments show that Fast-MCTD achieves up to 100x speedup over standard MCTD while maintaining or improving planning performance. Remarkably, it even outperforms Diffuser in inference speed on some tasks, despite Diffuser requiring no search and yielding weaker solutions. These results position Fast-MCTD as a practical and scalable solution for diffusion-based inference-time reasoning.
Slot-MLLM: Object-Centric Visual Tokenization for Multimodal LLM
May 26, 2025Abstract:Recently, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have emerged as a key approach in achieving artificial general intelligence. In particular, vision-language MLLMs have been developed to generate not only text but also visual outputs from multimodal inputs. This advancement requires efficient image tokens that LLMs can process effectively both in input and output. However, existing image tokenization methods for MLLMs typically capture only global abstract concepts or uniformly segmented image patches, restricting MLLMs' capability to effectively understand or generate detailed visual content, particularly at the object level. To address this limitation, we propose an object-centric visual tokenizer based on Slot Attention specifically for MLLMs. In particular, based on the Q-Former encoder, diffusion decoder, and residual vector quantization, our proposed discretized slot tokens can encode local visual details while maintaining high-level semantics, and also align with textual data to be integrated seamlessly within a unified next-token prediction framework of LLMs. The resulting Slot-MLLM demonstrates significant performance improvements over baselines with previous visual tokenizers across various vision-language tasks that entail local detailed comprehension and generation. Notably, this work is the first demonstration of the feasibility of object-centric slot attention performed with MLLMs and in-the-wild natural images.
Adaptive Cyclic Diffusion for Inference Scaling
May 20, 2025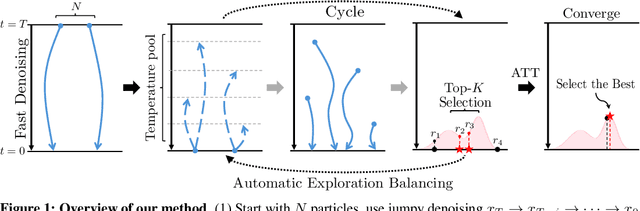
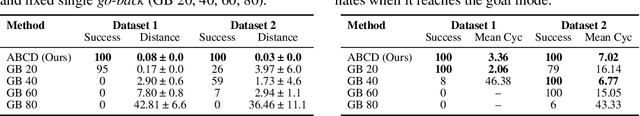
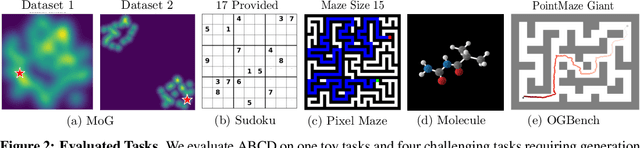
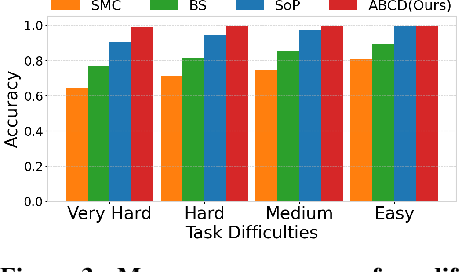
Abstract:Diffusion models have demonstrated strong generative capabilities across domains ranging from image synthesis to complex reasoning tasks. However, most inference-time scaling methods rely on fixed denoising schedules, limiting their ability to allocate computation based on instance difficulty or task-specific demands adaptively. We introduce the challenge of adaptive inference-time scaling-dynamically adjusting computational effort during inference-and propose Adaptive Bi-directional Cyclic Diffusion (ABCD), a flexible, search-based inference framework. ABCD refines outputs through bi-directional diffusion cycles while adaptively controlling exploration depth and termination. It comprises three components: Cyclic Diffusion Search, Automatic Exploration-Exploitation Balancing, and Adaptive Thinking Time. Experiments show that ABCD improves performance across diverse tasks while maintaining computational efficiency.
Search-Based Correction of Reasoning Chains for Language Models
May 17, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning has advanced the capabilities and transparency of language models (LMs); however, reasoning chains can contain inaccurate statements that reduce performance and trustworthiness. To address this, we introduce a new self-correction framework that augments each reasoning step in a CoT with a latent variable indicating its veracity, enabling modeling of all possible truth assignments rather than assuming correctness throughout. To efficiently explore this expanded space, we introduce Search Corrector, a discrete search algorithm over boolean-valued veracity assignments. It efficiently performs otherwise intractable inference in the posterior distribution over veracity assignments by leveraging the LM's joint likelihood over veracity and the final answer as a proxy reward. This efficient inference-time correction method facilitates supervised fine-tuning of an Amortized Corrector by providing pseudo-labels for veracity. The Amortized Corrector generalizes self-correction, enabling accurate zero-shot veracity inference in novel contexts. Empirical results demonstrate that Search Corrector reliably identifies errors in logical (ProntoQA) and mathematical reasoning (GSM8K) benchmarks. The Amortized Corrector achieves comparable zero-shot accuracy and improves final answer accuracy by up to 25%.
Extendable Long-Horizon Planning via Hierarchical Multiscale Diffusion
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:This paper tackles a novel problem, extendable long-horizon planning-enabling agents to plan trajectories longer than those in training data without compounding errors. To tackle this, we propose the Hierarchical Multiscale Diffuser (HM-Diffuser) and Progressive Trajectory Extension (PTE), an augmentation method that iteratively generates longer trajectories by stitching shorter ones. HM-Diffuser trains on these extended trajectories using a hierarchical structure, efficiently handling tasks across multiple temporal scales. Additionally, we introduce Adaptive Plan Pondering and the Recursive HM-Diffuser, which consolidate hierarchical layers into a single model to process temporal scales recursively. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, advancing diffusion-based planners for scalable long-horizon planning.
Token-Efficient Long Video Understanding for Multimodal LLMs
Mar 06, 2025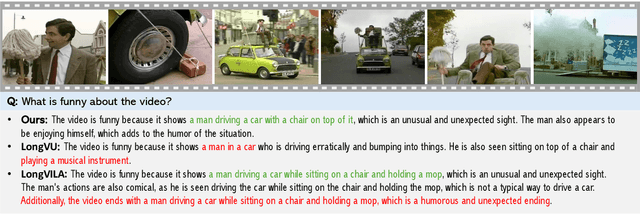
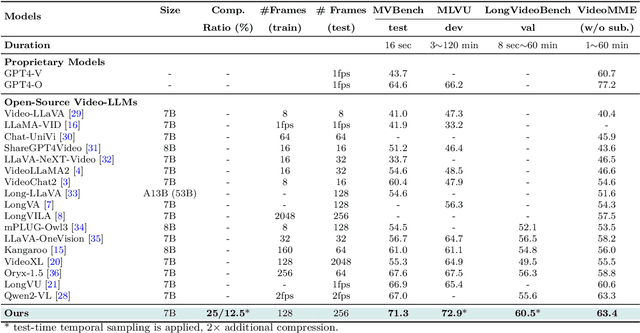
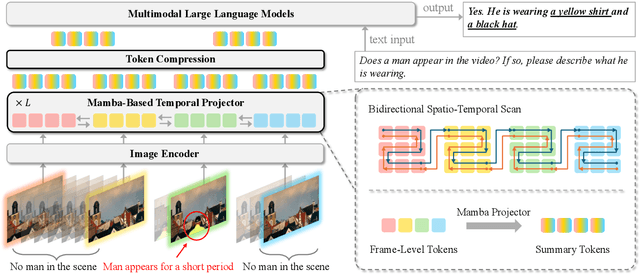
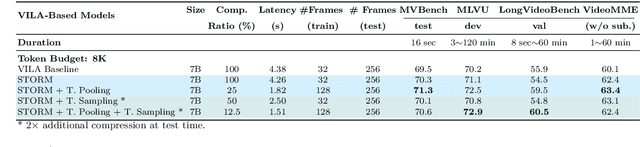
Abstract:Recent advances in video-based multimodal large language models (Video-LLMs) have significantly improved video understanding by processing videos as sequences of image frames. However, many existing methods treat frames independently in the vision backbone, lacking explicit temporal modeling, which limits their ability to capture dynamic patterns and efficiently handle long videos. To address these limitations, we introduce STORM (\textbf{S}patiotemporal \textbf{TO}ken \textbf{R}eduction for \textbf{M}ultimodal LLMs), a novel architecture incorporating a dedicated temporal encoder between the image encoder and the LLM. Our temporal encoder leverages the Mamba State Space Model to integrate temporal information into image tokens, generating enriched representations that preserve inter-frame dynamics across the entire video sequence. This enriched encoding not only enhances video reasoning capabilities but also enables effective token reduction strategies, including test-time sampling and training-based temporal and spatial pooling, substantially reducing computational demands on the LLM without sacrificing key temporal information. By integrating these techniques, our approach simultaneously reduces training and inference latency while improving performance, enabling efficient and robust video understanding over extended temporal contexts. Extensive evaluations show that STORM achieves state-of-the-art results across various long video understanding benchmarks (more than 5\% improvement on MLVU and LongVideoBench) while reducing the computation costs by up to $8\times$ and the decoding latency by 2.4-2.9$\times$ for the fixed numbers of input frames. Project page is available at https://research.nvidia.com/labs/lpr/storm
Monte Carlo Tree Diffusion for System 2 Planning
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:Diffusion models have recently emerged as a powerful tool for planning. However, unlike Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)-whose performance naturally improves with additional test-time computation (TTC), standard diffusion-based planners offer only limited avenues for TTC scalability. In this paper, we introduce Monte Carlo Tree Diffusion (MCTD), a novel framework that integrates the generative strength of diffusion models with the adaptive search capabilities of MCTS. Our method reconceptualizes denoising as a tree-structured process, allowing partially denoised plans to be iteratively evaluated, pruned, and refined. By selectively expanding promising trajectories while retaining the flexibility to revisit and improve suboptimal branches, MCTD achieves the benefits of MCTS such as controlling exploration-exploitation trade-offs within the diffusion framework. Empirical results on challenging long-horizon tasks show that MCTD outperforms diffusion baselines, yielding higher-quality solutions as TTC increases.
Dreamweaver: Learning Compositional World Representations from Pixels
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Humans have an innate ability to decompose their perceptions of the world into objects and their attributes, such as colors, shapes, and movement patterns. This cognitive process enables us to imagine novel futures by recombining familiar concepts. However, replicating this ability in artificial intelligence systems has proven challenging, particularly when it comes to modeling videos into compositional concepts and generating unseen, recomposed futures without relying on auxiliary data, such as text, masks, or bounding boxes. In this paper, we propose Dreamweaver, a neural architecture designed to discover hierarchical and compositional representations from raw videos and generate compositional future simulations. Our approach leverages a novel Recurrent Block-Slot Unit (RBSU) to decompose videos into their constituent objects and attributes. In addition, Dreamweaver uses a multi-future-frame prediction objective to capture disentangled representations for dynamic concepts more effectively as well as static concepts. In experiments, we demonstrate our model outperforms current state-of-the-art baselines for world modeling when evaluated under the DCI framework across multiple datasets. Furthermore, we show how the modularized concept representations of our model enable compositional imagination, allowing the generation of novel videos by recombining attributes from different objects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge