Steffen Staab
Universitaet Erlangen-Nuernberg, IMMD 8
Geometric Structural Knowledge Graph Foundation Model
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Structural knowledge graph foundation models aim to generalize reasoning to completely new graphs with unseen entities and relations. A key limitation of existing approaches like Ultra is their reliance on a single relational transformation (e.g., element-wise multiplication) in message passing, which can constrain expressiveness and fail to capture diverse relational and structural patterns exhibited on diverse graphs. In this paper, we propose Gamma, a novel foundation model that introduces multi-head geometric attention to knowledge graph reasoning. Gamma replaces the single relational transformation with multiple parallel ones, including real, complex, split-complex, and dual number based transformations, each designed to model different relational structures. A relational conditioned attention fusion mechanism then adaptively fuses them at link level via a lightweight gating with entropy regularization, allowing the model to robustly emphasize the most appropriate relational bias for each triple pattern. We present a full formalization of these algebraic message functions and discuss how their combination increases expressiveness beyond any single space. Comprehensive experiments on 56 diverse knowledge graphs demonstrate that Gamma consistently outperforms Ultra in zero-shot inductive link prediction, with a 5.5% improvement in mean reciprocal rank on the inductive benchmarks and a 4.4% improvement across all benchmarks, highlighting benefits from complementary geometric representations.
GR-Agent: Adaptive Graph Reasoning Agent under Incomplete Knowledge
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) achieve strong results on knowledge graph question answering (KGQA), but most benchmarks assume complete knowledge graphs (KGs) where direct supporting triples exist. This reduces evaluation to shallow retrieval and overlooks the reality of incomplete KGs, where many facts are missing and answers must be inferred from existing facts. We bridge this gap by proposing a methodology for constructing benchmarks under KG incompleteness, which removes direct supporting triples while ensuring that alternative reasoning paths required to infer the answer remain. Experiments on benchmarks constructed using our methodology show that existing methods suffer consistent performance degradation under incompleteness, highlighting their limited reasoning ability. To overcome this limitation, we present the Adaptive Graph Reasoning Agent (GR-Agent). It first constructs an interactive environment from the KG, and then formalizes KGQA as agent environment interaction within this environment. GR-Agent operates over an action space comprising graph reasoning tools and maintains a memory of potential supporting reasoning evidence, including relevant relations and reasoning paths. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GR-Agent outperforms non-training baselines and performs comparably to training-based methods under both complete and incomplete settings.
Defect-aware Hybrid Prompt Optimization via Progressive Tuning for Zero-Shot Multi-type Anomaly Detection and Segmentation
Dec 10, 2025



Abstract:Recent vision language models (VLMs) like CLIP have demonstrated impressive anomaly detection performance under significant distribution shift by utilizing high-level semantic information through text prompts. However, these models often neglect fine-grained details, such as which kind of anomalies, like "hole", "cut", "scratch" that could provide more specific insight into the nature of anomalies. We argue that recognizing fine-grained anomaly types 1) enriches the representation of "abnormal" with structured semantics, narrowing the gap between coarse anomaly signals and fine-grained defect categories; 2) enables manufacturers to understand the root causes of the anomaly and implement more targeted and appropriate corrective measures quickly. While incorporating such detailed semantic information is crucial, designing handcrafted prompts for each defect type is both time-consuming and susceptible to human bias. For this reason, we introduce DAPO, a novel approach for Defect-aware Prompt Optimization based on progressive tuning for the zero-shot multi-type and binary anomaly detection and segmentation under distribution shifts. Our approach aligns anomaly-relevant image features with their corresponding text semantics by learning hybrid defect-aware prompts with both fixed textual anchors and learnable token embeddings. We conducted experiments on public benchmarks (MPDD, VisA, MVTec-AD, MAD, and Real-IAD) and an internal dataset. The results suggest that compared to the baseline models, DAPO achieves a 3.7% average improvement in AUROC and average precision metrics at the image level under distribution shift, and a 6.5% average improvement in localizing novel anomaly types under zero-shot settings.
The Illusion of Diminishing Returns: Measuring Long Horizon Execution in LLMs
Sep 11, 2025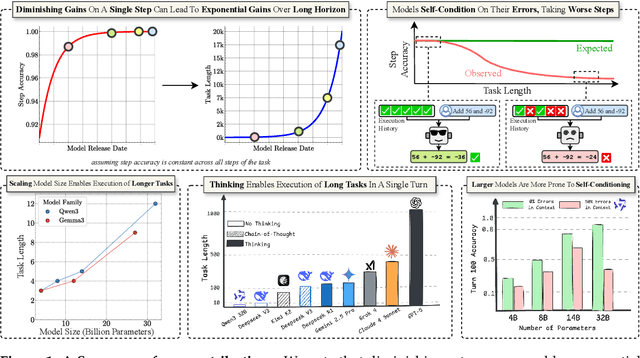
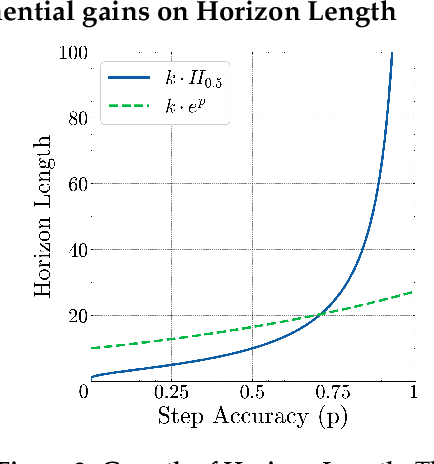
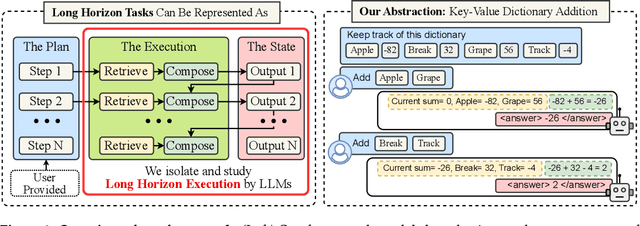
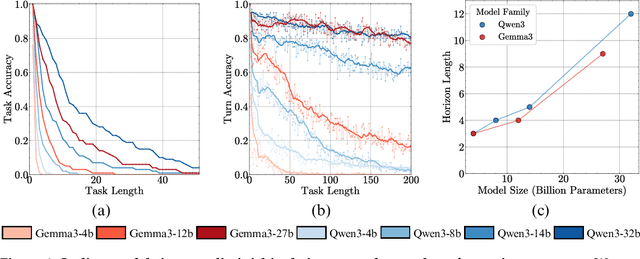
Abstract:Does continued scaling of large language models (LLMs) yield diminishing returns? Real-world value often stems from the length of task an agent can complete. We start this work by observing the simple but counterintuitive fact that marginal gains in single-step accuracy can compound into exponential improvements in the length of a task a model can successfully complete. Then, we argue that failures of LLMs when simple tasks are made longer arise from mistakes in execution, rather than an inability to reason. We propose isolating execution capability, by explicitly providing the knowledge and plan needed to solve a long-horizon task. We find that larger models can correctly execute significantly more turns even when small models have 100\% single-turn accuracy. We observe that the per-step accuracy of models degrades as the number of steps increases. This is not just due to long-context limitations -- curiously, we observe a self-conditioning effect -- models become more likely to make mistakes when the context contains their errors from prior turns. Self-conditioning does not reduce by just scaling the model size. In contrast, recent thinking models do not self-condition, and can also execute much longer tasks in a single turn. We conclude by benchmarking frontier thinking models on the length of task they can execute in a single turn. Overall, by focusing on the ability to execute, we hope to reconcile debates on how LLMs can solve complex reasoning problems yet fail at simple tasks when made longer, and highlight the massive benefits of scaling model size and sequential test-time compute for long-horizon tasks.
What Breaks Knowledge Graph based RAG? Empirical Insights into Reasoning under Incomplete Knowledge
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (KG-RAG) is an increasingly explored approach for combining the reasoning capabilities of large language models with the structured evidence of knowledge graphs. However, current evaluation practices fall short: existing benchmarks often include questions that can be directly answered using existing triples in KG, making it unclear whether models perform reasoning or simply retrieve answers directly. Moreover, inconsistent evaluation metrics and lenient answer matching criteria further obscure meaningful comparisons. In this work, we introduce a general method for constructing benchmarks, together with an evaluation protocol, to systematically assess KG-RAG methods under knowledge incompleteness. Our empirical results show that current KG-RAG methods have limited reasoning ability under missing knowledge, often rely on internal memorization, and exhibit varying degrees of generalization depending on their design.
Mathematical Reasoning for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: A RAG-Based Approach for Complex Arithmetic Reasoning
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Autonomous UAV operation necessitates reliable mathematical reasoning for tasks such as trajectory planning and power management. While traditional flight control relies on hardcoded equations, recent Large Language Models (LLMs) offer potential for more flexible problem-solving but struggle with reliably selecting and applying correct mathematical formulations and executing precise multi-step arithmetic. We propose RAG-UAV, a retrieval-augmented generation framework designed to improve the mathematical reasoning of several LLMs (including GPT o1/Turbo, Llama-3.2/3.3, Mistral, and DeepSeek R1) in UAV-specific contexts by providing access to relevant domain literature. To conduct an initial assessment, we introduce the UAV-Math-Bench, a small problem set comprising 20 UAV-centric mathematical problems across four difficulty levels. Our experiments demonstrate that incorporating retrieval substantially increases exact answer accuracy (achieving up to 75% with o1), reduces instances of incorrect formulation selection (from 25% without RAG to 5% with RAG), decreases numerical errors, reducing Mean Squared Error (MSE) by orders of magnitude for the best-performing models. This pilot study indicates that RAG can enable general-purpose LLMs to function as more reliable tools for engineering analysis, although direct real-time flight control requires further investigation and validation on a larger scale. All benchmark data, question and answer are publicly available.
Towards Foundation Model on Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Temporal Knowledge Graphs (TKGs) store temporal facts with quadruple formats (s, p, o, t). Existing Temporal Knowledge Graph Embedding (TKGE) models perform link prediction tasks in transductive or semi-inductive settings, which means the entities, relations, and temporal information in the test graph are fully or partially observed during training. Such reliance on seen elements during inference limits the models' ability to transfer to new domains and generalize to real-world scenarios. A central limitation is the difficulty in learning representations for entities, relations, and timestamps that are transferable and not tied to dataset-specific vocabularies. To overcome these limitations, we introduce the first fully-inductive approach to temporal knowledge graph link prediction. Our model employs sinusoidal positional encodings to capture fine-grained temporal patterns and generates adaptive entity and relation representations using message passing conditioned on both local and global temporal contexts. Our model design is agnostic to temporal granularity and time span, effectively addressing temporal discrepancies across TKGs and facilitating time-aware structural information transfer. As a pretrained, scalable, and transferable model, POSTRA demonstrates strong zero-shot performance on unseen temporal knowledge graphs, effectively generalizing to novel entities, relations, and timestamps. Extensive theoretical analysis and empirical results show that a single pretrained model can improve zero-shot performance on various inductive temporal reasoning scenarios, marking a significant step toward a foundation model for temporal KGs.
SEMMA: A Semantic Aware Knowledge Graph Foundation Model
May 26, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Graph Foundation Models (KGFMs) have shown promise in enabling zero-shot reasoning over unseen graphs by learning transferable patterns. However, most existing KGFMs rely solely on graph structure, overlooking the rich semantic signals encoded in textual attributes. We introduce SEMMA, a dual-module KGFM that systematically integrates transferable textual semantics alongside structure. SEMMA leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to enrich relation identifiers, generating semantic embeddings that subsequently form a textual relation graph, which is fused with the structural component. Across 54 diverse KGs, SEMMA outperforms purely structural baselines like ULTRA in fully inductive link prediction. Crucially, we show that in more challenging generalization settings, where the test-time relation vocabulary is entirely unseen, structural methods collapse while SEMMA is 2x more effective. Our findings demonstrate that textual semantics are critical for generalization in settings where structure alone fails, highlighting the need for foundation models that unify structural and linguistic signals in knowledge reasoning.
Predicate-Conditional Conformalized Answer Sets for Knowledge Graph Embeddings
May 22, 2025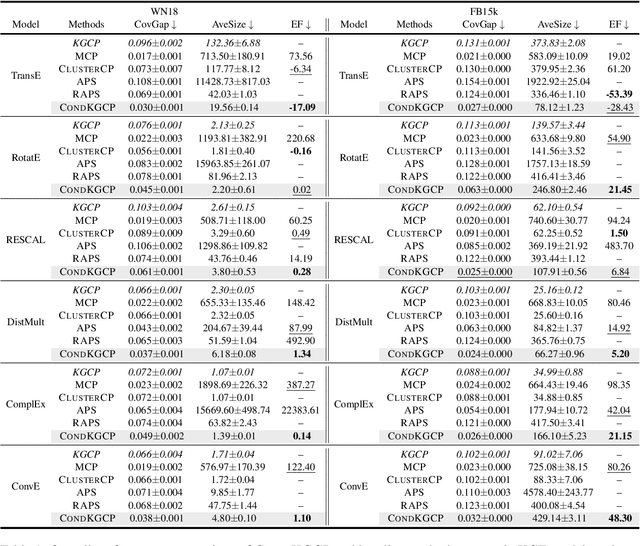
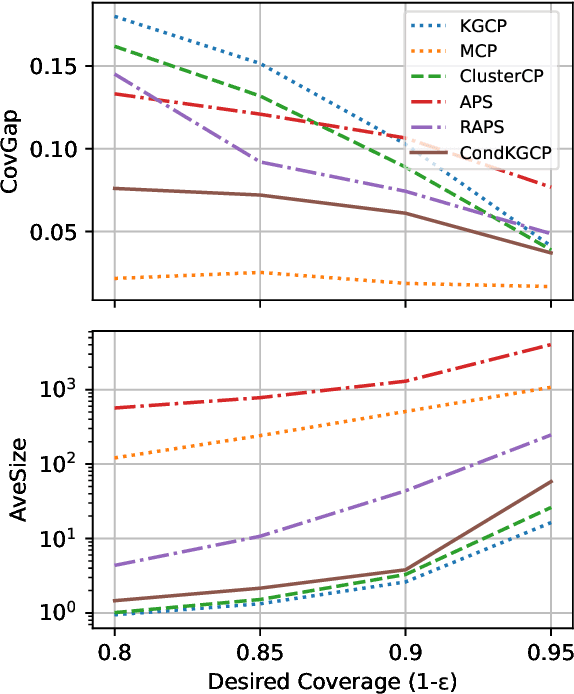
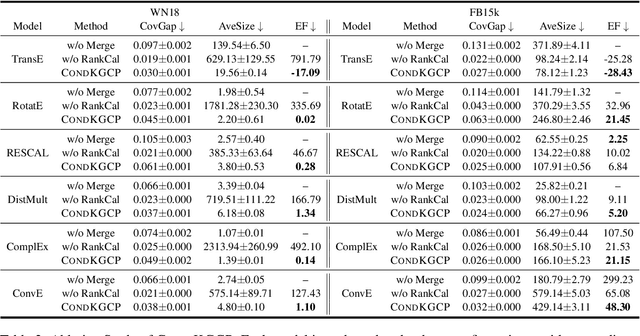
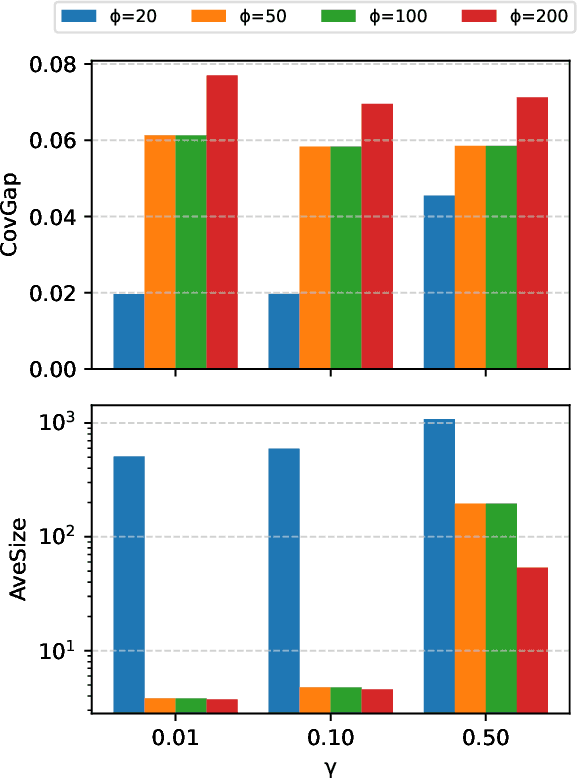
Abstract:Uncertainty quantification in Knowledge Graph Embedding (KGE) methods is crucial for ensuring the reliability of downstream applications. A recent work applies conformal prediction to KGE methods, providing uncertainty estimates by generating a set of answers that is guaranteed to include the true answer with a predefined confidence level. However, existing methods provide probabilistic guarantees averaged over a reference set of queries and answers (marginal coverage guarantee). In high-stakes applications such as medical diagnosis, a stronger guarantee is often required: the predicted sets must provide consistent coverage per query (conditional coverage guarantee). We propose CondKGCP, a novel method that approximates predicate-conditional coverage guarantees while maintaining compact prediction sets. CondKGCP merges predicates with similar vector representations and augments calibration with rank information. We prove the theoretical guarantees and demonstrate empirical effectiveness of CondKGCP by comprehensive evaluations.
MultiADS: Defect-aware Supervision for Multi-type Anomaly Detection and Segmentation in Zero-Shot Learning
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Precise optical inspection in industrial applications is crucial for minimizing scrap rates and reducing the associated costs. Besides merely detecting if a product is anomalous or not, it is crucial to know the distinct type of defect, such as a bent, cut, or scratch. The ability to recognize the "exact" defect type enables automated treatments of the anomalies in modern production lines. Current methods are limited to solely detecting whether a product is defective or not without providing any insights on the defect type, nevertheless detecting and identifying multiple defects. We propose MultiADS, a zero-shot learning approach, able to perform Multi-type Anomaly Detection and Segmentation. The architecture of MultiADS comprises CLIP and extra linear layers to align the visual- and textual representation in a joint feature space. To the best of our knowledge, our proposal, is the first approach to perform a multi-type anomaly segmentation task in zero-shot learning. Contrary to the other baselines, our approach i) generates specific anomaly masks for each distinct defect type, ii) learns to distinguish defect types, and iii) simultaneously identifies multiple defect types present in an anomalous product. Additionally, our approach outperforms zero/few-shot learning SoTA methods on image-level and pixel-level anomaly detection and segmentation tasks on five commonly used datasets: MVTec-AD, Visa, MPDD, MAD and Real-IAD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge