Ruchir Puri
IBM
Think Locally, Explain Globally: Graph-Guided LLM Investigations via Local Reasoning and Belief Propagation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:LLM agents excel when environments are mostly static and the needed information fits in a model's context window, but they often fail in open-ended investigations where explanations must be constructed by iteratively mining evidence from massive, heterogeneous operational data. These investigations exhibit hidden dependency structure: entities interact, signals co-vary, and the importance of a fact may only become clear after other evidence is discovered. Because the context window is bounded, agents must summarize intermediate findings before their significance is known, increasing the risk of discarding key evidence. ReAct-style agents are especially brittle in this regime. Their retrieve-summarize-reason loop makes conclusions sensitive to exploration order and introduces run-to-run non-determinism, producing a reliability gap where Pass-at-k may be high but Majority-at-k remains low. Simply sampling more rollouts or generating longer reasoning traces does not reliably stabilize results, since hypotheses cannot be autonomously checked as new evidence arrives and there is no explicit mechanism for belief bookkeeping and revision. In addition, ReAct entangles semantic reasoning with controller duties such as tool orchestration and state tracking, so execution errors and plan drift degrade reasoning while consuming scarce context. We address these issues by formulating investigation as abductive reasoning over a dependency graph and proposing EoG (Explanations over Graphs), a disaggregated framework in which an LLM performs bounded local evidence mining and labeling (cause vs symptom) while a deterministic controller manages traversal, state, and belief propagation to compute a minimal explanatory frontier. On a representative ITBench diagnostics task, EoG improves both accuracy and run-to-run consistency over ReAct baselines, including a 7x average gain in Majority-at-k entity F1.
Report for NSF Workshop on AI for Electronic Design Automation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:This report distills the discussions and recommendations from the NSF Workshop on AI for Electronic Design Automation (EDA), held on December 10, 2024 in Vancouver alongside NeurIPS 2024. Bringing together experts across machine learning and EDA, the workshop examined how AI-spanning large language models (LLMs), graph neural networks (GNNs), reinforcement learning (RL), neurosymbolic methods, etc.-can facilitate EDA and shorten design turnaround. The workshop includes four themes: (1) AI for physical synthesis and design for manufacturing (DFM), discussing challenges in physical manufacturing process and potential AI applications; (2) AI for high-level and logic-level synthesis (HLS/LLS), covering pragma insertion, program transformation, RTL code generation, etc.; (3) AI toolbox for optimization and design, discussing frontier AI developments that could potentially be applied to EDA tasks; and (4) AI for test and verification, including LLM-assisted verification tools, ML-augmented SAT solving, security/reliability challenges, etc. The report recommends NSF to foster AI/EDA collaboration, invest in foundational AI for EDA, develop robust data infrastructures, promote scalable compute infrastructure, and invest in workforce development to democratize hardware design and enable next-generation hardware systems. The workshop information can be found on the website https://ai4eda-workshop.github.io/.
Customizing a Large Language Model for VHDL Design of High-Performance Microprocessors
May 14, 2025Abstract:The use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in hardware design has taken off in recent years, principally through its incorporation in tools that increase chip designer productivity. There has been considerable discussion about the use of LLMs in RTL specifications of chip designs, for which the two most popular languages are Verilog and VHDL. LLMs and their use in Verilog design has received significant attention due to the higher popularity of the language, but little attention so far has been given to VHDL despite its continued popularity in the industry. There has also been little discussion about the unique needs of organizations that engage in high-performance processor design, and techniques to deploy AI solutions in these settings. In this paper, we describe our journey in developing a Large Language Model (LLM) specifically for the purpose of explaining VHDL code, a task that has particular importance in an organization with decades of experience and assets in high-performance processor design. We show how we developed test sets specific to our needs and used them for evaluating models as we performed extended pretraining (EPT) of a base LLM. Expert evaluation of the code explanations produced by the EPT model increased to 69% compared to a base model rating of 43%. We further show how we developed an LLM-as-a-judge to gauge models similar to expert evaluators. This led us to deriving and evaluating a host of new models, including an instruction-tuned version of the EPT model with an expected expert evaluator rating of 71%. Our experiments also indicate that with the potential use of newer base models, this rating can be pushed to 85% and beyond. We conclude with a discussion on further improving the quality of hardware design LLMs using exciting new developments in the Generative AI world.
ITBench: Evaluating AI Agents across Diverse Real-World IT Automation Tasks
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:Realizing the vision of using AI agents to automate critical IT tasks depends on the ability to measure and understand effectiveness of proposed solutions. We introduce ITBench, a framework that offers a systematic methodology for benchmarking AI agents to address real-world IT automation tasks. Our initial release targets three key areas: Site Reliability Engineering (SRE), Compliance and Security Operations (CISO), and Financial Operations (FinOps). The design enables AI researchers to understand the challenges and opportunities of AI agents for IT automation with push-button workflows and interpretable metrics. ITBench includes an initial set of 94 real-world scenarios, which can be easily extended by community contributions. Our results show that agents powered by state-of-the-art models resolve only 13.8% of SRE scenarios, 25.2% of CISO scenarios, and 0% of FinOps scenarios. We expect ITBench to be a key enabler of AI-driven IT automation that is correct, safe, and fast.
Transforming the Hybrid Cloud for Emerging AI Workloads
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:This white paper, developed through close collaboration between IBM Research and UIUC researchers within the IIDAI Institute, envisions transforming hybrid cloud systems to meet the growing complexity of AI workloads through innovative, full-stack co-design approaches, emphasizing usability, manageability, affordability, adaptability, efficiency, and scalability. By integrating cutting-edge technologies such as generative and agentic AI, cross-layer automation and optimization, unified control plane, and composable and adaptive system architecture, the proposed framework addresses critical challenges in energy efficiency, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Incorporating quantum computing as it matures will enable quantum-accelerated simulations for materials science, climate modeling, and other high-impact domains. Collaborative efforts between academia and industry are central to this vision, driving advancements in foundation models for material design and climate solutions, scalable multimodal data processing, and enhanced physics-based AI emulators for applications like weather forecasting and carbon sequestration. Research priorities include advancing AI agentic systems, LLM as an Abstraction (LLMaaA), AI model optimization and unified abstractions across heterogeneous infrastructure, end-to-end edge-cloud transformation, efficient programming model, middleware and platform, secure infrastructure, application-adaptive cloud systems, and new quantum-classical collaborative workflows. These ideas and solutions encompass both theoretical and practical research questions, requiring coordinated input and support from the research community. This joint initiative aims to establish hybrid clouds as secure, efficient, and sustainable platforms, fostering breakthroughs in AI-driven applications and scientific discovery across academia, industry, and society.
Scaling Granite Code Models to 128K Context
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces long-context Granite code models that support effective context windows of up to 128K tokens. Our solution for scaling context length of Granite 3B/8B code models from 2K/4K to 128K consists of a light-weight continual pretraining by gradually increasing its RoPE base frequency with repository-level file packing and length-upsampled long-context data. Additionally, we also release instruction-tuned models with long-context support which are derived by further finetuning the long context base models on a mix of permissively licensed short and long-context instruction-response pairs. While comparing to the original short-context Granite code models, our long-context models achieve significant improvements on long-context tasks without any noticeable performance degradation on regular code completion benchmarks (e.g., HumanEval). We release all our long-context Granite code models under an Apache 2.0 license for both research and commercial use.
The infrastructure powering IBM's Gen AI model development
Jul 07, 2024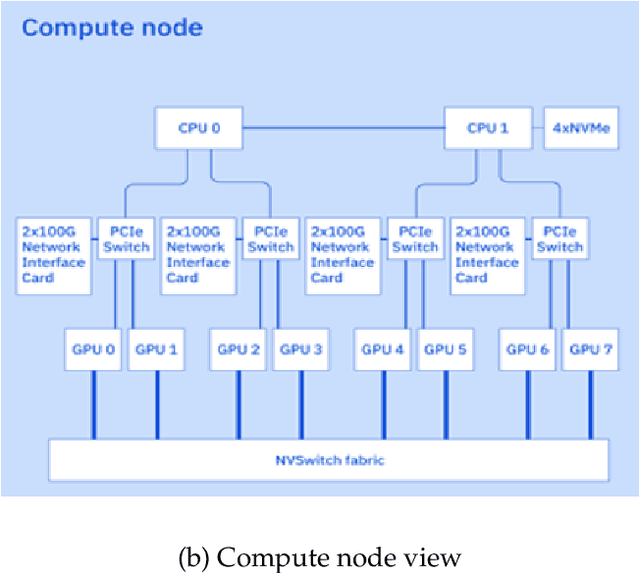
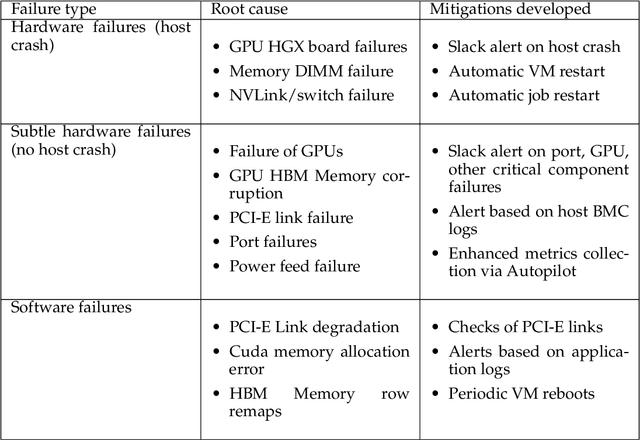
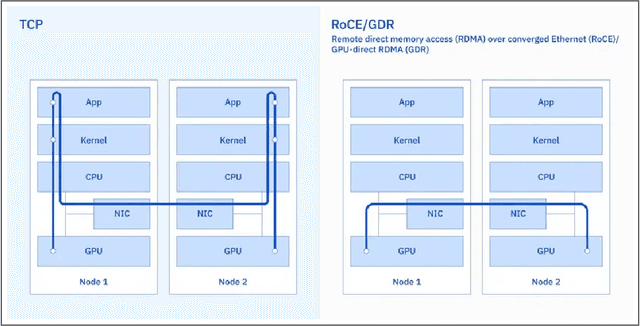
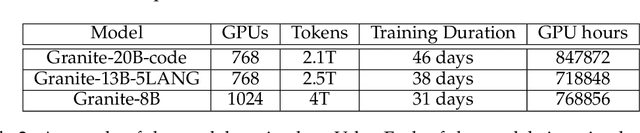
Abstract:AI Infrastructure plays a key role in the speed and cost-competitiveness of developing and deploying advanced AI models. The current demand for powerful AI infrastructure for model training is driven by the emergence of generative AI and foundational models, where on occasion thousands of GPUs must cooperate on a single training job for the model to be trained in a reasonable time. Delivering efficient and high-performing AI training requires an end-to-end solution that combines hardware, software and holistic telemetry to cater for multiple types of AI workloads. In this report, we describe IBM's hybrid cloud infrastructure that powers our generative AI model development. This infrastructure includes (1) Vela: an AI-optimized supercomputing capability directly integrated into the IBM Cloud, delivering scalable, dynamic, multi-tenant and geographically distributed infrastructure for large-scale model training and other AI workflow steps and (2) Blue Vela: a large-scale, purpose-built, on-premises hosting environment that is optimized to support our largest and most ambitious AI model training tasks. Vela provides IBM with the dual benefit of high performance for internal use along with the flexibility to adapt to an evolving commercial landscape. Blue Vela provides us with the benefits of rapid development of our largest and most ambitious models, as well as future-proofing against the evolving model landscape in the industry. Taken together, they provide IBM with the ability to rapidly innovate in the development of both AI models and commercial offerings.
Qiskit HumanEval: An Evaluation Benchmark For Quantum Code Generative Models
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:Quantum programs are typically developed using quantum Software Development Kits (SDKs). The rapid advancement of quantum computing necessitates new tools to streamline this development process, and one such tool could be Generative Artificial intelligence (GenAI). In this study, we introduce and use the Qiskit HumanEval dataset, a hand-curated collection of tasks designed to benchmark the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to produce quantum code using Qiskit - a quantum SDK. This dataset consists of more than 100 quantum computing tasks, each accompanied by a prompt, a canonical solution, a comprehensive test case, and a difficulty scale to evaluate the correctness of the generated solutions. We systematically assess the performance of a set of LLMs against the Qiskit HumanEval dataset's tasks and focus on the models ability in producing executable quantum code. Our findings not only demonstrate the feasibility of using LLMs for generating quantum code but also establish a new benchmark for ongoing advancements in the field and encourage further exploration and development of GenAI-driven tools for quantum code generation.
Ask-EDA: A Design Assistant Empowered by LLM, Hybrid RAG and Abbreviation De-hallucination
Jun 03, 2024Abstract:Electronic design engineers are challenged to find relevant information efficiently for a myriad of tasks within design construction, verification and technology development. Large language models (LLM) have the potential to help improve productivity by serving as conversational agents that effectively function as subject-matter experts. In this paper we demonstrate Ask-EDA, a chat agent designed to serve as a 24x7 expert available to provide guidance to design engineers. Ask-EDA leverages LLM, hybrid retrieval augmented generation (RAG) and abbreviation de-hallucination (ADH) techniques to deliver more relevant and accurate responses. We curated three evaluation datasets, namely q2a-100, cmds-100 and abbr-100. Each dataset is tailored to assess a distinct aspect: general design question answering, design command handling and abbreviation resolution. We demonstrated that hybrid RAG offers over a 40% improvement in Recall on the q2a-100 dataset and over a 60% improvement on the cmds-100 dataset compared to not using RAG, while ADH yields over a 70% enhancement in Recall on the abbr-100 dataset. The evaluation results show that Ask-EDA can effectively respond to design-related inquiries.
Qiskit Code Assistant: Training LLMs for generating Quantum Computing Code
May 29, 2024
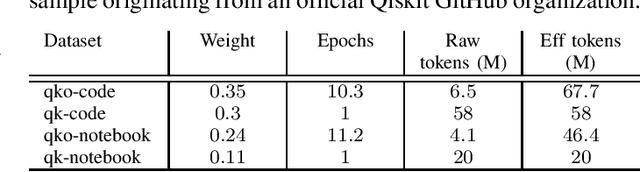
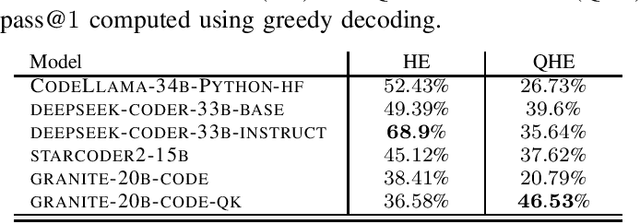
Abstract:Code Large Language Models (Code LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools, revolutionizing the software development landscape by automating the coding process and reducing time and effort required to build applications. This paper focuses on training Code LLMs to specialize in the field of quantum computing. We begin by discussing the unique needs of quantum computing programming, which differ significantly from classical programming approaches or languages. A Code LLM specializing in quantum computing requires a foundational understanding of quantum computing and quantum information theory. However, the scarcity of available quantum code examples and the rapidly evolving field, which necessitates continuous dataset updates, present significant challenges. Moreover, we discuss our work on training Code LLMs to produce high-quality quantum code using the Qiskit library. This work includes an examination of the various aspects of the LLMs used for training and the specific training conditions, as well as the results obtained with our current models. To evaluate our models, we have developed a custom benchmark, similar to HumanEval, which includes a set of tests specifically designed for the field of quantum computing programming using Qiskit. Our findings indicate that our model outperforms existing state-of-the-art models in quantum computing tasks. We also provide examples of code suggestions, comparing our model to other relevant code LLMs. Finally, we introduce a discussion on the potential benefits of Code LLMs for quantum computing computational scientists, researchers, and practitioners. We also explore various features and future work that could be relevant in this context.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge