Qiyuan Tian
AnyAD: Unified Any-Modality Anomaly Detection in Incomplete Multi-Sequence MRI
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Reliable anomaly detection in brain MRI remains challenging due to the scarcity of annotated abnormal cases and the frequent absence of key imaging modalities in real clinical workflows. Existing single-class or multi-class anomaly detection (AD) models typically rely on fixed modality configurations, require repetitive training, or fail to generalize to unseen modality combinations, limiting their clinical scalability. In this work, we present a unified Any-Modality AD framework that performs robust anomaly detection and localization under arbitrary MRI modality availability. The framework integrates a dual-pathway DINOv2 encoder with a feature distribution alignment mechanism that statistically aligns incomplete-modality features with full-modality representations, enabling stable inference even with severe modality dropout. To further enhance semantic consistency, we introduce an Intrinsic Normal Prototypes (INPs) extractor and an INP-guided decoder that reconstruct only normal anatomical patterns while naturally amplifying abnormal deviations. Through randomized modality masking and indirect feature completion during training, the model learns to adapt to all modality configurations without re-training. Extensive experiments on BraTS2018, MU-Glioma-Post, and Pretreat-MetsToBrain-Masks demonstrate that our approach consistently surpasses state-of-the-art industrial and medical AD baselines across 7 modality combinations, achieving superior generalization. This study establishes a scalable paradigm for multimodal medical AD under real-world, imperfect modality conditions. Our source code is available at https://github.com/wuchangw/AnyAD.
No Modality Left Behind: Adapting to Missing Modalities via Knowledge Distillation for Brain Tumor Segmentation
Sep 18, 2025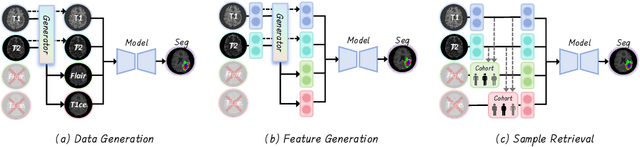
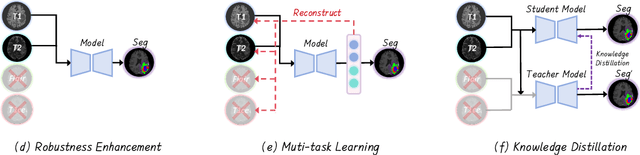
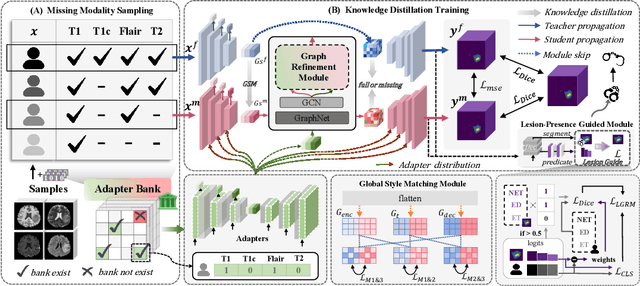
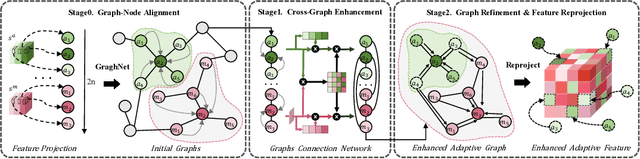
Abstract:Accurate brain tumor segmentation is essential for preoperative evaluation and personalized treatment. Multi-modal MRI is widely used due to its ability to capture complementary tumor features across different sequences. However, in clinical practice, missing modalities are common, limiting the robustness and generalizability of existing deep learning methods that rely on complete inputs, especially under non-dominant modality combinations. To address this, we propose AdaMM, a multi-modal brain tumor segmentation framework tailored for missing-modality scenarios, centered on knowledge distillation and composed of three synergistic modules. The Graph-guided Adaptive Refinement Module explicitly models semantic associations between generalizable and modality-specific features, enhancing adaptability to modality absence. The Bi-Bottleneck Distillation Module transfers structural and textural knowledge from teacher to student models via global style matching and adversarial feature alignment. The Lesion-Presence-Guided Reliability Module predicts prior probabilities of lesion types through an auxiliary classification task, effectively suppressing false positives under incomplete inputs. Extensive experiments on the BraTS 2018 and 2024 datasets demonstrate that AdaMM consistently outperforms existing methods, exhibiting superior segmentation accuracy and robustness, particularly in single-modality and weak-modality configurations. In addition, we conduct a systematic evaluation of six categories of missing-modality strategies, confirming the superiority of knowledge distillation and offering practical guidance for method selection and future research. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Quanato607/AdaMM.
Diff5T: Benchmarking Human Brain Diffusion MRI with an Extensive 5.0 Tesla K-Space and Spatial Dataset
Dec 09, 2024

Abstract:Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) provides critical insights into the microstructural and connectional organization of the human brain. However, the availability of high-field, open-access datasets that include raw k-space data for advanced research remains limited. To address this gap, we introduce Diff5T, a first comprehensive 5.0 Tesla diffusion MRI dataset focusing on the human brain. This dataset includes raw k-space data and reconstructed diffusion images, acquired using a variety of imaging protocols. Diff5T is designed to support the development and benchmarking of innovative methods in artifact correction, image reconstruction, image preprocessing, diffusion modelling and tractography. The dataset features a wide range of diffusion parameters, including multiple b-values and gradient directions, allowing extensive research applications in studying human brain microstructure and connectivity. With its emphasis on open accessibility and detailed benchmarks, Diff5T serves as a valuable resource for advancing human brain mapping research using diffusion MRI, fostering reproducibility, and enabling collaboration across the neuroscience and medical imaging communities.
Artificial Intelligence without Restriction Surpassing Human Intelligence with Probability One: Theoretical Insight into Secrets of the Brain with AI Twins of the Brain
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has apparently become one of the most important techniques discovered by humans in history while the human brain is widely recognized as one of the most complex systems in the universe. One fundamental critical question which would affect human sustainability remains open: Will artificial intelligence (AI) evolve to surpass human intelligence in the future? This paper shows that in theory new AI twins with fresh cellular level of AI techniques for neuroscience could approximate the brain and its functioning systems (e.g. perception and cognition functions) with any expected small error and AI without restrictions could surpass human intelligence with probability one in the end. This paper indirectly proves the validity of the conjecture made by Frank Rosenblatt 70 years ago about the potential capabilities of AI, especially in the realm of artificial neural networks. Intelligence is just one of fortuitous but sophisticated creations of the nature which has not been fully discovered. Like mathematics and physics, with no restrictions artificial intelligence would lead to a new subject with its self-contained systems and principles. We anticipate that this paper opens new doors for 1) AI twins and other AI techniques to be used in cellular level of efficient neuroscience dynamic analysis, functioning analysis of the brain and brain illness solutions; 2) new worldwide collaborative scheme for interdisciplinary teams concurrently working on and modelling different types of neurons and synapses and different level of functioning subsystems of the brain with AI techniques; 3) development of low energy of AI techniques with the aid of fundamental neuroscience properties; and 4) new controllable, explainable and safe AI techniques with reasoning capabilities of discovering principles in nature.
Enhance the Image: Super Resolution using Artificial Intelligence in MRI
Jun 19, 2024



Abstract:This chapter provides an overview of deep learning techniques for improving the spatial resolution of MRI, ranging from convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, to more advanced models including transformers, diffusion models, and implicit neural representations. Our exploration extends beyond the methodologies to scrutinize the impact of super-resolved images on clinical and neuroscientific assessments. We also cover various practical topics such as network architectures, image evaluation metrics, network loss functions, and training data specifics, including downsampling methods for simulating low-resolution images and dataset selection. Finally, we discuss existing challenges and potential future directions regarding the feasibility and reliability of deep learning-based MRI super-resolution, with the aim to facilitate its wider adoption to benefit various clinical and neuroscientific applications.
Artificial Intelligence for Neuro MRI Acquisition: A Review
Jun 10, 2024Abstract:Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has significantly benefited from the resurgence of artificial intelligence (AI). By leveraging AI's capabilities in large-scale optimization and pattern recognition, innovative methods are transforming the MRI acquisition workflow, including planning, sequence design, and correction of acquisition artifacts. These emerging algorithms demonstrate substantial potential in enhancing the efficiency and throughput of acquisition steps. This review discusses several pivotal AI-based methods in neuro MRI acquisition, focusing on their technological advances, impact on clinical practice, and potential risks.
3D-EPI Blip-Up/Down Acquisition with CAIPI and Joint Hankel Structured Low-Rank Reconstruction for Rapid Distortion-Free High-Resolution T2* Mapping
Dec 01, 2022Abstract:Purpose: This work aims to develop a novel distortion-free 3D-EPI acquisition and image reconstruction technique for fast and robust, high-resolution, whole-brain imaging as well as quantitative T2* mapping. Methods: 3D-Blip-Up and -Down Acquisition (3D-BUDA) sequence is designed for both single- and multi-echo 3D GRE-EPI imaging using multiple shots with blip-up and -down readouts to encode B0 field map information. Complementary k-space coverage is achieved using controlled aliasing in parallel imaging (CAIPI) sampling across the shots. For image reconstruction, an iterative hard-thresholding algorithm is employed to minimize the cost function that combines field map information informed parallel imaging with the structured low-rank constraint for multi-shot 3D-BUDA data. Extending 3D-BUDA to multi-echo imaging permits T2* mapping. For this, we propose constructing a joint Hankel matrix along both echo and shot dimensions to improve the reconstruction. Results: Experimental results on in vivo multi-echo data demonstrate that, by performing joint reconstruction along with both echo and shot dimensions, reconstruction accuracy is improved compared to standard 3D-BUDA reconstruction. CAIPI sampling is further shown to enhance the image quality. For T2* mapping, T2* values from 3D-Joint-CAIPI-BUDA and reference multi-echo GRE are within limits of agreement as quantified by Bland-Altman analysis. Conclusions: The proposed technique enables rapid 3D distortion-free high-resolution imaging and T2* mapping. Specifically, 3D-BUDA enables 1-mm isotropic whole-brain imaging in 22 s at 3 T and 9 s on a 7 T scanner. The combination of multi-echo 3D-BUDA with CAIPI acquisition and joint reconstruction enables distortion-free whole-brain T2* mapping in 47 s at 1.1x1.1x1.0 mm3 resolution.
SRNR: Training neural networks for Super-Resolution MRI using Noisy high-resolution Reference data
Nov 10, 2022Abstract:Neural network (NN) based approaches for super-resolution MRI typically require high-SNR high-resolution reference data acquired in many subjects, which is time consuming and a barrier to feasible and accessible implementation. We propose to train NNs for Super-Resolution using Noisy Reference data (SRNR), leveraging the mechanism of the classic NN-based denoising method Noise2Noise. We systematically demonstrate that results from NNs trained using noisy and high-SNR references are similar for both simulated and empirical data. SRNR suggests a smaller number of repetitions of high-resolution reference data can be used to simplify the training data preparation for super-resolution MRI.
Wave-Encoded Model-based Deep Learning for Highly Accelerated Imaging with Joint Reconstruction
Feb 06, 2022Abstract:Purpose: To propose a wave-encoded model-based deep learning (wave-MoDL) strategy for highly accelerated 3D imaging and joint multi-contrast image reconstruction, and further extend this to enable rapid quantitative imaging using an interleaved look-locker acquisition sequence with T2 preparation pulse (3D-QALAS). Method: Recently introduced MoDL technique successfully incorporates convolutional neural network (CNN)-based regularizers into physics-based parallel imaging reconstruction using a small number of network parameters. Wave-CAIPI is an emerging parallel imaging method that accelerates the imaging speed by employing sinusoidal gradients in the phase- and slice-encoding directions during the readout to take better advantage of 3D coil sensitivity profiles. In wave-MoDL, we propose to combine the wave-encoding strategy with unrolled network constraints to accelerate the acquisition speed while enforcing wave-encoded data consistency. We further extend wave-MoDL to reconstruct multi-contrast data with controlled aliasing in parallel imaging (CAIPI) sampling patterns to leverage similarity between multiple images to improve the reconstruction quality. Result: Wave-MoDL enables a 47-second MPRAGE acquisition at 1 mm resolution at 16-fold acceleration. For quantitative imaging, wave-MoDL permits a 2-minute acquisition for T1, T2, and proton density mapping at 1 mm resolution at 12-fold acceleration, from which contrast weighted images can be synthesized as well. Conclusion: Wave-MoDL allows rapid MR acquisition and high-fidelity image reconstruction and may facilitate clinical and neuroscientific applications by incorporating unrolled neural networks into wave-CAIPI reconstruction.
Quantifying the uncertainty of neural networks using Monte Carlo dropout for deep learning based quantitative MRI
Dec 02, 2021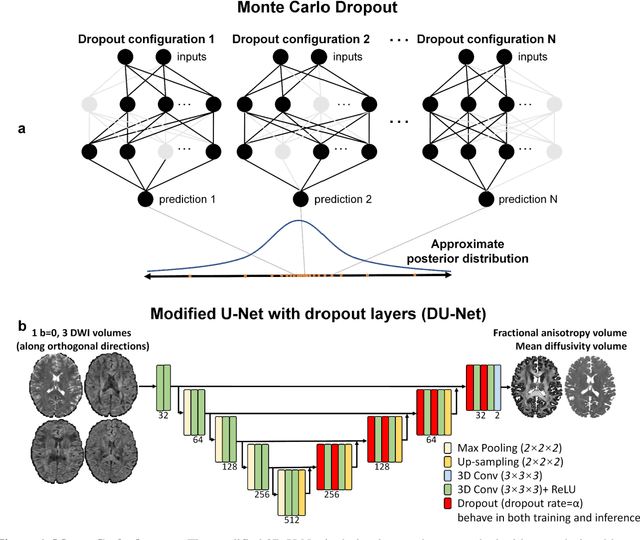
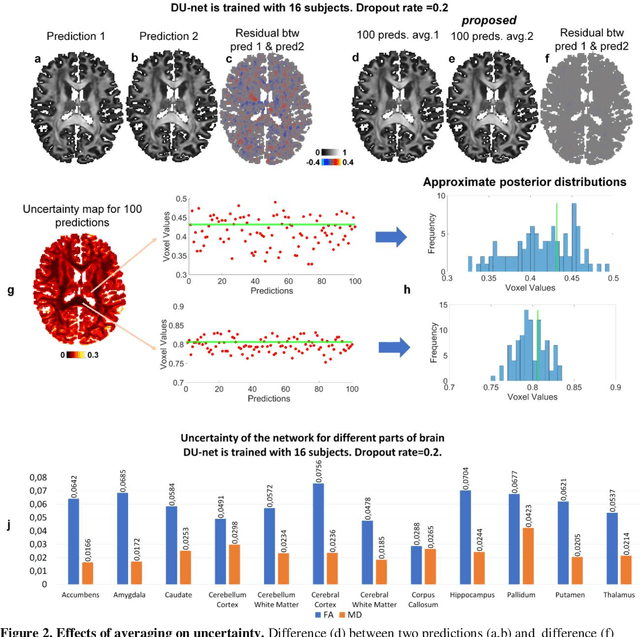
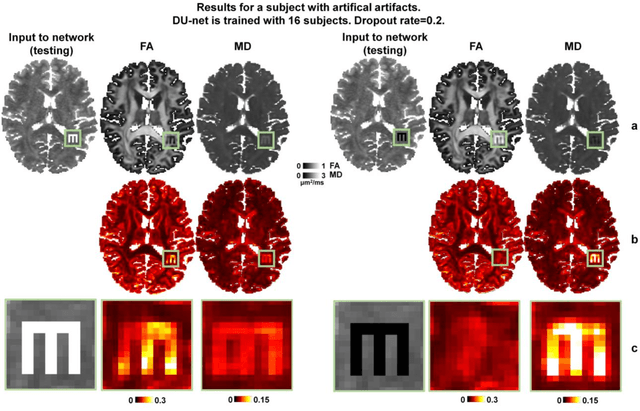
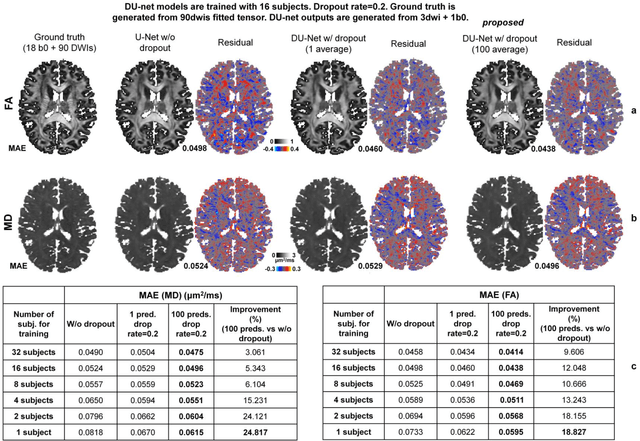
Abstract:Dropout is conventionally used during the training phase as regularization method and for quantifying uncertainty in deep learning. We propose to use dropout during training as well as inference steps, and average multiple predictions to improve the accuracy, while reducing and quantifying the uncertainty. The results are evaluated for fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) maps which are obtained from only 3 direction scans. With our method, accuracy can be improved significantly compared to network outputs without dropout, especially when the training dataset is small. Moreover, confidence maps are generated which may aid in diagnosis of unseen pathology or artifacts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge