Qin Guo
UniMC: Taming Diffusion Transformer for Unified Keypoint-Guided Multi-Class Image Generation
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Although significant advancements have been achieved in the progress of keypoint-guided Text-to-Image diffusion models, existing mainstream keypoint-guided models encounter challenges in controlling the generation of more general non-rigid objects beyond humans (e.g., animals). Moreover, it is difficult to generate multiple overlapping humans and animals based on keypoint controls solely. These challenges arise from two main aspects: the inherent limitations of existing controllable methods and the lack of suitable datasets. First, we design a DiT-based framework, named UniMC, to explore unifying controllable multi-class image generation. UniMC integrates instance- and keypoint-level conditions into compact tokens, incorporating attributes such as class, bounding box, and keypoint coordinates. This approach overcomes the limitations of previous methods that struggled to distinguish instances and classes due to their reliance on skeleton images as conditions. Second, we propose HAIG-2.9M, a large-scale, high-quality, and diverse dataset designed for keypoint-guided human and animal image generation. HAIG-2.9M includes 786K images with 2.9M instances. This dataset features extensive annotations such as keypoints, bounding boxes, and fine-grained captions for both humans and animals, along with rigorous manual inspection to ensure annotation accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate the high quality of HAIG-2.9M and the effectiveness of UniMC, particularly in heavy occlusions and multi-class scenarios.
Long-Term TalkingFace Generation via Motion-Prior Conditional Diffusion Model
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in conditional diffusion models have shown promise for generating realistic TalkingFace videos, yet challenges persist in achieving consistent head movement, synchronized facial expressions, and accurate lip synchronization over extended generations. To address these, we introduce the \textbf{M}otion-priors \textbf{C}onditional \textbf{D}iffusion \textbf{M}odel (\textbf{MCDM}), which utilizes both archived and current clip motion priors to enhance motion prediction and ensure temporal consistency. The model consists of three key elements: (1) an archived-clip motion-prior that incorporates historical frames and a reference frame to preserve identity and context; (2) a present-clip motion-prior diffusion model that captures multimodal causality for accurate predictions of head movements, lip sync, and expressions; and (3) a memory-efficient temporal attention mechanism that mitigates error accumulation by dynamically storing and updating motion features. We also release the \textbf{TalkingFace-Wild} dataset, a multilingual collection of over 200 hours of footage across 10 languages. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of MCDM in maintaining identity and motion continuity for long-term TalkingFace generation. Code, models, and datasets will be publicly available.
Focus on Your Instruction: Fine-grained and Multi-instruction Image Editing by Attention Modulation
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:Recently, diffusion-based methods, like InstructPix2Pix (IP2P), have achieved effective instruction-based image editing, requiring only natural language instructions from the user. However, these methods often inadvertently alter unintended areas and struggle with multi-instruction editing, resulting in compromised outcomes. To address these issues, we introduce the Focus on Your Instruction (FoI), a method designed to ensure precise and harmonious editing across multiple instructions without extra training or test-time optimization. In the FoI, we primarily emphasize two aspects: (1) precisely extracting regions of interest for each instruction and (2) guiding the denoising process to concentrate within these regions of interest. For the first objective, we identify the implicit grounding capability of IP2P from the cross-attention between instruction and image, then develop an effective mask extraction method. For the second objective, we introduce a cross attention modulation module for rough isolation of target editing regions and unrelated regions. Additionally, we introduce a mask-guided disentangle sampling strategy to further ensure clear region isolation. Experimental results demonstrate that FoI surpasses existing methods in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations, especially excelling in multi-instruction editing task.
Layered Rendering Diffusion Model for Zero-Shot Guided Image Synthesis
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces innovative solutions to enhance spatial controllability in diffusion models reliant on text queries. We present two key innovations: Vision Guidance and the Layered Rendering Diffusion (LRDiff) framework. Vision Guidance, a spatial layout condition, acts as a clue in the perturbed distribution, greatly narrowing down the search space, to focus on the image sampling process adhering to the spatial layout condition. The LRDiff framework constructs an image-rendering process with multiple layers, each of which applies the vision guidance to instructively estimate the denoising direction for a single object. Such a layered rendering strategy effectively prevents issues like unintended conceptual blending or mismatches, while allowing for more coherent and contextually accurate image synthesis. The proposed method provides a more efficient and accurate means of synthesising images that align with specific spatial and contextual requirements. We demonstrate through our experiments that our method provides better results than existing techniques both quantitatively and qualitatively. We apply our method to three practical applications: bounding box-to-image, semantic mask-to-image and image editing.
Neural Network-Based Histologic Remission Prediction In Ulcerative Colitis
Aug 28, 2023
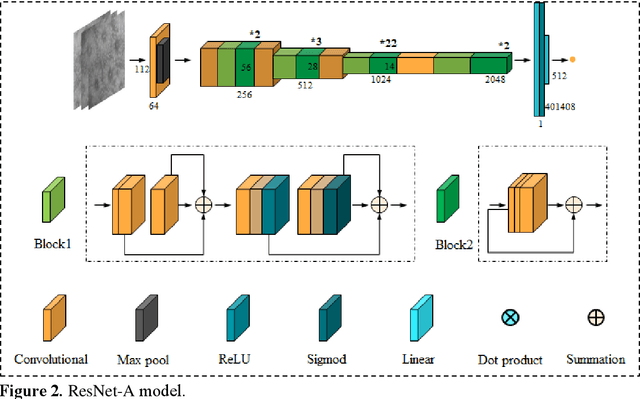
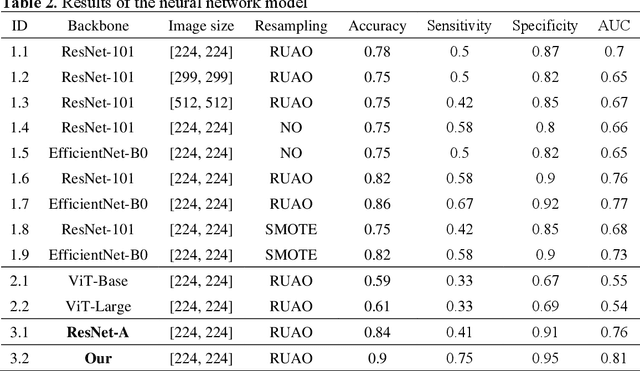
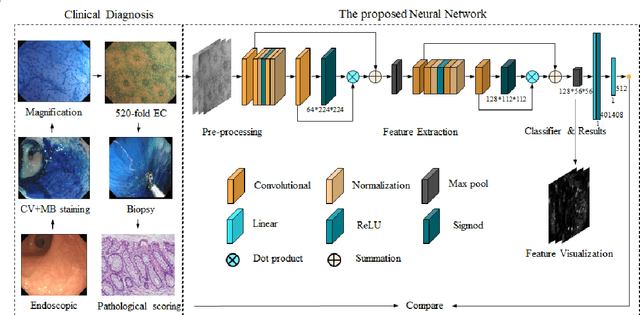
Abstract:BACKGROUND & AIMS: Histological remission (HR) is advocated and considered as a new therapeutic target in ulcerative colitis (UC). Diagnosis of histologic remission currently relies on biopsy; during this process, patients are at risk for bleeding, infection, and post-biopsy fibrosis. In addition, histologic response scoring is complex and time-consuming, and there is heterogeneity among pathologists. Endocytoscopy (EC) is a novel ultra-high magnification endoscopic technique that can provide excellent in vivo assessment of glands. Based on the EC technique, we propose a neural network model that can assess histological disease activity in UC using EC images to address the above issues. The experiment results demonstrate that the proposed method can assist patients in precise treatment and prognostic assessment. METHODS: We construct a neural network model for UC evaluation. A total of 5105 images of 154 intestinal segments from 87 patients undergoing EC treatment at a center in China between March 2022 and March 2023 are scored according to the Geboes score. Subsequently, 103 intestinal segments are used as the training set, 16 intestinal segments are used as the validation set for neural network training, and the remaining 35 intestinal segments are used as the test set to measure the model performance together with the validation set. RESULTS: By treating HR as a negative category and histologic activity as a positive category, the proposed neural network model can achieve an accuracy of 0.9, a specificity of 0.95, a sensitivity of 0.75, and an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.81. CONCLUSION: We develop a specific neural network model that can distinguish histologic remission/activity in EC images of UC, which helps to accelerate clinical histological diagnosis. keywords: ulcerative colitis; Endocytoscopy; Geboes score; neural network.
ChatFace: Chat-Guided Real Face Editing via Diffusion Latent Space Manipulation
May 24, 2023Abstract:Editing real facial images is a crucial task in computer vision with significant demand in various real-world applications. While GAN-based methods have showed potential in manipulating images especially when combined with CLIP, these methods are limited in their ability to reconstruct real images due to challenging GAN inversion capability. Despite the successful image reconstruction achieved by diffusion-based methods, there are still challenges in effectively manipulating fine-gained facial attributes with textual instructions.To address these issues and facilitate convenient manipulation of real facial images, we propose a novel approach that conduct text-driven image editing in the semantic latent space of diffusion model. By aligning the temporal feature of the diffusion model with the semantic condition at generative process, we introduce a stable manipulation strategy, which perform precise zero-shot manipulation effectively. Furthermore, we develop an interactive system named ChatFace, which combines the zero-shot reasoning ability of large language models to perform efficient manipulations in diffusion semantic latent space. This system enables users to perform complex multi-attribute manipulations through dialogue, opening up new possibilities for interactive image editing. Extensive experiments confirmed that our approach outperforms previous methods and enables precise editing of real facial images, making it a promising candidate for real-world applications. Project page: https://dongxuyue.github.io/chatface/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge