Ping Huang
Breaking Down Video LLM Benchmarks: Knowledge, Spatial Perception, or True Temporal Understanding?
May 20, 2025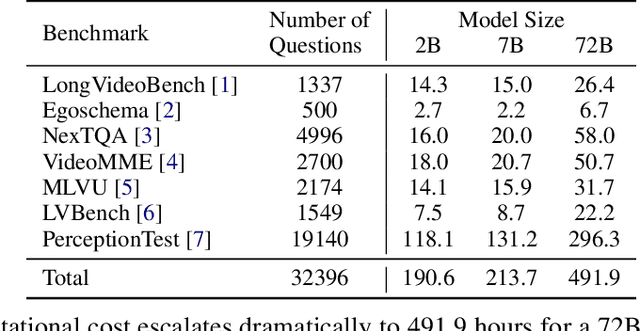
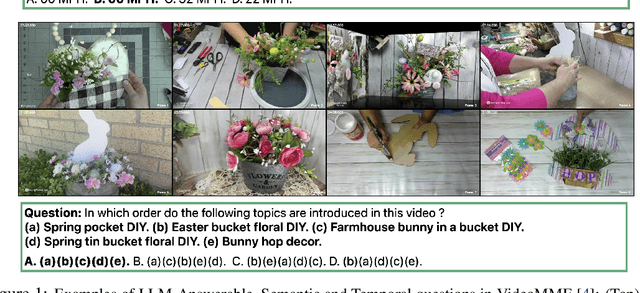
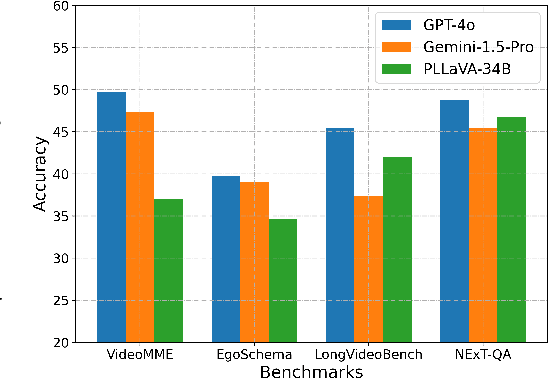
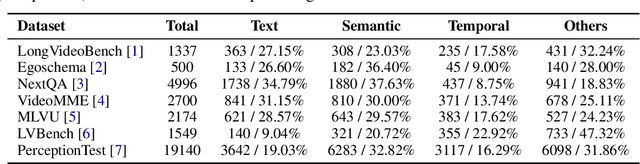
Abstract:Existing video understanding benchmarks often conflate knowledge-based and purely image-based questions, rather than clearly isolating a model's temporal reasoning ability, which is the key aspect that distinguishes video understanding from other modalities. We identify two major limitations that obscure whether higher scores truly indicate stronger understanding of the dynamic content in videos: (1) strong language priors, where models can answer questions without watching the video; and (2) shuffling invariance, where models maintain similar performance on certain questions even when video frames are temporally shuffled. To alleviate these issues, we propose VBenchComp, an automated pipeline that categorizes questions into different domains: LLM-Answerable, Semantic, and Temporal. Specifically, LLM-Answerable questions can be answered without viewing the video; Semantic questions remain answerable even when the video frames are shuffled; and Temporal questions require understanding the correct temporal order of frames. The rest of the questions are labeled as Others. This can enable fine-grained evaluation of different capabilities of a video LLM. Our analysis reveals nuanced model weaknesses that are hidden by traditional overall scores, and we offer insights and recommendations for designing future benchmarks that more accurately assess video LLMs.
StreamBridge: Turning Your Offline Video Large Language Model into a Proactive Streaming Assistant
May 08, 2025Abstract:We present StreamBridge, a simple yet effective framework that seamlessly transforms offline Video-LLMs into streaming-capable models. It addresses two fundamental challenges in adapting existing models into online scenarios: (1) limited capability for multi-turn real-time understanding, and (2) lack of proactive response mechanisms. Specifically, StreamBridge incorporates (1) a memory buffer combined with a round-decayed compression strategy, supporting long-context multi-turn interactions, and (2) a decoupled, lightweight activation model that can be effortlessly integrated into existing Video-LLMs, enabling continuous proactive responses. To further support StreamBridge, we construct Stream-IT, a large-scale dataset tailored for streaming video understanding, featuring interleaved video-text sequences and diverse instruction formats. Extensive experiments show that StreamBridge significantly improves the streaming understanding capabilities of offline Video-LLMs across various tasks, outperforming even proprietary models such as GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Pro. Simultaneously, it achieves competitive or superior performance on standard video understanding benchmarks.
Swin-X2S: Reconstructing 3D Shape from 2D Biplanar X-ray with Swin Transformers
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:The conversion from 2D X-ray to 3D shape holds significant potential for improving diagnostic efficiency and safety. However, existing reconstruction methods often rely on hand-crafted features, manual intervention, and prior knowledge, resulting in unstable shape errors and additional processing costs. In this paper, we introduce Swin-X2S, an end-to-end deep learning method for directly reconstructing 3D segmentation and labeling from 2D biplanar orthogonal X-ray images. Swin-X2S employs an encoder-decoder architecture: the encoder leverages 2D Swin Transformer for X-ray information extraction, while the decoder employs 3D convolution with cross-attention to integrate structural features from orthogonal views. A dimension-expanding module is introduced to bridge the encoder and decoder, ensuring a smooth conversion from 2D pixels to 3D voxels. We evaluate proposed method through extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments across nine publicly available datasets covering four anatomies (femur, hip, spine, and rib), with a total of 54 categories. Significant improvements over previous methods have been observed not only in the segmentation and labeling metrics but also in the clinically relevant parameters that are of primary concern in practical applications, which demonstrates the promise of Swin-X2S to provide an effective option for anatomical shape reconstruction in clinical scenarios. Code implementation is available at: \url{https://github.com/liukuan5625/Swin-X2S}.
Synth4Seg -- Learning Defect Data Synthesis for Defect Segmentation using Bi-level Optimization
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:Defect segmentation is crucial for quality control in advanced manufacturing, yet data scarcity poses challenges for state-of-the-art supervised deep learning. Synthetic defect data generation is a popular approach for mitigating data challenges. However, many current methods simply generate defects following a fixed set of rules, which may not directly relate to downstream task performance. This can lead to suboptimal performance and may even hinder the downstream task. To solve this problem, we leverage a novel bi-level optimization-based synthetic defect data generation framework. We use an online synthetic defect generation module grounded in the commonly-used Cut\&Paste framework, and adopt an efficient gradient-based optimization algorithm to solve the bi-level optimization problem. We achieve simultaneous training of the defect segmentation network, and learn various parameters of the data synthesis module by maximizing the validation performance of the trained defect segmentation network. Our experimental results on benchmark datasets under limited data settings show that the proposed bi-level optimization method can be used for learning the most effective locations for pasting synthetic defects thereby improving the segmentation performance by up to 18.3\% when compared to pasting defects at random locations. We also demonstrate up to 2.6\% performance gain by learning the importance weights for different augmentation-specific defect data sources when compared to giving equal importance to all the data sources.
A Prompt Refinement-based Large Language Model for Metro Passenger Flow Forecasting under Delay Conditions
Oct 19, 2024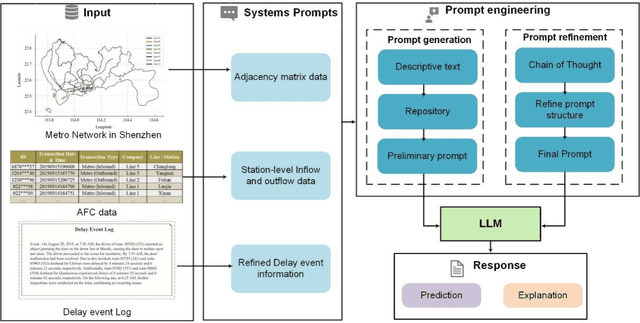
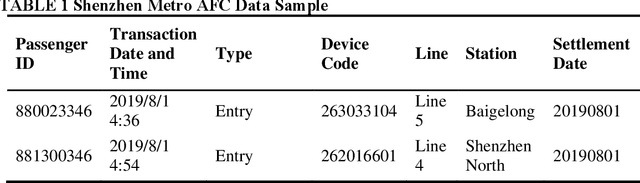
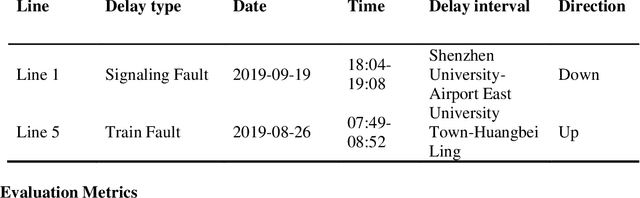
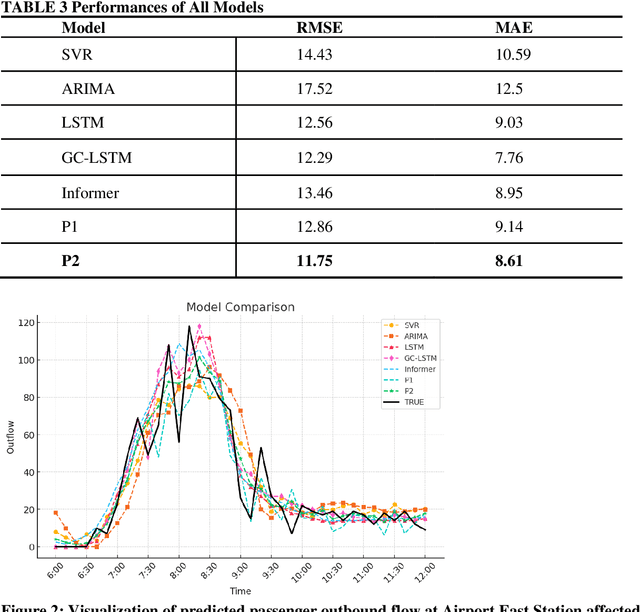
Abstract:Accurate short-term forecasts of passenger flow in metro systems under delay conditions are crucial for emergency response and service recovery, which pose significant challenges and are currently under-researched. Due to the rare occurrence of delay events, the limited sample size under delay condictions make it difficult for conventional models to effectively capture the complex impacts of delays on passenger flow, resulting in low forecasting accuracy. Recognizing the strengths of large language models (LLMs) in few-shot learning due to their powerful pre-training, contextual understanding, ability to perform zero-shot and few-shot reasoning, to address the issues that effectively generalize and adapt with minimal data, we propose a passenger flow forecasting framework under delay conditions that synthesizes an LLM with carefully designed prompt engineering. By Refining prompt design, we enable the LLM to understand delay event information and the pattern from historical passenger flow data, thus overcoming the challenges of passenger flow forecasting under delay conditions. The propmpt engineering in the framework consists of two main stages: systematic prompt generation and prompt refinement. In the prompt generation stage, multi-source data is transformed into descriptive texts understandable by the LLM and stored. In the prompt refinement stage, we employ the multidimensional Chain of Thought (CoT) method to refine the prompts. We verify the proposed framework by conducting experiments using real-world datasets specifically targeting passenger flow forecasting under delay conditions of Shenzhen metro in China. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model performs particularly well in forecasting passenger flow under delay conditions.
Smart Audit System Empowered by LLM
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Manufacturing quality audits are pivotal for ensuring high product standards in mass production environments. Traditional auditing processes, however, are labor-intensive and reliant on human expertise, posing challenges in maintaining transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement across complex global supply chains. To address these challenges, we propose a smart audit system empowered by large language models (LLMs). Our approach introduces three innovations: a dynamic risk assessment model that streamlines audit procedures and optimizes resource allocation; a manufacturing compliance copilot that enhances data processing, retrieval, and evaluation for a self-evolving manufacturing knowledge base; and a Re-act framework commonality analysis agent that provides real-time, customized analysis to empower engineers with insights for supplier improvement. These enhancements elevate audit efficiency and effectiveness, with testing scenarios demonstrating an improvement of over 24%.
ODGEN: Domain-specific Object Detection Data Generation with Diffusion Models
May 24, 2024Abstract:Modern diffusion-based image generative models have made significant progress and become promising to enrich training data for the object detection task. However, the generation quality and the controllability for complex scenes containing multi-class objects and dense objects with occlusions remain limited. This paper presents ODGEN, a novel method to generate high-quality images conditioned on bounding boxes, thereby facilitating data synthesis for object detection. Given a domain-specific object detection dataset, we first fine-tune a pre-trained diffusion model on both cropped foreground objects and entire images to fit target distributions. Then we propose to control the diffusion model using synthesized visual prompts with spatial constraints and object-wise textual descriptions. ODGEN exhibits robustness in handling complex scenes and specific domains. Further, we design a dataset synthesis pipeline to evaluate ODGEN on 7 domain-specific benchmarks to demonstrate its effectiveness. Adding training data generated by ODGEN improves up to 25.3% mAP@.50:.95 with object detectors like YOLOv5 and YOLOv7, outperforming prior controllable generative methods. In addition, we design an evaluation protocol based on COCO-2014 to validate ODGEN in general domains and observe an advantage up to 5.6% in mAP@.50:.95 against existing methods.
NeRO: Neural Road Surface Reconstruction
May 17, 2024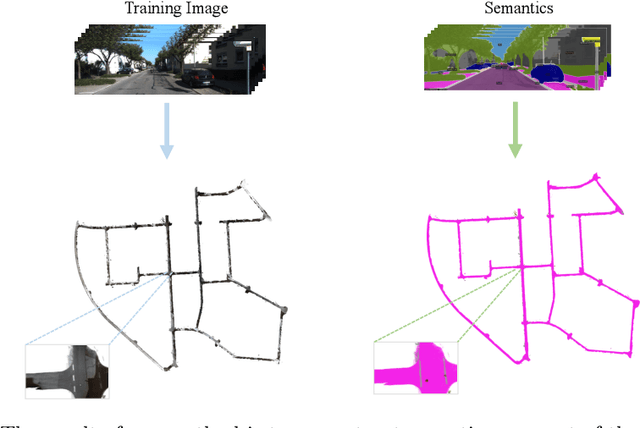
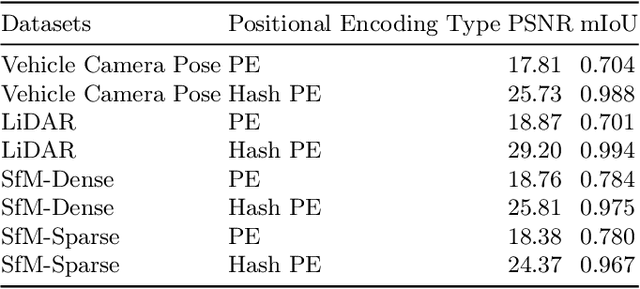
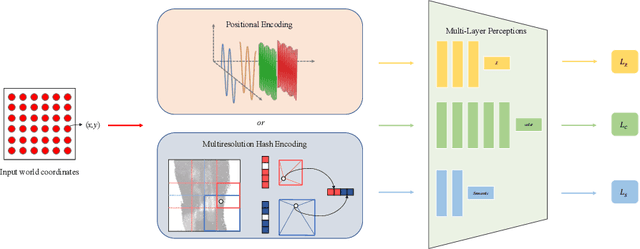

Abstract:In computer vision and graphics, the accurate reconstruction of road surfaces is pivotal for various applications, especially in autonomous driving. This paper introduces a novel method leveraging the Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) framework to reconstruct road surfaces in height, color, and semantic information by input world coordinates x and y. Our approach NeRO uses encoding techniques based on MLPs, significantly improving the performance of the complex details, speeding up the training speed, and reducing neural network size. The effectiveness of this method is demonstrated through its superior performance, which indicates a promising direction for rendering road surfaces with semantics applications, particularly in applications demanding visualization of road conditions, 4D labeling, and semantic groupings.
Semantic Is Enough: Only Semantic Information For NeRF Reconstruction
Mar 24, 2024



Abstract:Recent research that combines implicit 3D representation with semantic information, like Semantic-NeRF, has proven that NeRF model could perform excellently in rendering 3D structures with semantic labels. This research aims to extend the Semantic Neural Radiance Fields (Semantic-NeRF) model by focusing solely on semantic output and removing the RGB output component. We reformulate the model and its training procedure to leverage only the cross-entropy loss between the model semantic output and the ground truth semantic images, removing the colour data traditionally used in the original Semantic-NeRF approach. We then conduct a series of identical experiments using the original and the modified Semantic-NeRF model. Our primary objective is to obverse the impact of this modification on the model performance by Semantic-NeRF, focusing on tasks such as scene understanding, object detection, and segmentation. The results offer valuable insights into the new way of rendering the scenes and provide an avenue for further research and development in semantic-focused 3D scene understanding.
VISION Datasets: A Benchmark for Vision-based InduStrial InspectiON
Jun 18, 2023Abstract:Despite progress in vision-based inspection algorithms, real-world industrial challenges -- specifically in data availability, quality, and complex production requirements -- often remain under-addressed. We introduce the VISION Datasets, a diverse collection of 14 industrial inspection datasets, uniquely poised to meet these challenges. Unlike previous datasets, VISION brings versatility to defect detection, offering annotation masks across all splits and catering to various detection methodologies. Our datasets also feature instance-segmentation annotation, enabling precise defect identification. With a total of 18k images encompassing 44 defect types, VISION strives to mirror a wide range of real-world production scenarios. By supporting two ongoing challenge competitions on the VISION Datasets, we hope to foster further advancements in vision-based industrial inspection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge