Xiaoning Ma
Smart Audit System Empowered by LLM
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Manufacturing quality audits are pivotal for ensuring high product standards in mass production environments. Traditional auditing processes, however, are labor-intensive and reliant on human expertise, posing challenges in maintaining transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement across complex global supply chains. To address these challenges, we propose a smart audit system empowered by large language models (LLMs). Our approach introduces three innovations: a dynamic risk assessment model that streamlines audit procedures and optimizes resource allocation; a manufacturing compliance copilot that enhances data processing, retrieval, and evaluation for a self-evolving manufacturing knowledge base; and a Re-act framework commonality analysis agent that provides real-time, customized analysis to empower engineers with insights for supplier improvement. These enhancements elevate audit efficiency and effectiveness, with testing scenarios demonstrating an improvement of over 24%.
Unified Regularity Measures for Sample-wise Learning and Generalization
Aug 09, 2021
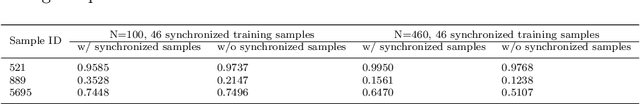
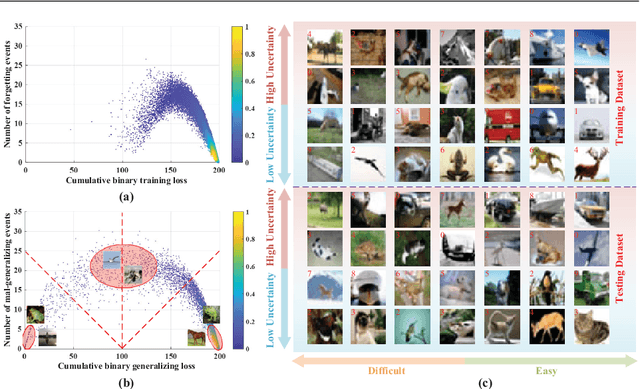
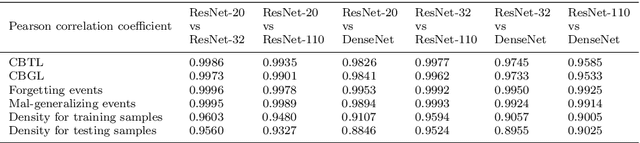
Abstract:Fundamental machine learning theory shows that different samples contribute unequally both in learning and testing processes. Contemporary studies on DNN imply that such sample di?erence is rooted on the distribution of intrinsic pattern information, namely sample regularity. Motivated by the recent discovery on network memorization and generalization, we proposed a pair of sample regularity measures for both processes with a formulation-consistent representation. Specifically, cumulative binary training/generalizing loss (CBTL/CBGL), the cumulative number of correct classi?cations of the training/testing sample within training stage, is proposed to quantize the stability in memorization-generalization process; while forgetting/mal-generalizing events, i.e., the mis-classification of previously learned or generalized sample, are utilized to represent the uncertainty of sample regularity with respect to optimization dynamics. Experiments validated the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed approaches for mini-batch SGD optimization. Further applications on training/testing sample selection show the proposed measures sharing the uni?ed computing procedure could benefit for both tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge