Donghai Zhang
NeRO: Neural Road Surface Reconstruction
May 17, 2024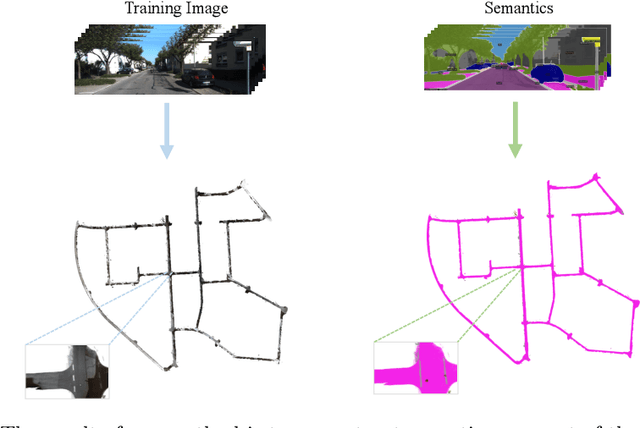
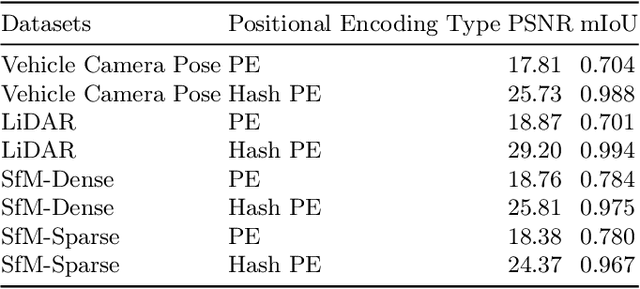
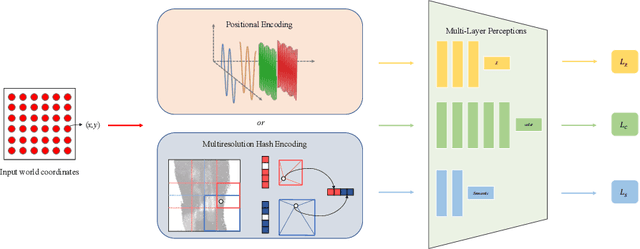

Abstract:In computer vision and graphics, the accurate reconstruction of road surfaces is pivotal for various applications, especially in autonomous driving. This paper introduces a novel method leveraging the Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) framework to reconstruct road surfaces in height, color, and semantic information by input world coordinates x and y. Our approach NeRO uses encoding techniques based on MLPs, significantly improving the performance of the complex details, speeding up the training speed, and reducing neural network size. The effectiveness of this method is demonstrated through its superior performance, which indicates a promising direction for rendering road surfaces with semantics applications, particularly in applications demanding visualization of road conditions, 4D labeling, and semantic groupings.
Semantic Is Enough: Only Semantic Information For NeRF Reconstruction
Mar 24, 2024



Abstract:Recent research that combines implicit 3D representation with semantic information, like Semantic-NeRF, has proven that NeRF model could perform excellently in rendering 3D structures with semantic labels. This research aims to extend the Semantic Neural Radiance Fields (Semantic-NeRF) model by focusing solely on semantic output and removing the RGB output component. We reformulate the model and its training procedure to leverage only the cross-entropy loss between the model semantic output and the ground truth semantic images, removing the colour data traditionally used in the original Semantic-NeRF approach. We then conduct a series of identical experiments using the original and the modified Semantic-NeRF model. Our primary objective is to obverse the impact of this modification on the model performance by Semantic-NeRF, focusing on tasks such as scene understanding, object detection, and segmentation. The results offer valuable insights into the new way of rendering the scenes and provide an avenue for further research and development in semantic-focused 3D scene understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge