Pengcheng Wang
Mean Flow Policy with Instantaneous Velocity Constraint for One-step Action Generation
Feb 14, 2026Abstract:Learning expressive and efficient policy functions is a promising direction in reinforcement learning (RL). While flow-based policies have recently proven effective in modeling complex action distributions with a fast deterministic sampling process, they still face a trade-off between expressiveness and computational burden, which is typically controlled by the number of flow steps. In this work, we propose mean velocity policy (MVP), a new generative policy function that models the mean velocity field to achieve the fastest one-step action generation. To ensure its high expressiveness, an instantaneous velocity constraint (IVC) is introduced on the mean velocity field during training. We theoretically prove that this design explicitly serves as a crucial boundary condition, thereby improving learning accuracy and enhancing policy expressiveness. Empirically, our MVP achieves state-of-the-art success rates across several challenging robotic manipulation tasks from Robomimic and OGBench. It also delivers substantial improvements in training and inference speed over existing flow-based policy baselines.
DADP: Domain Adaptive Diffusion Policy
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Learning domain adaptive policies that can generalize to unseen transition dynamics, remains a fundamental challenge in learning-based control. Substantial progress has been made through domain representation learning to capture domain-specific information, thus enabling domain-aware decision making. We analyze the process of learning domain representations through dynamical prediction and find that selecting contexts adjacent to the current step causes the learned representations to entangle static domain information with varying dynamical properties. Such mixture can confuse the conditioned policy, thereby constraining zero-shot adaptation. To tackle the challenge, we propose DADP (Domain Adaptive Diffusion Policy), which achieves robust adaptation through unsupervised disentanglement and domain-aware diffusion injection. First, we introduce Lagged Context Dynamical Prediction, a strategy that conditions future state estimation on a historical offset context; by increasing this temporal gap, we unsupervisedly disentangle static domain representations by filtering out transient properties. Second, we integrate the learned domain representations directly into the generative process by biasing the prior distribution and reformulating the diffusion target. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks across locomotion and manipulation demonstrate the superior performance, and the generalizability of DADP over prior methods. More visualization results are available on the https://outsider86.github.io/DomainAdaptiveDiffusionPolicy/.
WarmServe: Enabling One-for-Many GPU Prewarming for Multi-LLM Serving
Dec 10, 2025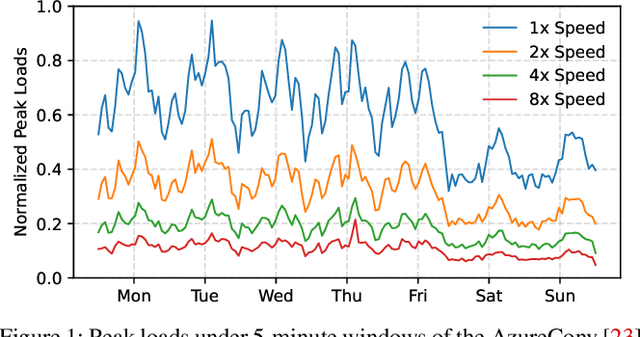
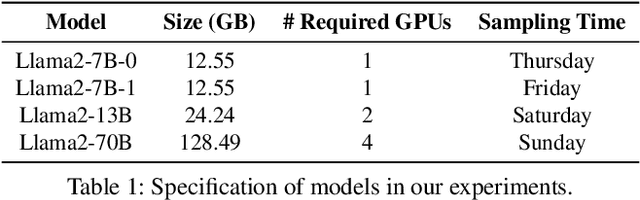
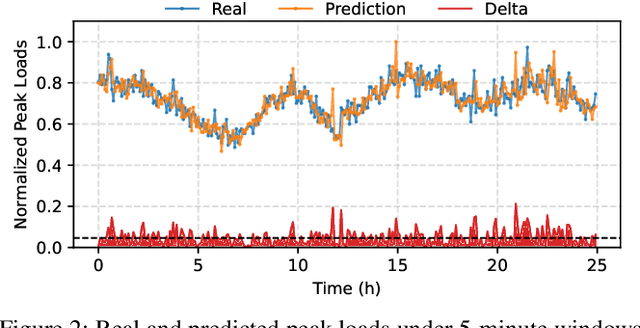
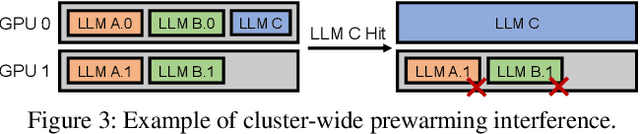
Abstract:Deploying multiple models within shared GPU clusters is promising for improving resource efficiency in large language model (LLM) serving. Existing multi-LLM serving systems optimize GPU utilization at the cost of worse inference performance, especially time-to-first-token (TTFT). We identify the root cause of such compromise as their unawareness of future workload characteristics. In contrast, recent analysis on real-world traces has shown the high periodicity and long-term predictability of LLM serving workloads. We propose universal GPU workers to enable one-for-many GPU prewarming that loads models with knowledge of future workloads. Based on universal GPU workers, we design and build WarmServe, a multi-LLM serving system that (1) mitigates cluster-wide prewarming interference by adopting an evict-aware model placement strategy, (2) prepares universal GPU workers in advance by proactive prewarming, and (3) manages GPU memory with a zero-overhead memory switching mechanism. Evaluation under real-world datasets shows that WarmServe improves TTFT by up to 50.8$\times$ compared to the state-of-the-art autoscaling-based system, while being capable of serving up to 2.5$\times$ more requests compared to the GPU-sharing system.
CLO: Efficient LLM Inference System with CPU-Light KVCache Offloading via Algorithm-System Co-Design
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:The growth of million-token LLMs exposes the scalability limits of inference systems, where the KVCache dominates memory usage and data transfer overhead. Recent offloading systems migrate the KVCache to CPU memory and incorporate top-k attention to reduce the volume of data transferred from the CPU, while further applying system-level optimizations such as on-GPU caching and prefetching to lower transfer overhead. However, they overlook the CPU bottleneck in three aspects: (1) substantial overhead of fine-grained dynamic cache management performed on the CPU side, (2) significant transfer overhead from poor PCIe bandwidth utilization caused by heavy gathering operations at the CPU side, and (3) GPU runtime bubbles introduced by coarse-grained CPU-centric synchronization. To address these challenges, we propose CLO, a CPU-light KVCache offloading system via algorithm-system co-design. CLO features: (1) a coarse-grained head-wise approximate on-GPU caching strategy with negligible cache management cost, (2) seamless combination of data prefetching and on-GPU persistent caching for lower transfer overhead, (3) a zero-copy transfer engine to fully exploit PCIe bandwidth, and a GPU-centric synchronization method to eliminate GPU stalls. Evaluation on two widely-used LLMs demonstrates that CLO achieves comparable accuracy to state-of-the-art systems, while substantially minimizing CPU overhead, fully utilizing PCIe bandwidth, thus improving decoding throughput by 9.3%-66.6%. Our results highlight that algorithm-system co-design is essential for memory-constrained LLM inference on modern GPU platforms. We open source CLO at https://github.com/CommediaJW/CLO.
ReCast: Reliability-aware Codebook Assisted Lightweight Time Series Forecasting
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Time series forecasting is crucial for applications in various domains. Conventional methods often rely on global decomposition into trend, seasonal, and residual components, which become ineffective for real-world series dominated by local, complex, and highly dynamic patterns. Moreover, the high model complexity of such approaches limits their applicability in real-time or resource-constrained environments. In this work, we propose a novel \textbf{RE}liability-aware \textbf{C}odebook-\textbf{AS}sisted \textbf{T}ime series forecasting framework (\textbf{ReCast}) that enables lightweight and robust prediction by exploiting recurring local shapes. ReCast encodes local patterns into discrete embeddings through patch-wise quantization using a learnable codebook, thereby compactly capturing stable regular structures. To compensate for residual variations not preserved by quantization, ReCast employs a dual-path architecture comprising a quantization path for efficient modeling of regular structures and a residual path for reconstructing irregular fluctuations. A central contribution of ReCast is a reliability-aware codebook update strategy, which incrementally refines the codebook via weighted corrections. These correction weights are derived by fusing multiple reliability factors from complementary perspectives by a distributionally robust optimization (DRO) scheme, ensuring adaptability to non-stationarity and robustness to distribution shifts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ReCast outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) models in accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability to distribution shifts.
What's on Your Plate? Inferring Chinese Cuisine Intake from Wearable IMUs
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Accurate food intake detection is vital for dietary monitoring and chronic disease prevention. Traditional self-report methods are prone to recall bias, while camera-based approaches raise concerns about privacy. Furthermore, existing wearable-based methods primarily focus on a limited number of food types, such as hamburgers and pizza, failing to address the vast diversity of Chinese cuisine. To bridge this gap, we propose CuisineSense, a system that classifies Chinese food types by integrating hand motion cues from a smartwatch with head dynamics from smart glasses. To filter out irrelevant daily activities, we design a two-stage detection pipeline. The first stage identifies eating states by distinguishing characteristic temporal patterns from non-eating behaviors. The second stage then conducts fine-grained food type recognition based on the motions captured during food intake. To evaluate CuisineSense, we construct a dataset comprising 27.5 hours of IMU recordings across 11 food categories and 10 participants. Experiments demonstrate that CuisineSense achieves high accuracy in both eating state detection and food classification, offering a practical solution for unobtrusive, wearable-based dietary monitoring.The system code is publicly available at https://github.com/joeeeeyin/CuisineSense.git.
HD3C: Efficient Medical Data Classification for Embedded Devices
Sep 18, 2025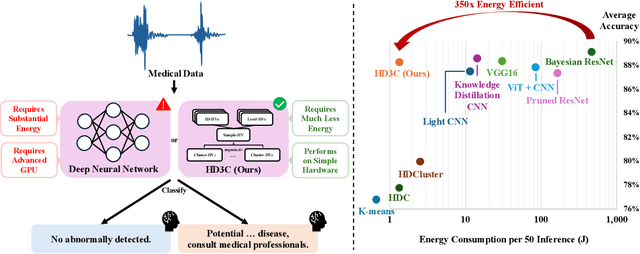
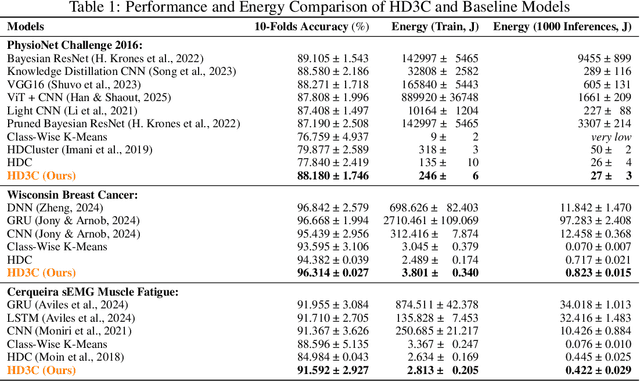
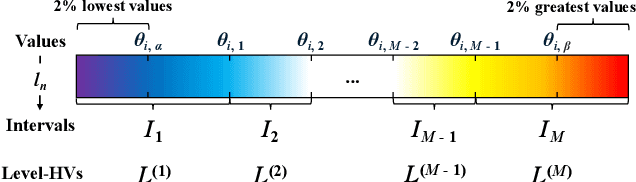
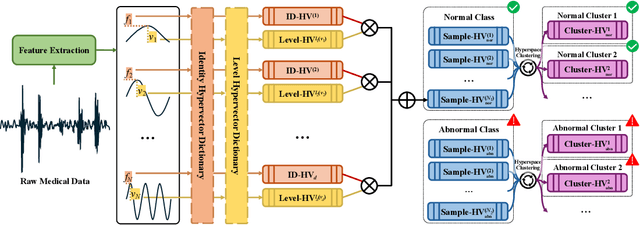
Abstract:Energy-efficient medical data classification is essential for modern disease screening, particularly in home and field healthcare where embedded devices are prevalent. While deep learning models achieve state-of-the-art accuracy, their substantial energy consumption and reliance on GPUs limit deployment on such platforms. We present Hyperdimensional Computing with Class-Wise Clustering (HD3C), a lightweight classification framework designed for low-power environments. HD3C encodes data into high-dimensional hypervectors, aggregates them into multiple cluster-specific prototypes, and performs classification through similarity search in hyperspace. We evaluate HD3C across three medical classification tasks; on heart sound classification, HD3C is $350\times$ more energy-efficient than Bayesian ResNet with less than 1% accuracy difference. Moreover, HD3C demonstrates exceptional robustness to noise, limited training data, and hardware error, supported by both theoretical analysis and empirical results, highlighting its potential for reliable deployment in real-world settings. Code is available at https://github.com/jianglanwei/HD3C.
Interactive Hybrid Rice Breeding with Parametric Dual Projection
Jul 16, 2025



Abstract:Hybrid rice breeding crossbreeds different rice lines and cultivates the resulting hybrids in fields to select those with desirable agronomic traits, such as higher yields. Recently, genomic selection has emerged as an efficient way for hybrid rice breeding. It predicts the traits of hybrids based on their genes, which helps exclude many undesired hybrids, largely reducing the workload of field cultivation. However, due to the limited accuracy of genomic prediction models, breeders still need to combine their experience with the models to identify regulatory genes that control traits and select hybrids, which remains a time-consuming process. To ease this process, in this paper, we proposed a visual analysis method to facilitate interactive hybrid rice breeding. Regulatory gene identification and hybrid selection naturally ensemble a dual-analysis task. Therefore, we developed a parametric dual projection method with theoretical guarantees to facilitate interactive dual analysis. Based on this dual projection method, we further developed a gene visualization and a hybrid visualization to verify the identified regulatory genes and hybrids. The effectiveness of our method is demonstrated through the quantitative evaluation of the parametric dual projection method, identified regulatory genes and desired hybrids in the case study, and positive feedback from breeders.
Residual Policy Gradient: A Reward View of KL-regularized Objective
Mar 14, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement Learning and Imitation Learning have achieved widespread success in many domains but remain constrained during real-world deployment. One of the main issues is the additional requirements that were not considered during training. To address this challenge, policy customization has been introduced, aiming to adapt a prior policy while preserving its inherent properties and meeting new task-specific requirements. A principled approach to policy customization is Residual Q-Learning (RQL), which formulates the problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) and derives a family of value-based learning algorithms. However, RQL has not yet been applied to policy gradient methods, which restricts its applicability, especially in tasks where policy gradient has already proven more effective. In this work, we first derive a concise form of Soft Policy Gradient as a preliminary. Building on this, we introduce Residual Policy Gradient (RPG), which extends RQL to policy gradient methods, allowing policy customization in gradient-based RL settings. With the view of RPG, we rethink the KL-regularized objective widely used in RL fine-tuning. We show that under certain assumptions, KL-regularized objective leads to a maximum-entropy policy that balances the inherent properties and task-specific requirements on a reward-level. Our experiments in MuJoCo demonstrate the effectiveness of Soft Policy Gradient and Residual Policy Gradient.
TD-M(PC)$^2$: Improving Temporal Difference MPC Through Policy Constraint
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Model-based reinforcement learning algorithms that combine model-based planning and learned value/policy prior have gained significant recognition for their high data efficiency and superior performance in continuous control. However, we discover that existing methods that rely on standard SAC-style policy iteration for value learning, directly using data generated by the planner, often result in \emph{persistent value overestimation}. Through theoretical analysis and experiments, we argue that this issue is deeply rooted in the structural policy mismatch between the data generation policy that is always bootstrapped by the planner and the learned policy prior. To mitigate such a mismatch in a minimalist way, we propose a policy regularization term reducing out-of-distribution (OOD) queries, thereby improving value learning. Our method involves minimum changes on top of existing frameworks and requires no additional computation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach improves performance over baselines such as TD-MPC2 by large margins, particularly in 61-DoF humanoid tasks. View qualitative results at https://darthutopian.github.io/tdmpc_square/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge