Jeff Schneider
Carnegie Mellon University
Maximum Likelihood Reinforcement Learning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning is the method of choice to train models in sampling-based setups with binary outcome feedback, such as navigation, code generation, and mathematical problem solving. In such settings, models implicitly induce a likelihood over correct rollouts. However, we observe that reinforcement learning does not maximize this likelihood, and instead optimizes only a lower-order approximation. Inspired by this observation, we introduce Maximum Likelihood Reinforcement Learning (MaxRL), a sampling-based framework to approximate maximum likelihood using reinforcement learning techniques. MaxRL addresses the challenges of non-differentiable sampling by defining a compute-indexed family of sample-based objectives that interpolate between standard reinforcement learning and exact maximum likelihood as additional sampling compute is allocated. The resulting objectives admit a simple, unbiased policy-gradient estimator and converge to maximum likelihood optimization in the infinite-compute limit. Empirically, we show that MaxRL Pareto-dominates existing methods in all models and tasks we tested, achieving up to 20x test-time scaling efficiency gains compared to its GRPO-trained counterpart. We also observe MaxRL to scale better with additional data and compute. Our results suggest MaxRL is a promising framework for scaling RL training in correctness based settings.
Continual Policy Distillation from Distributed Reinforcement Learning Teachers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Continual Reinforcement Learning (CRL) aims to develop lifelong learning agents to continuously acquire knowledge across diverse tasks while mitigating catastrophic forgetting. This requires efficiently managing the stability-plasticity dilemma and leveraging prior experience to rapidly generalize to novel tasks. While various enhancement strategies for both aspects have been proposed, achieving scalable performance by directly applying RL to sequential task streams remains challenging. In this paper, we propose a novel teacher-student framework that decouples CRL into two independent processes: training single-task teacher models through distributed RL and continually distilling them into a central generalist model. This design is motivated by the observation that RL excels at solving single tasks, while policy distillation -- a relatively stable supervised learning process -- is well aligned with large foundation models and multi-task learning. Moreover, a mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture and a replay-based approach are employed to enhance the plasticity and stability of the continual policy distillation process. Extensive experiments on the Meta-World benchmark demonstrate that our framework enables efficient continual RL, recovering over 85% of teacher performance while constraining task-wise forgetting to within 10%.
Latent Policy Steering with Embodiment-Agnostic Pretrained World Models
Jul 17, 2025



Abstract:Learning visuomotor policies via imitation has proven effective across a wide range of robotic domains. However, the performance of these policies is heavily dependent on the number of training demonstrations, which requires expensive data collection in the real world. In this work, we aim to reduce data collection efforts when learning visuomotor robot policies by leveraging existing or cost-effective data from a wide range of embodiments, such as public robot datasets and the datasets of humans playing with objects (human data from play). Our approach leverages two key insights. First, we use optic flow as an embodiment-agnostic action representation to train a World Model (WM) across multi-embodiment datasets, and finetune it on a small amount of robot data from the target embodiment. Second, we develop a method, Latent Policy Steering (LPS), to improve the output of a behavior-cloned policy by searching in the latent space of the WM for better action sequences. In real world experiments, we observe significant improvements in the performance of policies trained with a small amount of data (over 50% relative improvement with 30 demonstrations and over 20% relative improvement with 50 demonstrations) by combining the policy with a WM pretrained on two thousand episodes sampled from the existing Open X-embodiment dataset across different robots or a cost-effective human dataset from play.
Multi-Timescale Dynamics Model Bayesian Optimization for Plasma Stabilization in Tokamaks
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Machine learning algorithms often struggle to control complex real-world systems. In the case of nuclear fusion, these challenges are exacerbated, as the dynamics are notoriously complex, data is poor, hardware is subject to failures, and experiments often affect dynamics beyond the experiment's duration. Existing tools like reinforcement learning, supervised learning, and Bayesian optimization address some of these challenges but fail to provide a comprehensive solution. To overcome these limitations, we present a multi-scale Bayesian optimization approach that integrates a high-frequency data-driven dynamics model with a low-frequency Gaussian process. By updating the Gaussian process between experiments, the method rapidly adapts to new data, refining the predictions of the less reliable dynamical model. We validate our approach by controlling tearing instabilities in the DIII-D nuclear fusion plant. Offline testing on historical data shows that our method significantly outperforms several baselines. Results on live experiments on the DIII-D tokamak, conducted under high-performance plasma scenarios prone to instabilities, shows a 50% success rate, marking a 117% improvement over historical outcomes.
Accelerating Diffusion Models in Offline RL via Reward-Aware Consistency Trajectory Distillation
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Although diffusion models have achieved strong results in decision-making tasks, their slow inference speed remains a key limitation. While the consistency model offers a potential solution, its applications to decision-making often struggle with suboptimal demonstrations or rely on complex concurrent training of multiple networks. In this work, we propose a novel approach to consistency distillation for offline reinforcement learning that directly incorporates reward optimization into the distillation process. Our method enables single-step generation while maintaining higher performance and simpler training. Empirical evaluations on the Gym MuJoCo benchmarks and long horizon planning demonstrate that our approach can achieve an 8.7% improvement over previous state-of-the-art while offering up to 142x speedup over diffusion counterparts in inference time.
Can Large Reasoning Models Self-Train?
May 27, 2025



Abstract:Scaling the performance of large language models (LLMs) increasingly depends on methods that reduce reliance on human supervision. Reinforcement learning from automated verification offers an alternative, but it incurs scalability limitations due to dependency upon human-designed verifiers. Self-training, where the model's own judgment provides the supervisory signal, presents a compelling direction. We propose an online self-training reinforcement learning algorithm that leverages the model's self-consistency to infer correctness signals and train without any ground-truth supervision. We apply the algorithm to challenging mathematical reasoning tasks and show that it quickly reaches performance levels rivaling reinforcement-learning methods trained explicitly on gold-standard answers. Additionally, we analyze inherent limitations of the algorithm, highlighting how the self-generated proxy reward initially correlated with correctness can incentivize reward hacking, where confidently incorrect outputs are favored. Our results illustrate how self-supervised improvement can achieve significant performance gains without external labels, while also revealing its fundamental challenges.
Policy-Driven World Model Adaptation for Robust Offline Model-based Reinforcement Learning
May 19, 2025Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) offers a powerful paradigm for data-driven control. Compared to model-free approaches, offline model-based RL (MBRL) explicitly learns a world model from a static dataset and uses it as a surrogate simulator, improving data efficiency and enabling potential generalization beyond the dataset support. However, most existing offline MBRL methods follow a two-stage training procedure: first learning a world model by maximizing the likelihood of the observed transitions, then optimizing a policy to maximize its expected return under the learned model. This objective mismatch results in a world model that is not necessarily optimized for effective policy learning. Moreover, we observe that policies learned via offline MBRL often lack robustness during deployment, and small adversarial noise in the environment can lead to significant performance degradation. To address these, we propose a framework that dynamically adapts the world model alongside the policy under a unified learning objective aimed at improving robustness. At the core of our method is a maximin optimization problem, which we solve by innovatively utilizing Stackelberg learning dynamics. We provide theoretical analysis to support our design and introduce computationally efficient implementations. We benchmark our algorithm on twelve noisy D4RL MuJoCo tasks and three stochastic Tokamak Control tasks, demonstrating its state-of-the-art performance.
Training a Generally Curious Agent
Feb 24, 2025



Abstract:Efficient exploration is essential for intelligent systems interacting with their environment, but existing language models often fall short in scenarios that require strategic information gathering. In this paper, we present PAPRIKA, a fine-tuning approach that enables language models to develop general decision-making capabilities that are not confined to particular environments. By training on synthetic interaction data from different tasks that require diverse strategies, PAPRIKA teaches models to explore and adapt their behavior on a new task based on environment feedback in-context without more gradient updates. Experimental results show that models fine-tuned with PAPRIKA can effectively transfer their learned decision-making capabilities to entirely unseen tasks without additional training. Unlike traditional training, our approach's primary bottleneck lies in sampling useful interaction data instead of model updates. To improve sample efficiency, we propose a curriculum learning strategy that prioritizes sampling trajectories from tasks with high learning potential. These results suggest a promising path towards AI systems that can autonomously solve novel sequential decision-making problems that require interactions with the external world.
TD-M(PC)$^2$: Improving Temporal Difference MPC Through Policy Constraint
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Model-based reinforcement learning algorithms that combine model-based planning and learned value/policy prior have gained significant recognition for their high data efficiency and superior performance in continuous control. However, we discover that existing methods that rely on standard SAC-style policy iteration for value learning, directly using data generated by the planner, often result in \emph{persistent value overestimation}. Through theoretical analysis and experiments, we argue that this issue is deeply rooted in the structural policy mismatch between the data generation policy that is always bootstrapped by the planner and the learned policy prior. To mitigate such a mismatch in a minimalist way, we propose a policy regularization term reducing out-of-distribution (OOD) queries, thereby improving value learning. Our method involves minimum changes on top of existing frameworks and requires no additional computation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach improves performance over baselines such as TD-MPC2 by large margins, particularly in 61-DoF humanoid tasks. View qualitative results at https://darthutopian.github.io/tdmpc_square/.
Bayes Adaptive Monte Carlo Tree Search for Offline Model-based Reinforcement Learning
Oct 15, 2024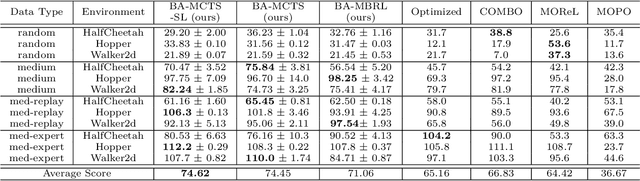
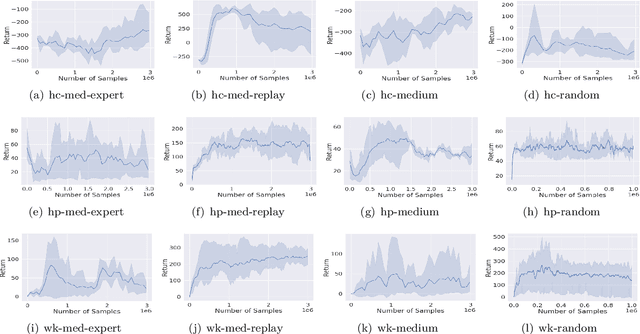
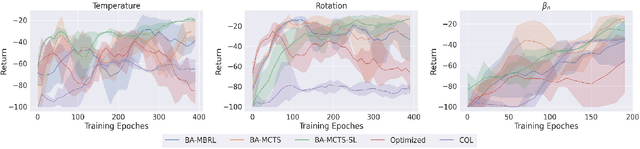
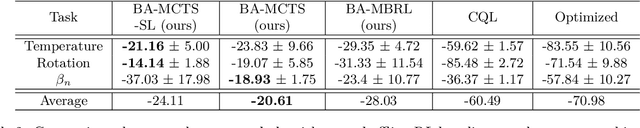
Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) is a powerful approach for data-driven decision-making and control. Compared to model-free methods, offline model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) explicitly learns world models from a static dataset and uses them as surrogate simulators, improving the data efficiency and enabling the learned policy to potentially generalize beyond the dataset support. However, there could be various MDPs that behave identically on the offline dataset and so dealing with the uncertainty about the true MDP can be challenging. In this paper, we propose modeling offline MBRL as a Bayes Adaptive Markov Decision Process (BAMDP), which is a principled framework for addressing model uncertainty. We further introduce a novel Bayes Adaptive Monte-Carlo planning algorithm capable of solving BAMDPs in continuous state and action spaces with stochastic transitions. This planning process is based on Monte Carlo Tree Search and can be integrated into offline MBRL as a policy improvement operator in policy iteration. Our ``RL + Search" framework follows in the footsteps of superhuman AIs like AlphaZero, improving on current offline MBRL methods by incorporating more computation input. The proposed algorithm significantly outperforms state-of-the-art model-based and model-free offline RL methods on twelve D4RL MuJoCo benchmark tasks and three target tracking tasks in a challenging, stochastic tokamak control simulator.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge