Nathan Kallus
GAAVI: Global Asymptotic Anytime Valid Inference for the Conditional Mean Function
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Inference on the conditional mean function (CMF) is central to tasks from adaptive experimentation to optimal treatment assignment and algorithmic fairness auditing. In this work, we provide a novel asymptotic anytime-valid test for a CMF global null (e.g., that all conditional means are zero) and contrasts between CMFs, enabling experimenters to make high confidence decisions at any time during the experiment beyond a minimum sample size. We provide mild conditions under which our tests achieve (i) asymptotic type-I error guarantees, (i) power one, and, unlike past tests, (iii) optimal sample complexity relative to a Gaussian location testing. By inverting our tests, we show how to construct function-valued asymptotic confidence sequences for the CMF and contrasts thereof. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world data show our method is well-powered across various distributions while preserving the nominal error rate under continuous monitoring.
Causal Inference on Networks under Misspecified Exposure Mappings: A Partial Identification Framework
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Estimating treatment effects in networks is challenging, as each potential outcome depends on the treatments of all other nodes in the network. To overcome this difficulty, existing methods typically impose an exposure mapping that compresses the treatment assignments in the network into a low-dimensional summary. However, if this mapping is misspecified, standard estimators for direct and spillover effects can be severely biased. We propose a novel partial identification framework for causal inference on networks to assess the robustness of treatment effects under misspecifications of the exposure mapping. Specifically, we derive sharp upper and lower bounds on direct and spillover effects under such misspecifications. As such, our framework presents a novel application of causal sensitivity analysis to exposure mappings. We instantiate our framework for three canonical exposure settings widely used in practice: (i) weighted means of the neighborhood treatments, (ii) threshold-based exposure mappings, and (iii) truncated neighborhood interference in the presence of higher-order spillovers. Furthermore, we develop orthogonal estimators for these bounds and prove that the resulting bound estimates are valid, sharp, and efficient. Our experiments show the bounds remain informative and provide reliable conclusions under misspecification of exposure mappings.
Exploration in the Limit
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:In fixed-confidence best arm identification (BAI), the objective is to quickly identify the optimal option while controlling the probability of error below a desired threshold. Despite the plethora of BAI algorithms, existing methods typically fall short in practical settings, as stringent exact error control requires using loose tail inequalities and/or parametric restrictions. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a relaxed formulation that requires valid error control asymptotically with respect to a minimum sample size. This aligns with many real-world settings that often involve weak signals, high desired significance, and post-experiment inference requirements, all of which necessitate long horizons. This allows us to achieve tighter optimality, while better handling flexible nonparametric outcome distributions and fully leveraging individual-level contexts. We develop a novel asymptotic anytime-valid confidence sequences over arm indices, and we use it to design a new BAI algorithm for our asymptotic framework. Our method flexibly incorporates covariates for variance reduction and ensures approximate error control in fully nonparametric settings. Under mild convergence assumptions, we provide asymptotic bounds on the sample complexity and show the worst-case sample complexity of our approach matches the best-case sample complexity of Gaussian BAI under exact error guarantees and known variances. Experiments suggest our approach reduces average sample complexities while maintaining error control.
Efficient Inference for Inverse Reinforcement Learning and Dynamic Discrete Choice Models
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) and dynamic discrete choice (DDC) models explain sequential decision-making by recovering reward functions that rationalize observed behavior. Flexible IRL methods typically rely on machine learning but provide no guarantees for valid inference, while classical DDC approaches impose restrictive parametric specifications and often require repeated dynamic programming. We develop a semiparametric framework for debiased inverse reinforcement learning that yields statistically efficient inference for a broad class of reward-dependent functionals in maximum entropy IRL and Gumbel-shock DDC models. We show that the log-behavior policy acts as a pseudo-reward that point-identifies policy value differences and, under a simple normalization, the reward itself. We then formalize these targets, including policy values under known and counterfactual softmax policies and functionals of the normalized reward, as smooth functionals of the behavior policy and transition kernel, establish pathwise differentiability, and derive their efficient influence functions. Building on this characterization, we construct automatic debiased machine-learning estimators that allow flexible nonparametric estimation of nuisance components while achieving $\sqrt{n}$-consistency, asymptotic normality, and semiparametric efficiency. Our framework extends classical inference for DDC models to nonparametric rewards and modern machine-learning tools, providing a unified and computationally tractable approach to statistical inference in IRL.
Stationary Reweighting Yields Local Convergence of Soft Fitted Q-Iteration
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Fitted Q-iteration (FQI) and its entropy-regularized variant, soft FQI, are central tools for value-based model-free offline reinforcement learning, but can behave poorly under function approximation and distribution shift. In the entropy-regularized setting, we show that the soft Bellman operator is locally contractive in the stationary norm of the soft-optimal policy, rather than in the behavior norm used by standard FQI. This geometric mismatch explains the instability of soft Q-iteration with function approximation in the absence of Bellman completeness. To restore contraction, we introduce stationary-reweighted soft FQI, which reweights each regression update using the stationary distribution of the current policy. We prove local linear convergence under function approximation with geometrically damped weight-estimation errors, assuming approximate realizability. Our analysis further suggests that global convergence may be recovered by gradually reducing the softmax temperature, and that this continuation approach can extend to the hardmax limit under a mild margin condition.
Bellman Calibration for V-Learning in Offline Reinforcement Learning
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We introduce Iterated Bellman Calibration, a simple, model-agnostic, post-hoc procedure for calibrating off-policy value predictions in infinite-horizon Markov decision processes. Bellman calibration requires that states with similar predicted long-term returns exhibit one-step returns consistent with the Bellman equation under the target policy. We adapt classical histogram and isotonic calibration to the dynamic, counterfactual setting by repeatedly regressing fitted Bellman targets onto a model's predictions, using a doubly robust pseudo-outcome to handle off-policy data. This yields a one-dimensional fitted value iteration scheme that can be applied to any value estimator. Our analysis provides finite-sample guarantees for both calibration and prediction under weak assumptions, and critically, without requiring Bellman completeness or realizability.
Fitted Q Evaluation Without Bellman Completeness via Stationary Weighting
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Fitted Q-evaluation (FQE) is a central method for off-policy evaluation in reinforcement learning, but it generally requires Bellman completeness: that the hypothesis class is closed under the evaluation Bellman operator. This requirement is challenging because enlarging the hypothesis class can worsen completeness. We show that the need for this assumption stems from a fundamental norm mismatch: the Bellman operator is gamma-contractive under the stationary distribution of the target policy, whereas FQE minimizes Bellman error under the behavior distribution. We propose a simple fix: reweight each regression step using an estimate of the stationary density ratio, thereby aligning FQE with the norm in which the Bellman operator contracts. This enables strong evaluation guarantees in the absence of realizability or Bellman completeness, avoiding the geometric error blow-up of standard FQE in this setting while maintaining the practicality of regression-based evaluation.
Semiparametric Preference Optimization: Your Language Model is Secretly a Single-Index Model
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Aligning large language models to preference data is commonly implemented by assuming a known link function between the distribution of observed preferences and the unobserved rewards (e.g., a logistic link as in Bradley-Terry). If the link is wrong, however, inferred rewards can be biased and policies be misaligned. We study policy alignment to preferences under an unknown and unrestricted link. We consider an $f$-divergence-constrained reward maximization problem and show that realizability of the solution in a policy class implies a semiparametric single-index binary choice model, where a scalar-valued index determined by a policy captures the dependence on demonstrations and the rest of the preference distribution is an unrestricted function thereof. Rather than focus on estimation of identifiable finite-dimensional structural parameters in the index as in econometrics, we focus on policy learning, focusing on error to the optimal policy and allowing unidentifiable and nonparametric indices. We develop a variety of policy learners based on profiling the link function, orthogonalizing the link function, and using link-agnostic bipartite ranking objectives. We analyze these and provide finite-sample policy error bounds that depend on generic functional complexity measures of the index class. We further consider practical implementations using first-order optimization suited to neural networks and batched data. The resulting methods are robust to unknown preference noise distribution and scale, while preserving the direct optimization of policies without explicitly fitting rewards.
The Value of Personalized Recommendations: Evidence from Netflix
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Personalized recommendation systems shape much of user choice online, yet their targeted nature makes separating out the value of recommendation and the underlying goods challenging. We build a discrete choice model that embeds recommendation-induced utility, low-rank heterogeneity, and flexible state dependence and apply the model to viewership data at Netflix. We exploit idiosyncratic variation introduced by the recommendation algorithm to identify and separately value these components as well as to recover model-free diversion ratios that we can use to validate our structural model. We use the model to evaluate counterfactuals that quantify the incremental engagement generated by personalized recommendations. First, we show that replacing the current recommender system with a matrix factorization or popularity-based algorithm would lead to 4% and 12% reduction in engagement, respectively, and decreased consumption diversity. Second, most of the consumption increase from recommendations comes from effective targeting, not mechanical exposure, with the largest gains for mid-popularity goods (as opposed to broadly appealing or very niche goods).
DiFFPO: Training Diffusion LLMs to Reason Fast and Furious via Reinforcement Learning
Oct 02, 2025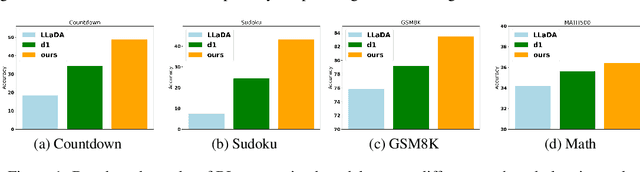
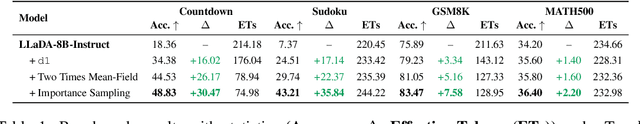
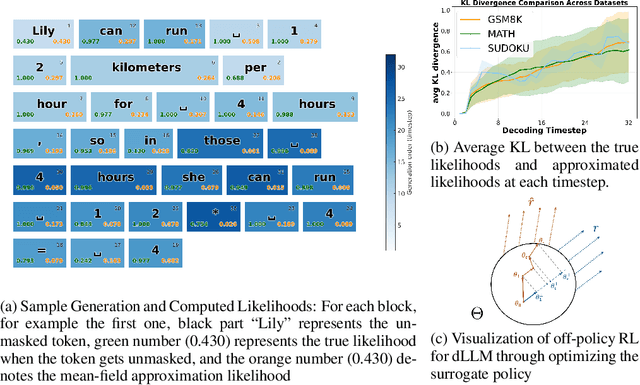
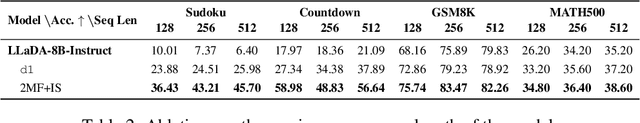
Abstract:We propose DiFFPO, Diffusion Fast and Furious Policy Optimization, a unified framework for training masked diffusion large language models (dLLMs) to reason not only better (furious), but also faster via reinforcement learning (RL). We first unify the existing baseline approach such as d1 by proposing to train surrogate policies via off-policy RL, whose likelihood is much more tractable as an approximation to the true dLLM policy. This naturally motivates a more accurate and informative two-stage likelihood approximation combined with importance sampling correction, which leads to generalized RL algorithms with better sample efficiency and superior task performance. Second, we propose a new direction of joint training efficient samplers/controllers of dLLMs policy. Via RL, we incentivize dLLMs' natural multi-token prediction capabilities by letting the model learn to adaptively allocate an inference threshold for each prompt. By jointly training the sampler, we yield better accuracies with lower number of function evaluations (NFEs) compared to training the model only, obtaining the best performance in improving the Pareto frontier of the inference-time compute of dLLMs. We showcase the effectiveness of our pipeline by training open source large diffusion language models over benchmark math and planning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge