Brian Cho
SNPL: Simultaneous Policy Learning and Evaluation for Safe Multi-Objective Policy Improvement
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:To design effective digital interventions, experimenters face the challenge of learning decision policies that balance multiple objectives using offline data. Often, they aim to develop policies that maximize goal outcomes, while ensuring there are no undesirable changes in guardrail outcomes. To provide credible recommendations, experimenters must not only identify policies that satisfy the desired changes in goal and guardrail outcomes, but also offer probabilistic guarantees about the changes these policies induce. In practice, however, policy classes are often large, and digital experiments tend to produce datasets with small effect sizes relative to noise. In this setting, standard approaches such as data splitting or multiple testing often result in unstable policy selection and/or insufficient statistical power. In this paper, we provide safe noisy policy learning (SNPL), a novel approach that leverages the concept of algorithmic stability to address these challenges. Our method enables policy learning while simultaneously providing high-confidence guarantees using the entire dataset, avoiding the need for data-splitting. We present finite-sample and asymptotic versions of our algorithm that ensure the recommended policy satisfies high-probability guarantees for avoiding guardrail regressions and/or achieving goal outcome improvements. We test both variants of our approach approach empirically on a real-world application of personalizing SMS delivery. Our results on real-world data suggest that our approach offers dramatic improvements in settings with large policy classes and low signal-to-noise across both finite-sample and asymptotic safety guarantees, offering up to 300\% improvements in detection rates and 150\% improvements in policy gains at significantly smaller sample sizes.
Reward Maximization for Pure Exploration: Minimax Optimal Good Arm Identification for Nonparametric Multi-Armed Bandits
Oct 21, 2024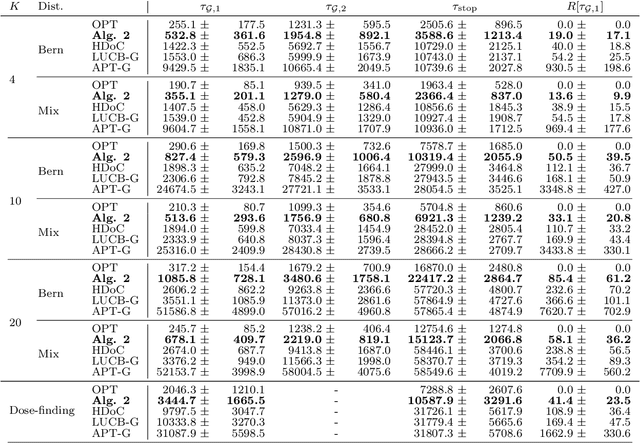
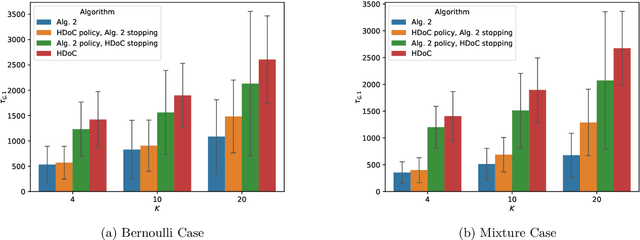
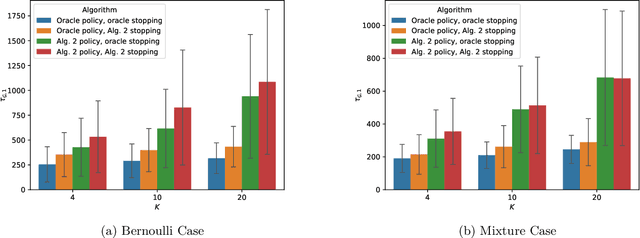

Abstract:In multi-armed bandits, the tasks of reward maximization and pure exploration are often at odds with each other. The former focuses on exploiting arms with the highest means, while the latter may require constant exploration across all arms. In this work, we focus on good arm identification (GAI), a practical bandit inference objective that aims to label arms with means above a threshold as quickly as possible. We show that GAI can be efficiently solved by combining a reward-maximizing sampling algorithm with a novel nonparametric anytime-valid sequential test for labeling arm means. We first establish that our sequential test maintains error control under highly nonparametric assumptions and asymptotically achieves the minimax optimal e-power, a notion of power for anytime-valid tests. Next, by pairing regret-minimizing sampling schemes with our sequential test, we provide an approach that achieves minimax optimal stopping times for labeling arms with means above a threshold, under an error probability constraint. Our empirical results validate our approach beyond the minimax setting, reducing the expected number of samples for all stopping times by at least 50% across both synthetic and real-world settings.
Peeking with PEAK: Sequential, Nonparametric Composite Hypothesis Tests for Means of Multiple Data Streams
Feb 16, 2024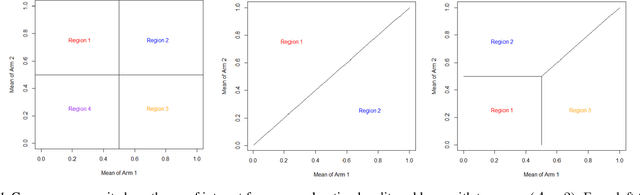
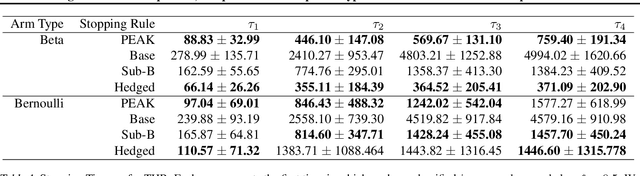
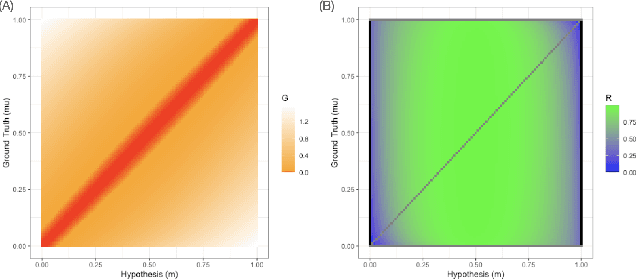
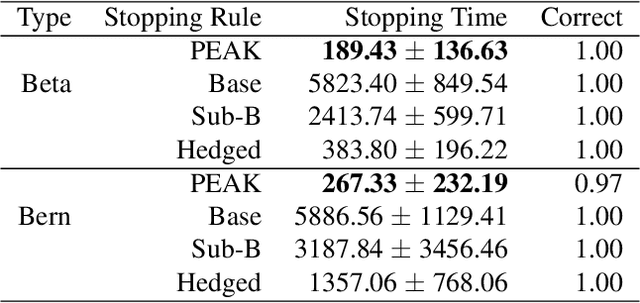
Abstract:We propose a novel nonparametric sequential test for composite hypotheses for means of multiple data streams. Our proposed method, \emph{peeking with expectation-based averaged capital} (PEAK), builds upon the testing-as-betting framework and provides a non-asymptotic $\alpha$-level test across any stopping time. PEAK is computationally tractable and efficiently rejects hypotheses that are incorrect across all potential distributions that satisfy our nonparametric assumption, enabling joint composite hypothesis testing on multiple streams of data. We numerically validate our theoretical findings under the best arm identification and threshold identification in the bandit setting, illustrating both the competitive performance and the computational efficiency of our method against state-of-the-art testing methods.
Rubric-Specific Approach to Automated Essay Scoring with Augmentation Training
Sep 06, 2023Abstract:Neural based approaches to automatic evaluation of subjective responses have shown superior performance and efficiency compared to traditional rule-based and feature engineering oriented solutions. However, it remains unclear whether the suggested neural solutions are sufficient replacements of human raters as we find recent works do not properly account for rubric items that are essential for automated essay scoring during model training and validation. In this paper, we propose a series of data augmentation operations that train and test an automated scoring model to learn features and functions overlooked by previous works while still achieving state-of-the-art performance in the Automated Student Assessment Prize dataset.
Kernel Debiased Plug-in Estimation
Jun 25, 2023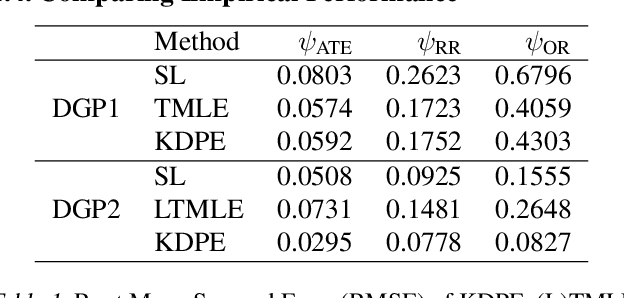
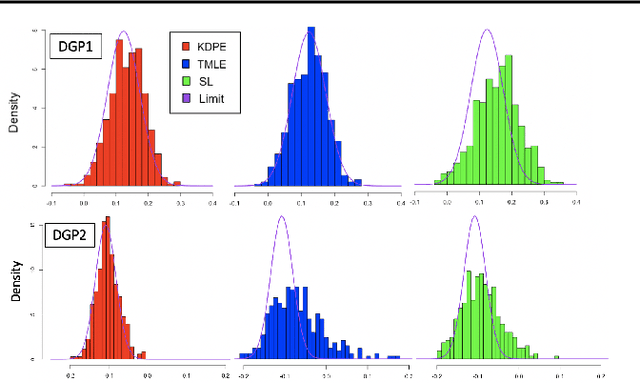
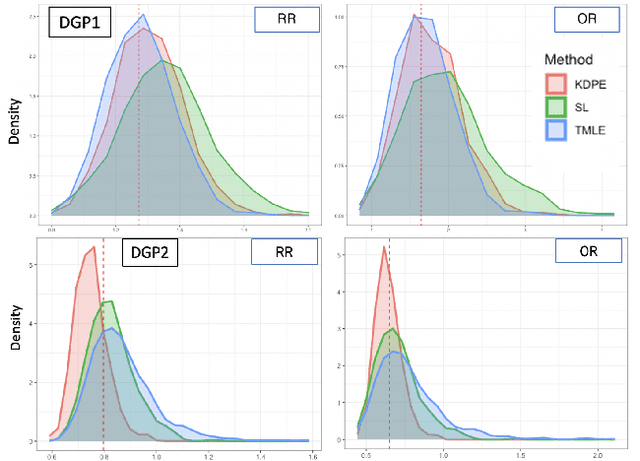
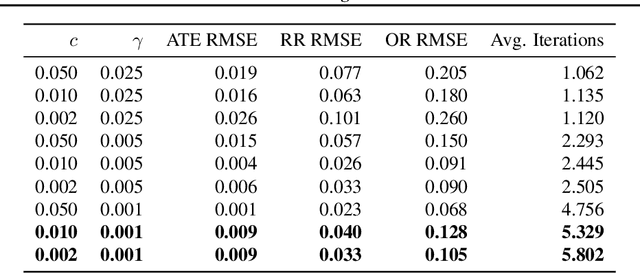
Abstract:We consider the problem of estimating a scalar target parameter in the presence of nuisance parameters. Replacing the unknown nuisance parameter with a nonparametric estimator, e.g.,a machine learning (ML) model, is convenient but has shown to be inefficient due to large biases. Modern methods, such as the targeted minimum loss-based estimation (TMLE) and double machine learning (DML), achieve optimal performance under flexible assumptions by harnessing ML estimates while mitigating the plug-in bias. To avoid a sub-optimal bias-variance trade-off, these methods perform a debiasing step of the plug-in pre-estimate. Existing debiasing methods require the influence function of the target parameter as input. However, deriving the IF requires specialized expertise and thus obstructs the adaptation of these methods by practitioners. We propose a novel way to debias plug-in estimators which (i) is efficient, (ii) does not require the IF to be implemented, (iii) is computationally tractable, and therefore can be readily adapted to new estimation problems and automated without analytic derivations by the user. We build on the TMLE framework and update a plug-in estimate with a regularized likelihood maximization step over a nonparametric model constructed with a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS), producing an efficient plug-in estimate for any regular target parameter. Our method, thus, offers the efficiency of competing debiasing techniques without sacrificing the utility of the plug-in approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge