Kernel Debiased Plug-in Estimation
Paper and Code
Jun 25, 2023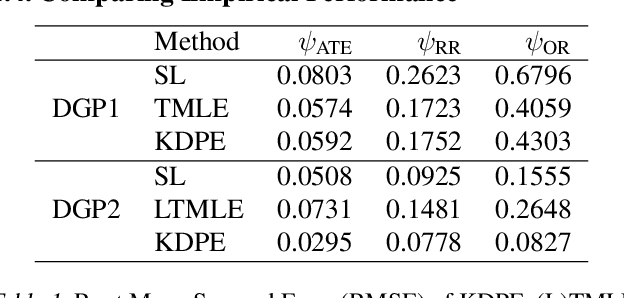
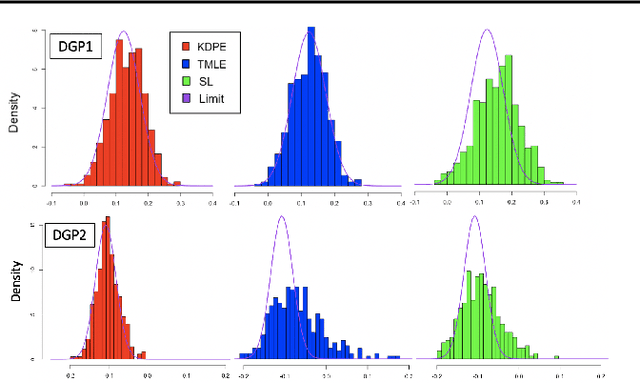
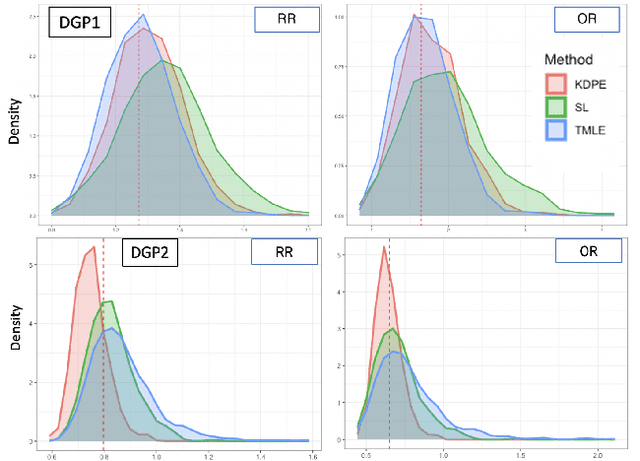
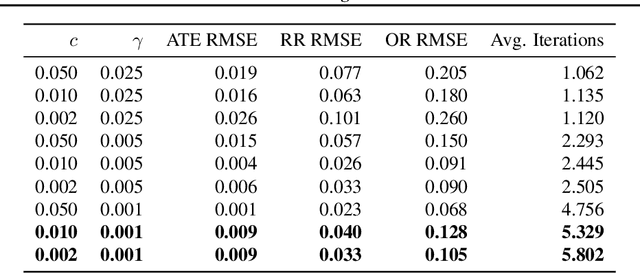
We consider the problem of estimating a scalar target parameter in the presence of nuisance parameters. Replacing the unknown nuisance parameter with a nonparametric estimator, e.g.,a machine learning (ML) model, is convenient but has shown to be inefficient due to large biases. Modern methods, such as the targeted minimum loss-based estimation (TMLE) and double machine learning (DML), achieve optimal performance under flexible assumptions by harnessing ML estimates while mitigating the plug-in bias. To avoid a sub-optimal bias-variance trade-off, these methods perform a debiasing step of the plug-in pre-estimate. Existing debiasing methods require the influence function of the target parameter as input. However, deriving the IF requires specialized expertise and thus obstructs the adaptation of these methods by practitioners. We propose a novel way to debias plug-in estimators which (i) is efficient, (ii) does not require the IF to be implemented, (iii) is computationally tractable, and therefore can be readily adapted to new estimation problems and automated without analytic derivations by the user. We build on the TMLE framework and update a plug-in estimate with a regularized likelihood maximization step over a nonparametric model constructed with a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS), producing an efficient plug-in estimate for any regular target parameter. Our method, thus, offers the efficiency of competing debiasing techniques without sacrificing the utility of the plug-in approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge