Lars van der Laan
Efficient Inference for Inverse Reinforcement Learning and Dynamic Discrete Choice Models
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) and dynamic discrete choice (DDC) models explain sequential decision-making by recovering reward functions that rationalize observed behavior. Flexible IRL methods typically rely on machine learning but provide no guarantees for valid inference, while classical DDC approaches impose restrictive parametric specifications and often require repeated dynamic programming. We develop a semiparametric framework for debiased inverse reinforcement learning that yields statistically efficient inference for a broad class of reward-dependent functionals in maximum entropy IRL and Gumbel-shock DDC models. We show that the log-behavior policy acts as a pseudo-reward that point-identifies policy value differences and, under a simple normalization, the reward itself. We then formalize these targets, including policy values under known and counterfactual softmax policies and functionals of the normalized reward, as smooth functionals of the behavior policy and transition kernel, establish pathwise differentiability, and derive their efficient influence functions. Building on this characterization, we construct automatic debiased machine-learning estimators that allow flexible nonparametric estimation of nuisance components while achieving $\sqrt{n}$-consistency, asymptotic normality, and semiparametric efficiency. Our framework extends classical inference for DDC models to nonparametric rewards and modern machine-learning tools, providing a unified and computationally tractable approach to statistical inference in IRL.
Stationary Reweighting Yields Local Convergence of Soft Fitted Q-Iteration
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Fitted Q-iteration (FQI) and its entropy-regularized variant, soft FQI, are central tools for value-based model-free offline reinforcement learning, but can behave poorly under function approximation and distribution shift. In the entropy-regularized setting, we show that the soft Bellman operator is locally contractive in the stationary norm of the soft-optimal policy, rather than in the behavior norm used by standard FQI. This geometric mismatch explains the instability of soft Q-iteration with function approximation in the absence of Bellman completeness. To restore contraction, we introduce stationary-reweighted soft FQI, which reweights each regression update using the stationary distribution of the current policy. We prove local linear convergence under function approximation with geometrically damped weight-estimation errors, assuming approximate realizability. Our analysis further suggests that global convergence may be recovered by gradually reducing the softmax temperature, and that this continuation approach can extend to the hardmax limit under a mild margin condition.
Bellman Calibration for V-Learning in Offline Reinforcement Learning
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We introduce Iterated Bellman Calibration, a simple, model-agnostic, post-hoc procedure for calibrating off-policy value predictions in infinite-horizon Markov decision processes. Bellman calibration requires that states with similar predicted long-term returns exhibit one-step returns consistent with the Bellman equation under the target policy. We adapt classical histogram and isotonic calibration to the dynamic, counterfactual setting by repeatedly regressing fitted Bellman targets onto a model's predictions, using a doubly robust pseudo-outcome to handle off-policy data. This yields a one-dimensional fitted value iteration scheme that can be applied to any value estimator. Our analysis provides finite-sample guarantees for both calibration and prediction under weak assumptions, and critically, without requiring Bellman completeness or realizability.
Fitted Q Evaluation Without Bellman Completeness via Stationary Weighting
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Fitted Q-evaluation (FQE) is a central method for off-policy evaluation in reinforcement learning, but it generally requires Bellman completeness: that the hypothesis class is closed under the evaluation Bellman operator. This requirement is challenging because enlarging the hypothesis class can worsen completeness. We show that the need for this assumption stems from a fundamental norm mismatch: the Bellman operator is gamma-contractive under the stationary distribution of the target policy, whereas FQE minimizes Bellman error under the behavior distribution. We propose a simple fix: reweight each regression step using an estimate of the stationary density ratio, thereby aligning FQE with the norm in which the Bellman operator contracts. This enables strong evaluation guarantees in the absence of realizability or Bellman completeness, avoiding the geometric error blow-up of standard FQE in this setting while maintaining the practicality of regression-based evaluation.
Hybrid Meta-learners for Estimating Heterogeneous Treatment Effects
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Estimating conditional average treatment effects (CATE) from observational data involves modeling decisions that differ from supervised learning, particularly concerning how to regularize model complexity. Previous approaches can be grouped into two primary "meta-learner" paradigms that impose distinct inductive biases. Indirect meta-learners first fit and regularize separate potential outcome (PO) models and then estimate CATE by taking their difference, whereas direct meta-learners construct and directly regularize estimators for the CATE function itself. Neither approach consistently outperforms the other across all scenarios: indirect learners perform well when the PO functions are simple, while direct learners outperform when the CATE is simpler than individual PO functions. In this paper, we introduce the Hybrid Learner (H-learner), a novel regularization strategy that interpolates between the direct and indirect regularizations depending on the dataset at hand. The H-learner achieves this by learning intermediate functions whose difference closely approximates the CATE without necessarily requiring accurate individual approximations of the POs themselves. We demonstrate empirically that intentionally allowing suboptimal fits to the POs improves the bias-variance tradeoff in estimating CATE. Experiments conducted on semi-synthetic and real-world benchmark datasets illustrate that the H-learner consistently operates at the Pareto frontier, effectively combining the strengths of both direct and indirect meta-learners.
Nonparametric Instrumental Variable Inference with Many Weak Instruments
May 12, 2025Abstract:We study inference on linear functionals in the nonparametric instrumental variable (NPIV) problem with a discretely-valued instrument under a many-weak-instruments asymptotic regime, where the number of instrument values grows with the sample size. A key motivating example is estimating long-term causal effects in a new experiment with only short-term outcomes, using past experiments to instrument for the effect of short- on long-term outcomes. Here, the assignment to a past experiment serves as the instrument: we have many past experiments but only a limited number of units in each. Since the structural function is nonparametric but constrained by only finitely many moment restrictions, point identification typically fails. To address this, we consider linear functionals of the minimum-norm solution to the moment restrictions, which is always well-defined. As the number of instrument levels grows, these functionals define an approximating sequence to a target functional, replacing point identification with a weaker asymptotic notion suited to discrete instruments. Extending the Jackknife Instrumental Variable Estimator (JIVE) beyond the classical parametric setting, we propose npJIVE, a nonparametric estimator for solutions to linear inverse problems with many weak instruments. We construct automatic debiased machine learning estimators for linear functionals of both the structural function and its minimum-norm projection, and establish their efficiency in the many-weak-instruments regime.
Generalized Venn and Venn-Abers Calibration with Applications in Conformal Prediction
Feb 08, 2025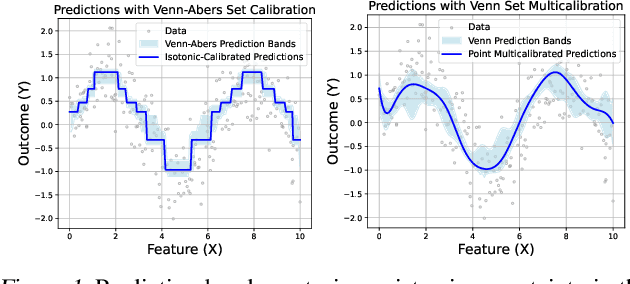
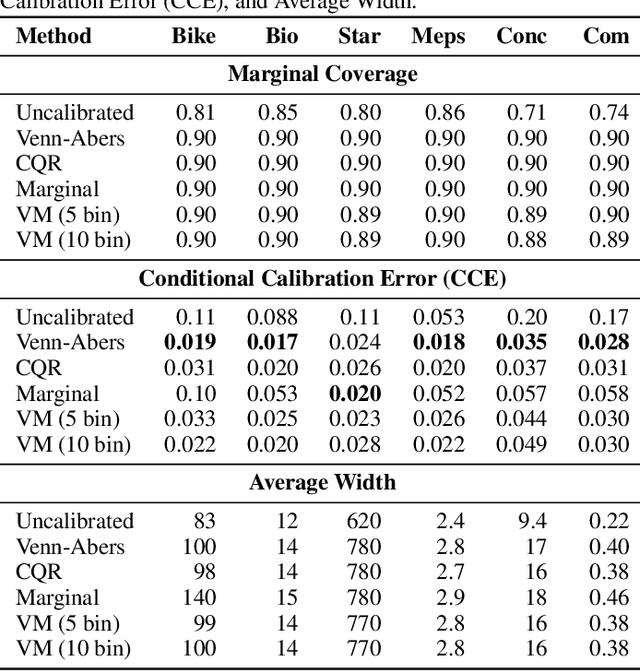
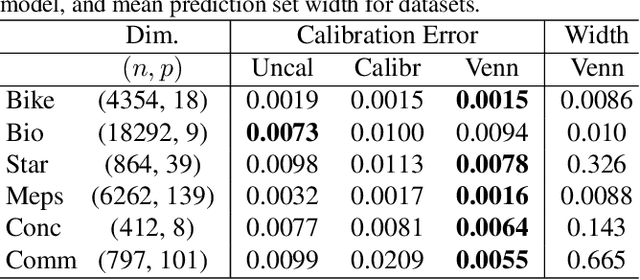
Abstract:Ensuring model calibration is critical for reliable predictions, yet popular distribution-free methods, such as histogram binning and isotonic regression, provide only asymptotic guarantees. We introduce a unified framework for Venn and Venn-Abers calibration, generalizing Vovk's binary classification approach to arbitrary prediction tasks and loss functions. Venn calibration leverages binning calibrators to construct prediction sets that contain at least one marginally perfectly calibrated point prediction in finite samples, capturing epistemic uncertainty in the calibration process. The width of these sets shrinks asymptotically to zero, converging to a conditionally calibrated point prediction. Furthermore, we propose Venn multicalibration, a novel methodology for finite-sample calibration across subpopulations. For quantile loss, group-conditional and multicalibrated conformal prediction arise as special cases of Venn multicalibration, and Venn calibration produces novel conformal prediction intervals that achieve quantile-conditional coverage. As a separate contribution, we extend distribution-free conditional calibration guarantees of histogram binning and isotonic calibration to general losses.
Automatic Double Reinforcement Learning in Semiparametric Markov Decision Processes with Applications to Long-Term Causal Inference
Jan 12, 2025


Abstract:Double reinforcement learning (DRL) enables statistically efficient inference on the value of a policy in a nonparametric Markov Decision Process (MDP) given trajectories generated by another policy. However, this approach necessarily requires stringent overlap between the state distributions, which is often violated in practice. To relax this requirement and extend DRL, we study efficient inference on linear functionals of the $Q$-function (of which policy value is a special case) in infinite-horizon, time-invariant MDPs under semiparametric restrictions on the $Q$-function. These restrictions can reduce the overlap requirement and lower the efficiency bound, yielding more precise estimates. As an important example, we study the evaluation of long-term value under domain adaptation, given a few short trajectories from the new domain and restrictions on the difference between the domains. This can be used for long-term causal inference. Our method combines flexible estimates of the $Q$-function and the Riesz representer of the functional of interest (e.g., the stationary state density ratio for policy value) and is automatic in that we do not need to know the form of the latter - only the functional we care about. To address potential model misspecification bias, we extend the adaptive debiased machine learning (ADML) framework of \citet{van2023adaptive} to construct nonparametrically valid and superefficient estimators that adapt to the functional form of the $Q$-function. As a special case, we propose a novel adaptive debiased plug-in estimator that uses isotonic-calibrated fitted $Q$-iteration - a new calibration algorithm for MDPs - to circumvent the computational challenges of estimating debiasing nuisances from min-max objectives.
Stabilized Inverse Probability Weighting via Isotonic Calibration
Nov 10, 2024Abstract:Inverse weighting with an estimated propensity score is widely used by estimation methods in causal inference to adjust for confounding bias. However, directly inverting propensity score estimates can lead to instability, bias, and excessive variability due to large inverse weights, especially when treatment overlap is limited. In this work, we propose a post-hoc calibration algorithm for inverse propensity weights that generates well-calibrated, stabilized weights from user-supplied, cross-fitted propensity score estimates. Our approach employs a variant of isotonic regression with a loss function specifically tailored to the inverse propensity weights. Through theoretical analysis and empirical studies, we demonstrate that isotonic calibration improves the performance of doubly robust estimators of the average treatment effect.
Automatic doubly robust inference for linear functionals via calibrated debiased machine learning
Nov 05, 2024Abstract:In causal inference, many estimands of interest can be expressed as a linear functional of the outcome regression function; this includes, for example, average causal effects of static, dynamic and stochastic interventions. For learning such estimands, in this work, we propose novel debiased machine learning estimators that are doubly robust asymptotically linear, thus providing not only doubly robust consistency but also facilitating doubly robust inference (e.g., confidence intervals and hypothesis tests). To do so, we first establish a key link between calibration, a machine learning technique typically used in prediction and classification tasks, and the conditions needed to achieve doubly robust asymptotic linearity. We then introduce calibrated debiased machine learning (C-DML), a unified framework for doubly robust inference, and propose a specific C-DML estimator that integrates cross-fitting, isotonic calibration, and debiased machine learning estimation. A C-DML estimator maintains asymptotic linearity when either the outcome regression or the Riesz representer of the linear functional is estimated sufficiently well, allowing the other to be estimated at arbitrarily slow rates or even inconsistently. We propose a simple bootstrap-assisted approach for constructing doubly robust confidence intervals. Our theoretical and empirical results support the use of C-DML to mitigate bias arising from the inconsistent or slow estimation of nuisance functions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge