Wen Sun
Step 3.5 Flash: Open Frontier-Level Intelligence with 11B Active Parameters
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:We introduce Step 3.5 Flash, a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model that bridges frontier-level agentic intelligence and computational efficiency. We focus on what matters most when building agents: sharp reasoning and fast, reliable execution. Step 3.5 Flash pairs a 196B-parameter foundation with 11B active parameters for efficient inference. It is optimized with interleaved 3:1 sliding-window/full attention and Multi-Token Prediction (MTP-3) to reduce the latency and cost of multi-round agentic interactions. To reach frontier-level intelligence, we design a scalable reinforcement learning framework that combines verifiable signals with preference feedback, while remaining stable under large-scale off-policy training, enabling consistent self-improvement across mathematics, code, and tool use. Step 3.5 Flash demonstrates strong performance across agent, coding, and math tasks, achieving 85.4% on IMO-AnswerBench, 86.4% on LiveCodeBench-v6 (2024.08-2025.05), 88.2% on tau2-Bench, 69.0% on BrowseComp (with context management), and 51.0% on Terminal-Bench 2.0, comparable to frontier models such as GPT-5.2 xHigh and Gemini 3.0 Pro. By redefining the efficiency frontier, Step 3.5 Flash provides a high-density foundation for deploying sophisticated agents in real-world industrial environments.
Step-DeepResearch Technical Report
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:As LLMs shift toward autonomous agents, Deep Research has emerged as a pivotal metric. However, existing academic benchmarks like BrowseComp often fail to meet real-world demands for open-ended research, which requires robust skills in intent recognition, long-horizon decision-making, and cross-source verification. To address this, we introduce Step-DeepResearch, a cost-effective, end-to-end agent. We propose a Data Synthesis Strategy Based on Atomic Capabilities to reinforce planning and report writing, combined with a progressive training path from agentic mid-training to SFT and RL. Enhanced by a Checklist-style Judger, this approach significantly improves robustness. Furthermore, to bridge the evaluation gap in the Chinese domain, we establish ADR-Bench for realistic deep research scenarios. Experimental results show that Step-DeepResearch (32B) scores 61.4% on Scale AI Research Rubrics. On ADR-Bench, it significantly outperforms comparable models and rivals SOTA closed-source models like OpenAI and Gemini DeepResearch. These findings prove that refined training enables medium-sized models to achieve expert-level capabilities at industry-leading cost-efficiency.
Step-GUI Technical Report
Dec 19, 2025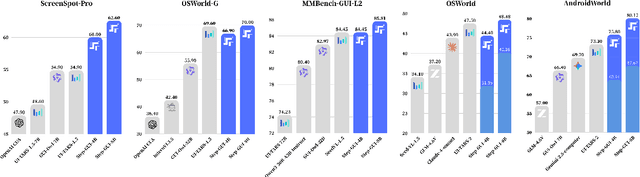
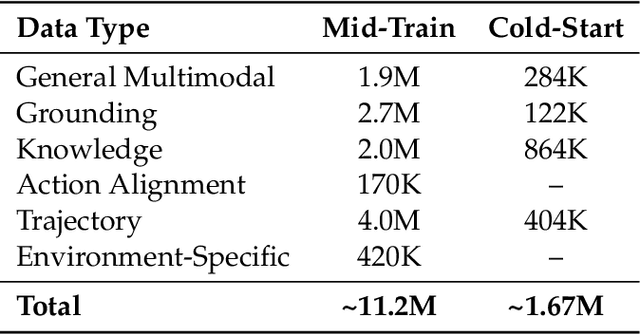
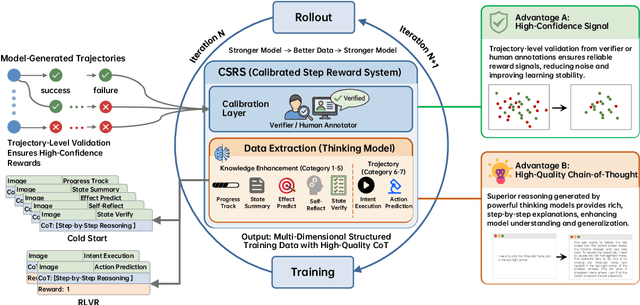

Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models unlock unprecedented opportunities for GUI automation. However, a fundamental challenge remains: how to efficiently acquire high-quality training data while maintaining annotation reliability? We introduce a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System, which converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals through trajectory-level calibration, achieving >90% annotation accuracy with 10-100x lower cost. Leveraging this pipeline, we introduce Step-GUI, a family of models (4B/8B) that achieves state-of-the-art GUI performance (8B: 80.2% AndroidWorld, 48.5% OSWorld, 62.6% ScreenShot-Pro) while maintaining robust general capabilities. As GUI agent capabilities improve, practical deployment demands standardized interfaces across heterogeneous devices while protecting user privacy. To this end, we propose GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture that combines low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models, enabling high-privacy execution where sensitive data stays on-device. Finally, to assess whether agents can handle authentic everyday usage, we introduce AndroidDaily, a benchmark grounded in real-world mobile usage patterns with 3146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency daily scenarios (8B: static 89.91%, end-to-end 52.50%). Our work advances the development of practical GUI agents and demonstrates strong potential for real-world deployment in everyday digital interactions.
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025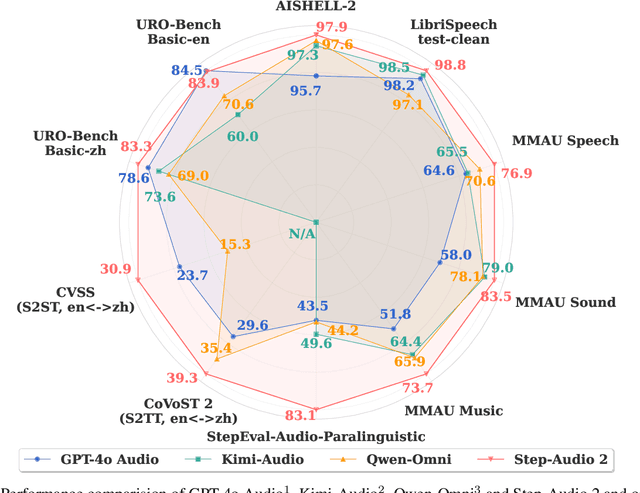

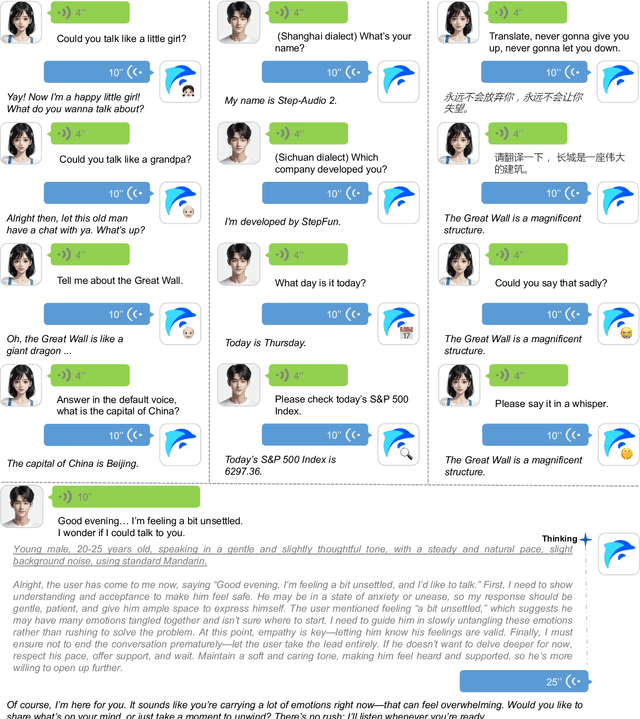

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
HieraEdgeNet: A Multi-Scale Edge-Enhanced Framework for Automated Pollen Recognition
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Automated pollen recognition is vital to paleoclimatology, biodiversity monitoring, and public health, yet conventional methods are hampered by inefficiency and subjectivity. Existing deep learning models often struggle to achieve the requisite localization accuracy for microscopic targets like pollen, which are characterized by their minute size, indistinct edges, and complex backgrounds. To overcome this limitation, we introduce HieraEdgeNet, a multi-scale edge-enhancement framework. The framework's core innovation is the introduction of three synergistic modules: the Hierarchical Edge Module (HEM), which explicitly extracts a multi-scale pyramid of edge features that corresponds to the semantic hierarchy at early network stages; the Synergistic Edge Fusion (SEF) module, for deeply fusing these edge priors with semantic information at each respective scale; and the Cross Stage Partial Omni-Kernel Module (CSPOKM), which maximally refines the most detail-rich feature layers using an Omni-Kernel operator - comprising anisotropic large-kernel convolutions and mixed-domain attention - all within a computationally efficient Cross-Stage Partial (CSP) framework. On a large-scale dataset comprising 120 pollen classes, HieraEdgeNet achieves a mean Average Precision (mAP@.5) of 0.9501, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art baseline models such as YOLOv12n and RT-DETR. Furthermore, qualitative analysis confirms that our approach generates feature representations that are more precisely focused on object boundaries. By systematically integrating edge information, HieraEdgeNet provides a robust and powerful solution for high-precision, high-efficiency automated detection of microscopic objects.
Scaling Offline RL via Efficient and Expressive Shortcut Models
May 28, 2025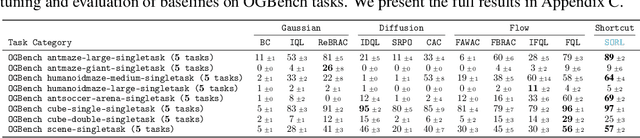
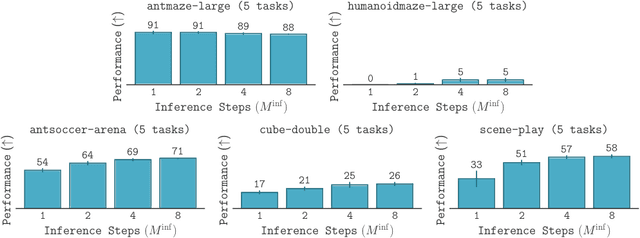
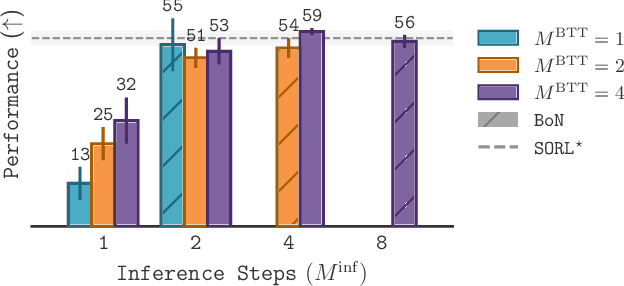
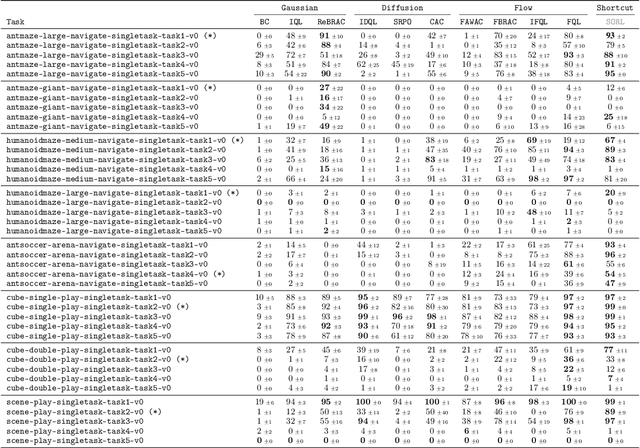
Abstract:Diffusion and flow models have emerged as powerful generative approaches capable of modeling diverse and multimodal behavior. However, applying these models to offline reinforcement learning (RL) remains challenging due to the iterative nature of their noise sampling processes, making policy optimization difficult. In this paper, we introduce Scalable Offline Reinforcement Learning (SORL), a new offline RL algorithm that leverages shortcut models - a novel class of generative models - to scale both training and inference. SORL's policy can capture complex data distributions and can be trained simply and efficiently in a one-stage training procedure. At test time, SORL introduces both sequential and parallel inference scaling by using the learned Q-function as a verifier. We demonstrate that SORL achieves strong performance across a range of offline RL tasks and exhibits positive scaling behavior with increased test-time compute. We release the code at nico-espinosadice.github.io/projects/sorl.
Efficient Controllable Diffusion via Optimal Classifier Guidance
May 27, 2025Abstract:The controllable generation of diffusion models aims to steer the model to generate samples that optimize some given objective functions. It is desirable for a variety of applications including image generation, molecule generation, and DNA/sequence generation. Reinforcement Learning (RL) based fine-tuning of the base model is a popular approach but it can overfit the reward function while requiring significant resources. We frame controllable generation as a problem of finding a distribution that optimizes a KL-regularized objective function. We present SLCD -- Supervised Learning based Controllable Diffusion, which iteratively generates online data and trains a small classifier to guide the generation of the diffusion model. Similar to the standard classifier-guided diffusion, SLCD's key computation primitive is classification and does not involve any complex concepts from RL or control. Via a reduction to no-regret online learning analysis, we show that under KL divergence, the output from SLCD provably converges to the optimal solution of the KL-regularized objective. Further, we empirically demonstrate that SLCD can generate high quality samples with nearly the same inference time as the base model in both image generation with continuous diffusion and biological sequence generation with discrete diffusion. Our code is available at https://github.com/Owen-Oertell/slcd
Accelerating RL for LLM Reasoning with Optimal Advantage Regression
May 27, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a powerful tool for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) to improve complex reasoning abilities. However, state-of-the-art policy optimization methods often suffer from high computational overhead and memory consumption, primarily due to the need for multiple generations per prompt and the reliance on critic networks or advantage estimates of the current policy. In this paper, we propose $A$*-PO, a novel two-stage policy optimization framework that directly approximates the optimal advantage function and enables efficient training of LLMs for reasoning tasks. In the first stage, we leverage offline sampling from a reference policy to estimate the optimal value function $V$*, eliminating the need for costly online value estimation. In the second stage, we perform on-policy updates using a simple least-squares regression loss with only a single generation per prompt. Theoretically, we establish performance guarantees and prove that the KL-regularized RL objective can be optimized without requiring complex exploration strategies. Empirically, $A$*-PO achieves competitive performance across a wide range of mathematical reasoning benchmarks, while reducing training time by up to 2$\times$ and peak memory usage by over 30% compared to PPO, GRPO, and REBEL. Implementation of $A$*-PO can be found at https://github.com/ZhaolinGao/A-PO.
Value-Guided Search for Efficient Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
May 23, 2025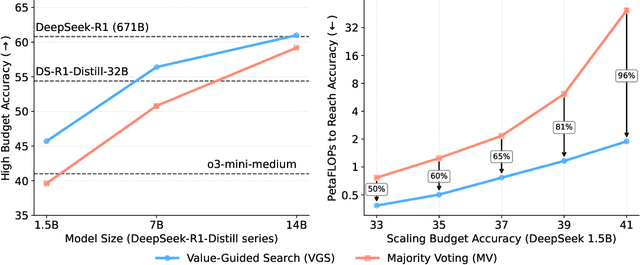

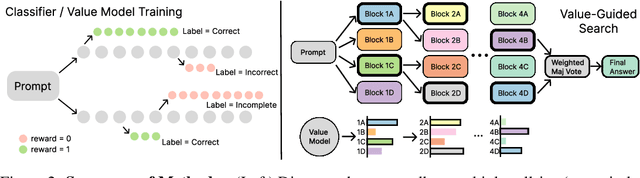
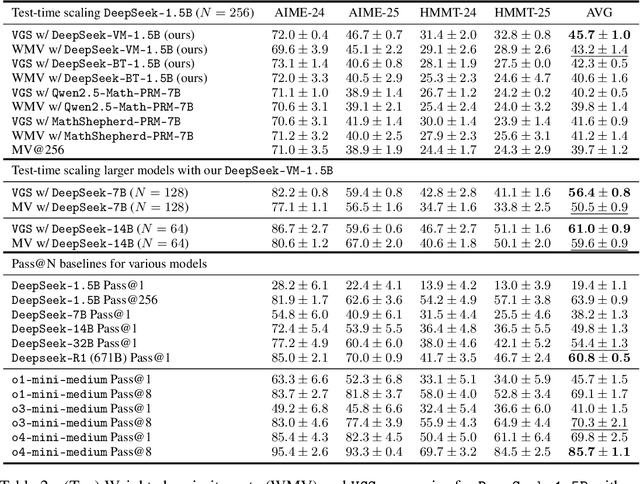
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a simple and efficient method for value model training on long-context reasoning traces. Compared to existing process reward models (PRMs), our method does not require a fine-grained notion of "step," which is difficult to define for long-context reasoning models. By collecting a dataset of 2.5 million reasoning traces, we train a 1.5B token-level value model and apply it to DeepSeek models for improved performance with test-time compute scaling. We find that block-wise value-guided search (VGS) with a final weighted majority vote achieves better test-time scaling than standard methods such as majority voting or best-of-n. With an inference budget of 64 generations, VGS with DeepSeek-R1-Distill-1.5B achieves an average accuracy of 45.7% across four competition math benchmarks (AIME 2024 & 2025, HMMT Feb 2024 & 2025), reaching parity with o3-mini-medium. Moreover, VGS significantly reduces the inference FLOPs required to achieve the same performance of majority voting. Our dataset, model and codebase are open-sourced.
Convergence Of Consistency Model With Multistep Sampling Under General Data Assumptions
May 06, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models accomplish remarkable success in data generation tasks across various domains. However, the iterative sampling process is computationally expensive. Consistency models are proposed to learn consistency functions to map from noise to data directly, which allows one-step fast data generation and multistep sampling to improve sample quality. In this paper, we study the convergence of consistency models when the self-consistency property holds approximately under the training distribution. Our analysis requires only mild data assumption and applies to a family of forward processes. When the target data distribution has bounded support or has tails that decay sufficiently fast, we show that the samples generated by the consistency model are close to the target distribution in Wasserstein distance; when the target distribution satisfies some smoothness assumption, we show that with an additional perturbation step for smoothing, the generated samples are close to the target distribution in total variation distance. We provide two case studies with commonly chosen forward processes to demonstrate the benefit of multistep sampling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge