Mingqiu Wang
Knowledge Graph Reasoning with Self-supervised Reinforcement Learning
May 22, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is an effective method of finding reasoning pathways in incomplete knowledge graphs (KGs). To overcome the challenges of a large action space, a self-supervised pre-training method is proposed to warm up the policy network before the RL training stage. To alleviate the distributional mismatch issue in general self-supervised RL (SSRL), in our supervised learning (SL) stage, the agent selects actions based on the policy network and learns from generated labels; this self-generation of labels is the intuition behind the name self-supervised. With this training framework, the information density of our SL objective is increased and the agent is prevented from getting stuck with the early rewarded paths. Our self-supervised RL (SSRL) method improves the performance of RL by pairing it with the wide coverage achieved by SL during pretraining, since the breadth of the SL objective makes it infeasible to train an agent with that alone. We show that our SSRL model meets or exceeds current state-of-the-art results on all Hits@k and mean reciprocal rank (MRR) metrics on four large benchmark KG datasets. This SSRL method can be used as a plug-in for any RL architecture for a KGR task. We adopt two RL architectures, i.e., MINERVA and MultiHopKG as our baseline RL models and experimentally show that our SSRL model consistently outperforms both baselines on all of these four KG reasoning tasks. Full code for the paper available at https://github.com/owenonline/Knowledge-Graph-Reasoning-with-Self-supervised-Reinforcement-Learning.
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Retrieval Augmented End-to-End Spoken Dialog Models
Feb 02, 2024



Abstract:We recently developed SLM, a joint speech and language model, which fuses a pretrained foundational speech model and a large language model (LLM), while preserving the in-context learning capability intrinsic to the pretrained LLM. In this paper, we apply SLM to speech dialog applications where the dialog states are inferred directly from the audio signal. Task-oriented dialogs often contain domain-specific entities, i.e., restaurants, hotels, train stations, and city names, which are difficult to recognize, however, critical for the downstream applications. Inspired by the RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) paradigm, we propose a retrieval augmented SLM (ReSLM) that overcomes this weakness. We first train a speech retriever to retrieve text entities mentioned in the audio. The retrieved entities are then added as text inputs to the underlying SLM to bias model predictions. We evaluated ReSLM on speech MultiWoz task (DSTC-11 challenge), and found that this retrieval augmentation boosts model performance, achieving joint goal accuracy (38.6% vs 32.7%), slot error rate (20.6% vs 24.8%) and ASR word error rate (5.5% vs 6.7%). While demonstrated on dialog state tracking, our approach is broadly applicable to other speech tasks requiring contextual information or domain-specific entities, such as contextual ASR with biasing capability.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
SLM: Bridge the thin gap between speech and text foundation models
Sep 30, 2023



Abstract:We present a joint Speech and Language Model (SLM), a multitask, multilingual, and dual-modal model that takes advantage of pretrained foundational speech and language models. SLM freezes the pretrained foundation models to maximally preserves their capabilities, and only trains a simple adapter with just 1\% (156M) of the foundation models' parameters. This adaptation not only leads SLM to achieve strong performance on conventional tasks such as speech recognition (ASR) and speech translation (AST), but also introduces the novel capability of zero-shot instruction-following for more diverse tasks: given a speech input and a text instruction, SLM is able to perform unseen generation tasks including contextual biasing ASR using real-time context, dialog generation, speech continuation, and question answering, etc. Our approach demonstrates that the representational gap between pretrained speech and language models might be narrower than one would expect, and can be bridged by a simple adaptation mechanism. As a result, SLM is not only efficient to train, but also inherits strong capabilities already acquired in foundation models of different modalities.
Speech-to-Text Adapter and Speech-to-Entity Retriever Augmented LLMs for Speech Understanding
Jun 08, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been applied in the speech domain, often incurring a performance drop due to misaligned between speech and language representations. To bridge this gap, we propose a joint speech and language model (SLM) using a Speech2Text adapter, which maps speech into text token embedding space without speech information loss. Additionally, using a CTC-based blank-filtering, we can reduce the speech sequence length to that of text. In speech MultiWoz dataset (DSTC11 challenge), SLM largely improves the dialog state tracking (DST) performance (24.7% to 28.4% accuracy). Further to address errors on rare entities, we augment SLM with a Speech2Entity retriever, which uses speech to retrieve relevant entities, and then adds them to the original SLM input as a prefix. With this retrieval-augmented SLM (ReSLM), the DST performance jumps to 34.6% accuracy. Moreover, augmenting the ASR task with the dialog understanding task improves the ASR performance from 9.4% to 8.5% WER.
MUX-PLMs: Pre-training Language Models with Data Multiplexing
Feb 24, 2023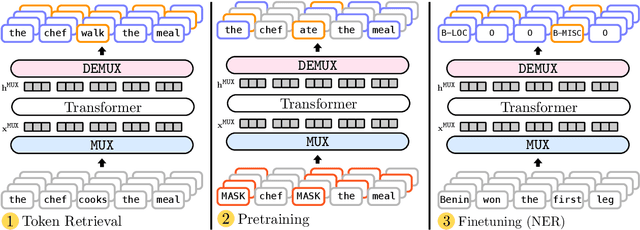
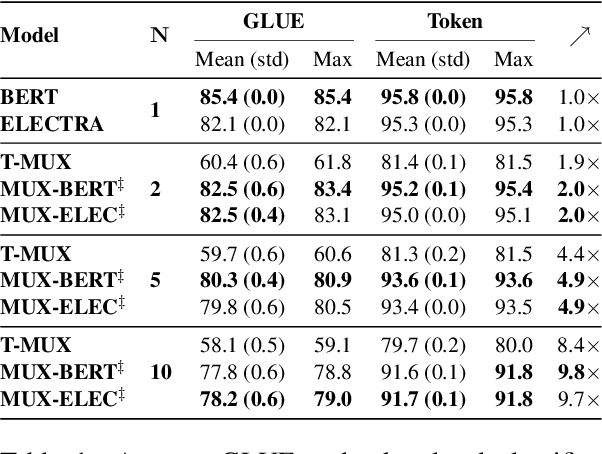
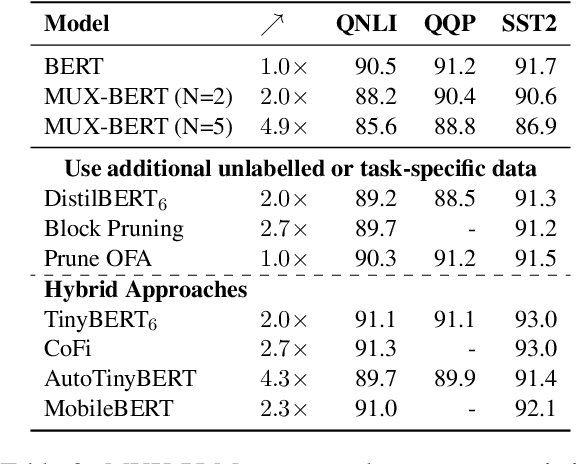
Abstract:Data multiplexing is a recently proposed method for improving a model's inference efficiency by processing multiple instances simultaneously using an ordered representation mixture. Prior work on data multiplexing only used task-specific Transformers without any pre-training, which limited their accuracy and generality. In this paper, we develop pre-trained multiplexed language models (MUX-PLMs) that can be widely finetuned on any downstream task. Our approach includes a three-stage training procedure and novel multiplexing and demultiplexing modules for improving throughput and downstream task accuracy. We demonstrate our method on BERT and ELECTRA pre-training objectives, with our MUX-BERT and MUX-ELECTRA models achieving 2x/5x inference speedup with a 2-4 \% drop in absolute performance on GLUE and 1-2 \% drop on token-level tasks.
AnyTOD: A Programmable Task-Oriented Dialog System
Dec 20, 2022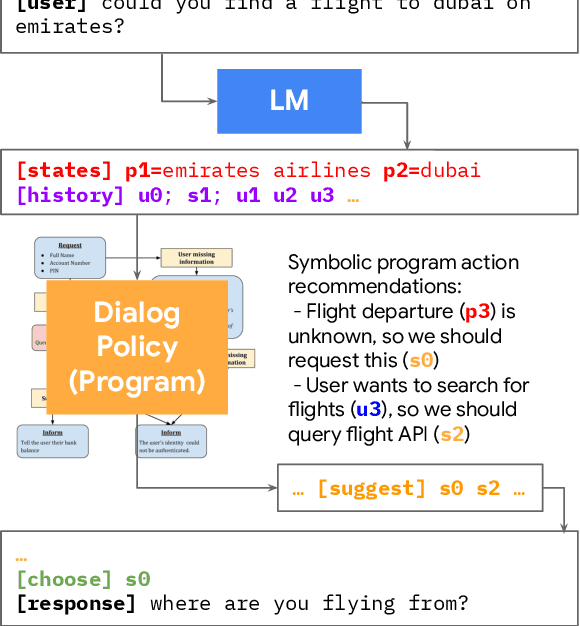
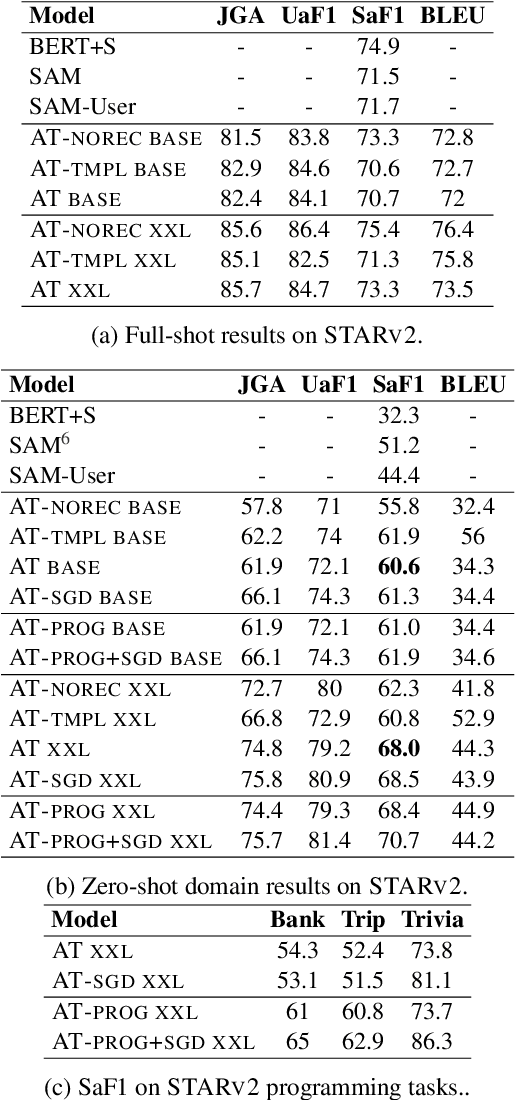
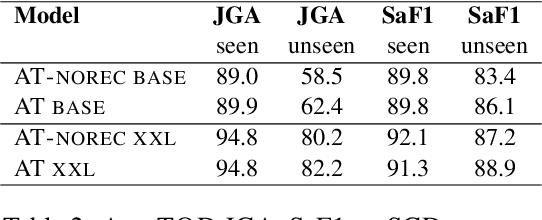
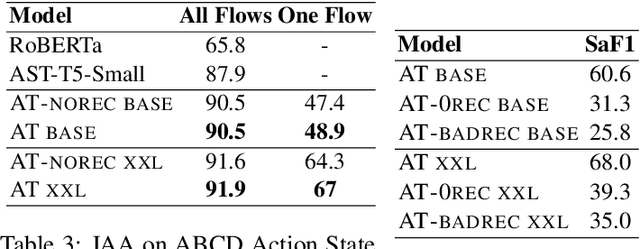
Abstract:We propose AnyTOD, an end-to-end task-oriented dialog (TOD) system with zero-shot capability for unseen tasks. We view TOD as a program executed by a language model (LM), where program logic and ontology is provided by a designer in the form of a schema. To enable generalization onto unseen schemas and programs without prior training, AnyTOD adopts a neuro-symbolic approach. A neural LM keeps track of events that occur during a conversation, and a symbolic program implementing the dialog policy is executed to recommend next actions AnyTOD should take. This approach drastically reduces data annotation and model training requirements, addressing a long-standing challenge in TOD research: rapidly adapting a TOD system to unseen tasks and domains. We demonstrate state-of-the-art results on the STAR and ABCD benchmarks, as well as AnyTOD's strong zero-shot transfer capability in low-resource settings. In addition, we release STARv2, an updated version of the STAR dataset with richer data annotations, for benchmarking zero-shot end-to-end TOD models.
Speech Aware Dialog System Technology Challenge (DSTC11)
Dec 16, 2022



Abstract:Most research on task oriented dialog modeling is based on written text input. However, users interact with practical dialog systems often using speech as input. Typically, systems convert speech into text using an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system, introducing errors. Furthermore, these systems do not address the differences in written and spoken language. The research on this topic is stymied by the lack of a public corpus. Motivated by these considerations, our goal in hosting the speech-aware dialog state tracking challenge was to create a public corpus or task which can be used to investigate the performance gap between the written and spoken forms of input, develop models that could alleviate this gap, and establish whether Text-to-Speech-based (TTS) systems is a reasonable surrogate to the more-labor intensive human data collection. We created three spoken versions of the popular written-domain MultiWoz task -- (a) TTS-Verbatim: written user inputs were converted into speech waveforms using a TTS system, (b) Human-Verbatim: humans spoke the user inputs verbatim, and (c) Human-paraphrased: humans paraphrased the user inputs. Additionally, we provided different forms of ASR output to encourage wider participation from teams that may not have access to state-of-the-art ASR systems. These included ASR transcripts, word time stamps, and latent representations of the audio (audio encoder outputs). In this paper, we describe the corpus, report results from participating teams, provide preliminary analyses of their results, and summarize the current state-of-the-art in this domain.
Transfer learning with high-dimensional quantile regression
Nov 26, 2022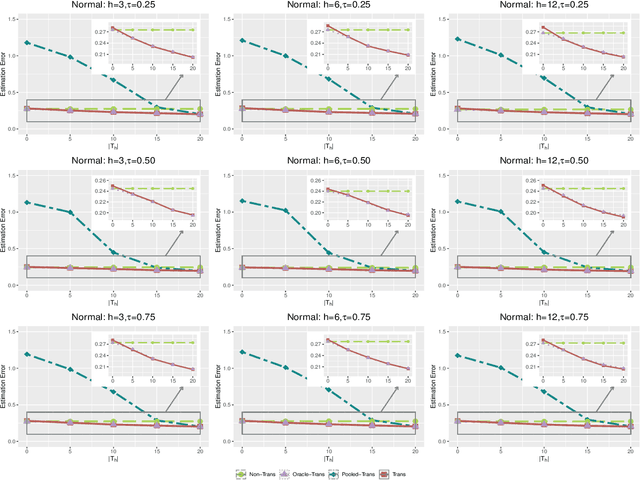
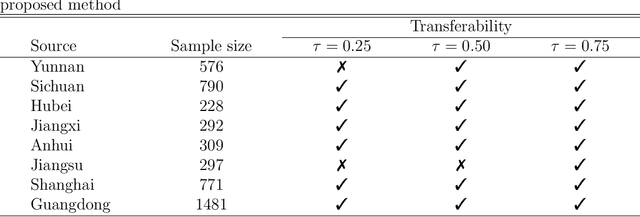
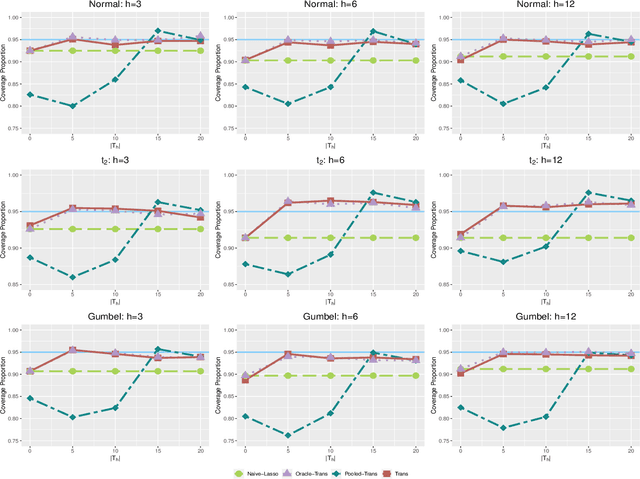
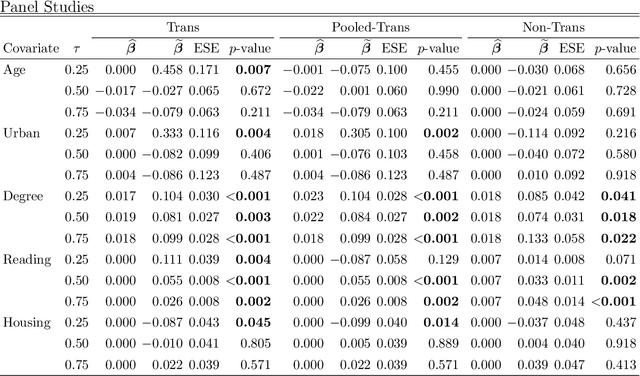
Abstract:Transfer learning has become an essential technique to exploit information from the source domain to boost performance of the target task. Despite the prevalence in high-dimensional data, heterogeneity and/or heavy tails tend to be discounted in current transfer learning approaches and thus may undermine the resulting performance. We propose a transfer learning procedure in the framework of high-dimensional quantile regression models to accommodate the heterogeneity and heavy tails in the source and target domains. We establish error bounds of the transfer learning estimator based on delicately selected transferable source domains, showing that lower error bounds can be achieved for critical selection criterion and larger sample size of source tasks. We further propose valid confidence interval and hypothesis test procedures for individual component of quantile regression coefficients by advocating a one-step debiased estimator of transfer learning estimator wherein the consistent variance estimation is proposed via the technique of transfer learning again. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method exhibits some favorable performances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge