Martin Rajchl
Weakly Supervised Estimation of Shadow Confidence Maps in Ultrasound Imaging
Nov 21, 2018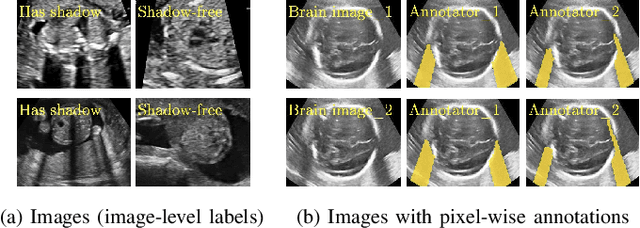

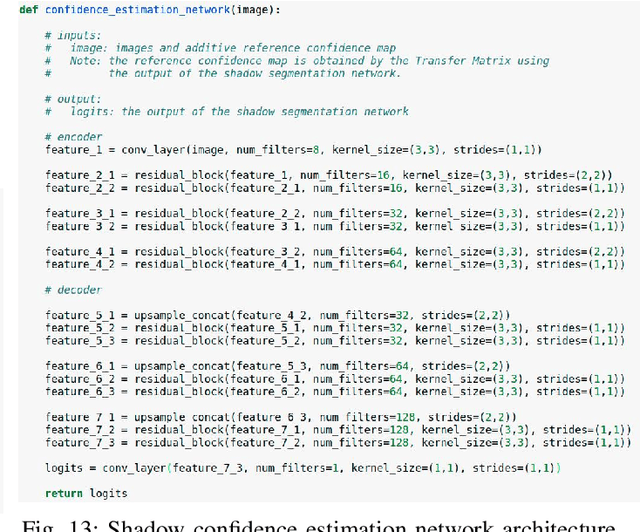
Abstract:Detecting acoustic shadows in ultrasound images is important in many clinical and engineering applications. Real-time feedback of acoustic shadows can guide sonographers to a standardized diagnostic viewing plane with minimal artifacts and can provide additional information for other automatic image analysis algorithms. However, automatically detecting shadow regions is challenging because pixel-wise annotation of acoustic shadows is subjective and time consuming. In this paper we propose a weakly supervised method for automatic confidence estimation of acoustic shadow regions, which is able to generate a dense shadow-focused confidence map. During training, a multi-task module for shadow segmentation is built to learn general shadow features according based image-level annotations as well as a small number of coarse pixel-wise shadow annotations. A transfer function is then established to extend the binary shadow segmentation to a reference confidence map. In addition, a confidence estimation network is proposed to learn the mapping between input images and the reference confidence maps. This confidence estimation network is able to predict shadow confidence maps directly from input images during inference. We evaluate DICE, soft DICE, recall, precision, mean squared error and inter-class correlation to verify the effectiveness of our method. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art qualitatively and quantitatively. We further demonstrate the applicability of our method by integrating shadow confidence maps into tasks such as ultrasound image classification, multi-view image fusion and automated biometric measurements.
Learning Interpretable Anatomical Features Through Deep Generative Models: Application to Cardiac Remodeling
Jul 18, 2018
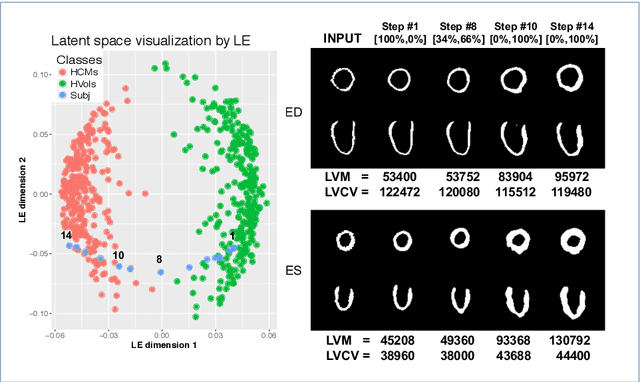
Abstract:Alterations in the geometry and function of the heart define well-established causes of cardiovascular disease. However, current approaches to the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases often rely on subjective human assessment as well as manual analysis of medical images. Both factors limit the sensitivity in quantifying complex structural and functional phenotypes. Deep learning approaches have recently achieved success for tasks such as classification or segmentation of medical images, but lack interpretability in the feature extraction and decision processes, limiting their value in clinical diagnosis. In this work, we propose a 3D convolutional generative model for automatic classification of images from patients with cardiac diseases associated with structural remodeling. The model leverages interpretable task-specific anatomic patterns learned from 3D segmentations. It further allows to visualise and quantify the learned pathology-specific remodeling patterns in the original input space of the images. This approach yields high accuracy in the categorization of healthy and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy subjects when tested on unseen MR images from our own multi-centre dataset (100%) as well on the ACDC MICCAI 2017 dataset (90%). We believe that the proposed deep learning approach is a promising step towards the development of interpretable classifiers for the medical imaging domain, which may help clinicians to improve diagnostic accuracy and enhance patient risk-stratification.
Deep Generative Models in the Real-World: An Open Challenge from Medical Imaging
Jun 14, 2018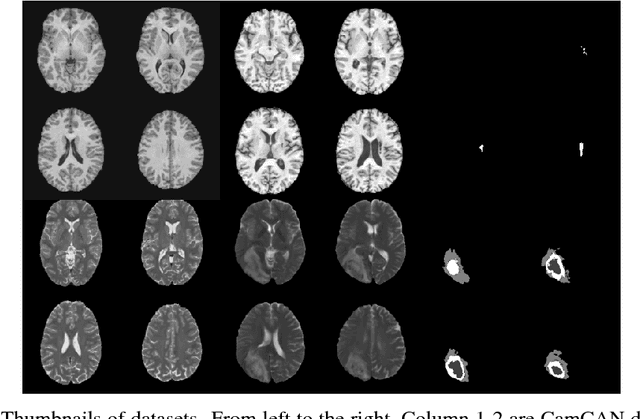
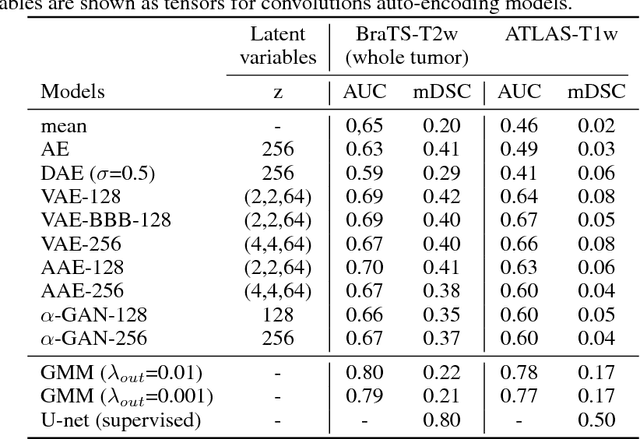
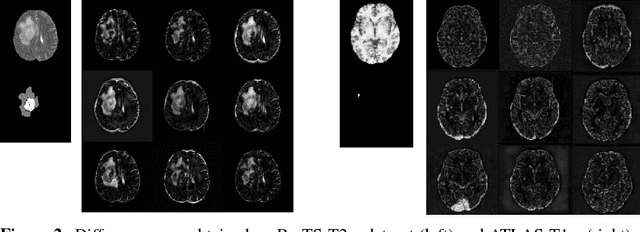
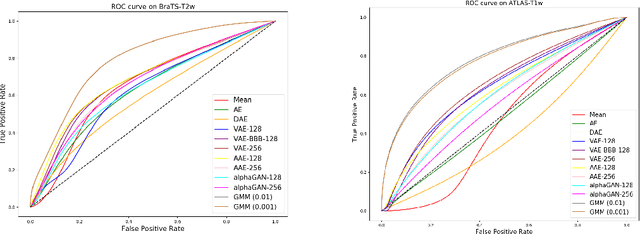
Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning led to novel generative modeling techniques that achieve unprecedented quality in generated samples and performance in learning complex distributions in imaging data. These new models in medical image computing have important applications that form clinically relevant and very challenging unsupervised learning problems. In this paper, we explore the feasibility of using state-of-the-art auto-encoder-based deep generative models, such as variational and adversarial auto-encoders, for one such task: abnormality detection in medical imaging. We utilize typical, publicly available datasets with brain scans from healthy subjects and patients with stroke lesions and brain tumors. We use the data from healthy subjects to train different auto-encoder based models to learn the distribution of healthy images and detect pathologies as outliers. Models that can better learn the data distribution should be able to detect outliers more accurately. We evaluate the detection performance of deep generative models and compare them with non-deep learning based approaches to provide a benchmark of the current state of research. We conclude that abnormality detection is a challenging task for deep generative models and large room exists for improvement. In order to facilitate further research, we aim to provide carefully pre-processed imaging data available to the research community.
NeuroNet: Fast and Robust Reproduction of Multiple Brain Image Segmentation Pipelines
Jun 11, 2018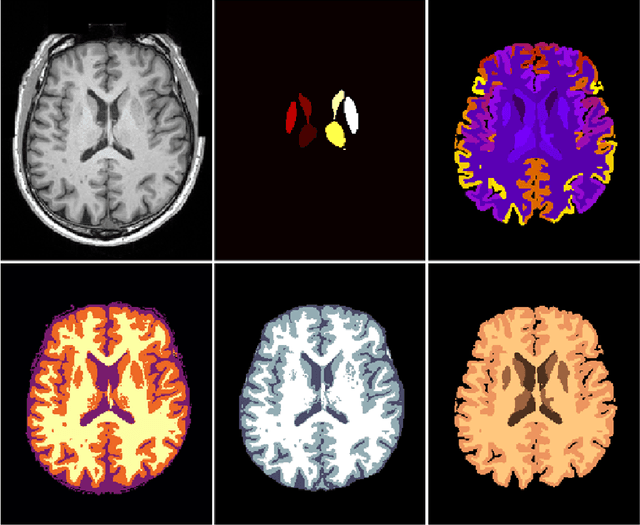
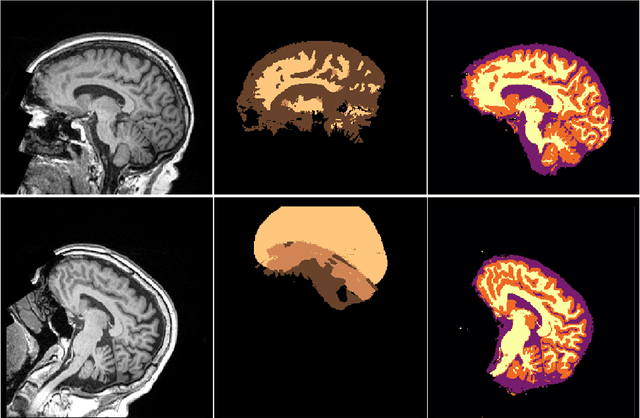
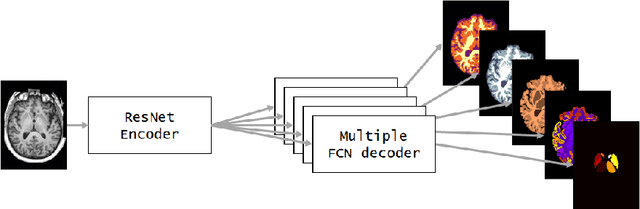
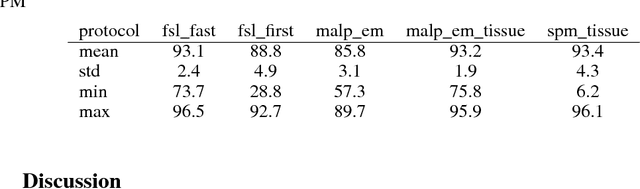
Abstract:NeuroNet is a deep convolutional neural network mimicking multiple popular and state-of-the-art brain segmentation tools including FSL, SPM, and MALPEM. The network is trained on 5,000 T1-weighted brain MRI scans from the UK Biobank Imaging Study that have been automatically segmented into brain tissue and cortical and sub-cortical structures using the standard neuroimaging pipelines. Training a single model from these complementary and partially overlapping label maps yields a new powerful "all-in-one", multi-output segmentation tool. The processing time for a single subject is reduced by an order of magnitude compared to running each individual software package. We demonstrate very good reproducibility of the original outputs while increasing robustness to variations in the input data. We believe NeuroNet could be an important tool in large-scale population imaging studies and serve as a new standard in neuroscience by reducing the risk of introducing bias when choosing a specific software package.
Implicit Weight Uncertainty in Neural Networks
May 25, 2018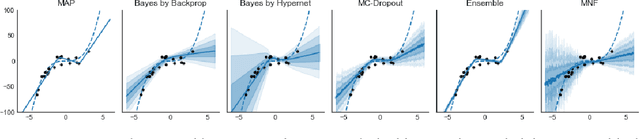
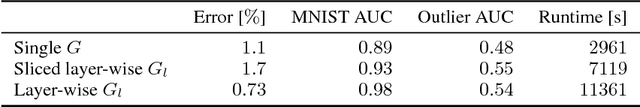
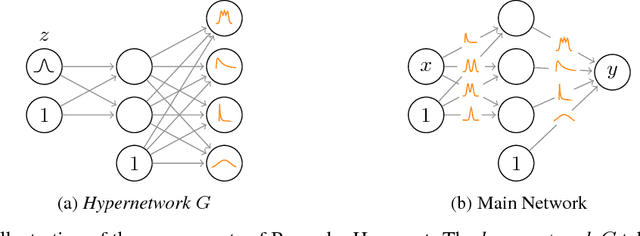
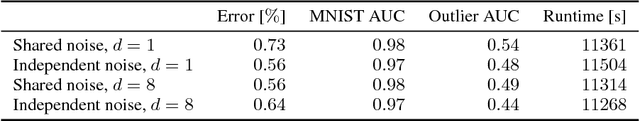
Abstract:Modern neural networks tend to be overconfident on unseen, noisy or incorrectly labelled data and do not produce meaningful uncertainty measures. Bayesian deep learning aims to address this shortcoming with variational approximations (such as Bayes by Backprop or Multiplicative Normalising Flows). However, current approaches have limitations regarding flexibility and scalability. We introduce Bayes by Hypernet (BbH), a new method of variational approximation that interprets hypernetworks as implicit distributions. It naturally uses neural networks to model arbitrarily complex distributions and scales to modern deep learning architectures. In our experiments, we demonstrate that our method achieves competitive accuracies and predictive uncertainties on MNIST and a CIFAR5 task, while being the most robust against adversarial attacks.
Automated cardiovascular magnetic resonance image analysis with fully convolutional networks
May 22, 2018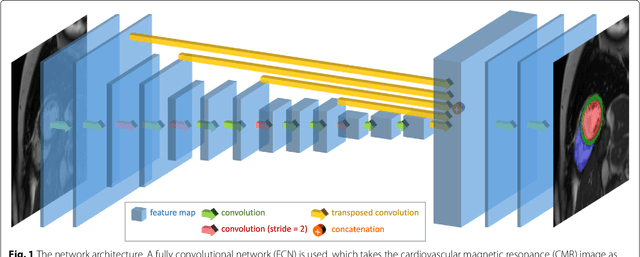

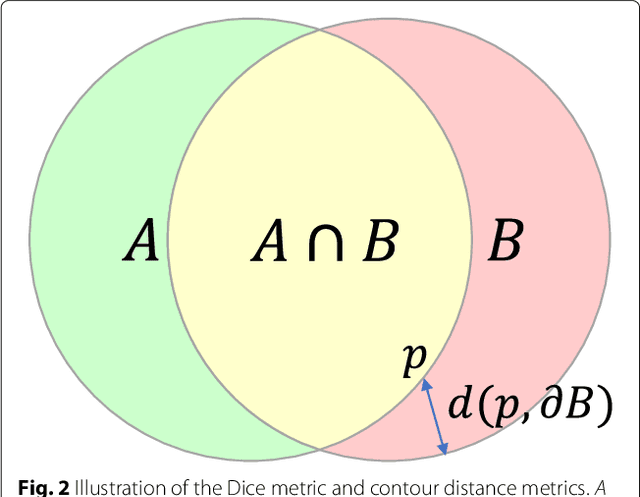
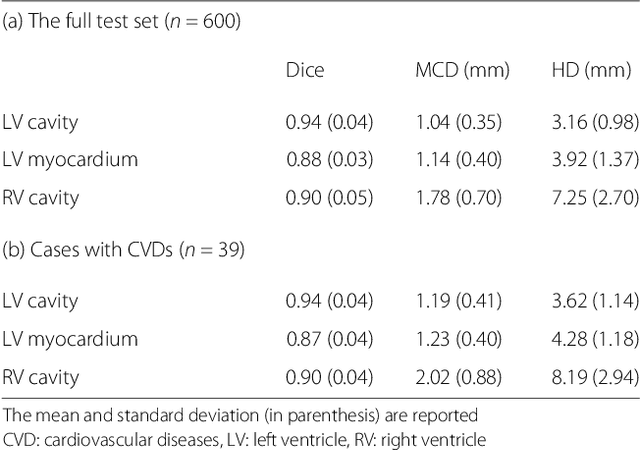
Abstract:Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging is a standard imaging modality for assessing cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), the leading cause of death globally. CMR enables accurate quantification of the cardiac chamber volume, ejection fraction and myocardial mass, providing information for diagnosis and monitoring of CVDs. However, for years, clinicians have been relying on manual approaches for CMR image analysis, which is time consuming and prone to subjective errors. It is a major clinical challenge to automatically derive quantitative and clinically relevant information from CMR images. Deep neural networks have shown a great potential in image pattern recognition and segmentation for a variety of tasks. Here we demonstrate an automated analysis method for CMR images, which is based on a fully convolutional network (FCN). The network is trained and evaluated on a large-scale dataset from the UK Biobank, consisting of 4,875 subjects with 93,500 pixelwise annotated images. The performance of the method has been evaluated using a number of technical metrics, including the Dice metric, mean contour distance and Hausdorff distance, as well as clinically relevant measures, including left ventricle (LV) end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and end-systolic volume (LVESV), LV mass (LVM); right ventricle (RV) end-diastolic volume (RVEDV) and end-systolic volume (RVESV). By combining FCN with a large-scale annotated dataset, the proposed automated method achieves a high performance on par with human experts in segmenting the LV and RV on short-axis CMR images and the left atrium (LA) and right atrium (RA) on long-axis CMR images.
DLTK: State of the Art Reference Implementations for Deep Learning on Medical Images
Nov 18, 2017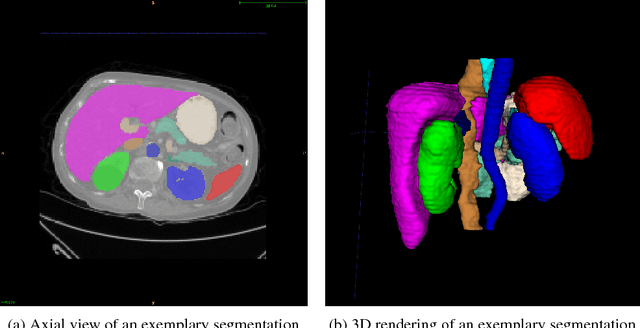
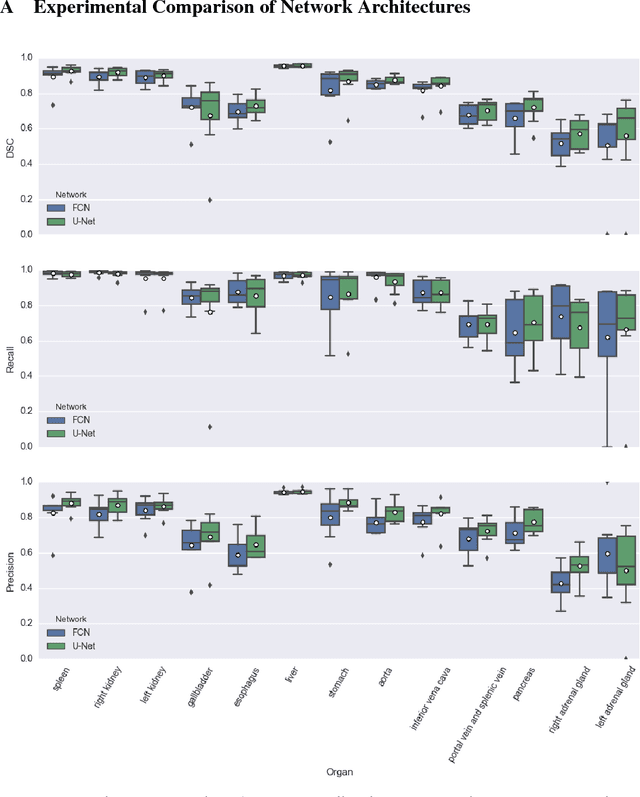
Abstract:We present DLTK, a toolkit providing baseline implementations for efficient experimentation with deep learning methods on biomedical images. It builds on top of TensorFlow and its high modularity and easy-to-use examples allow for a low-threshold access to state-of-the-art implementations for typical medical imaging problems. A comparison of DLTK's reference implementations of popular network architectures for image segmentation demonstrates new top performance on the publicly available challenge data "Multi-Atlas Labeling Beyond the Cranial Vault". The average test Dice similarity coefficient of $81.5$ exceeds the previously best performing CNN ($75.7$) and the accuracy of the challenge winning method ($79.0$).
Ensembles of Multiple Models and Architectures for Robust Brain Tumour Segmentation
Nov 04, 2017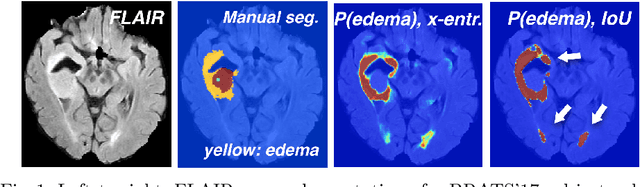
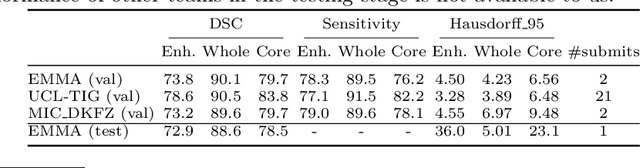
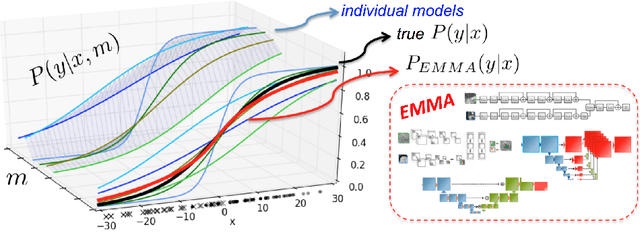
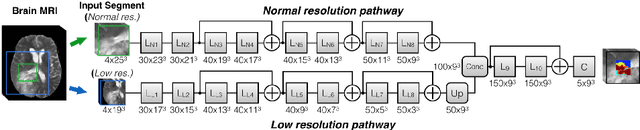
Abstract:Deep learning approaches such as convolutional neural nets have consistently outperformed previous methods on challenging tasks such as dense, semantic segmentation. However, the various proposed networks perform differently, with behaviour largely influenced by architectural choices and training settings. This paper explores Ensembles of Multiple Models and Architectures (EMMA) for robust performance through aggregation of predictions from a wide range of methods. The approach reduces the influence of the meta-parameters of individual models and the risk of overfitting the configuration to a particular database. EMMA can be seen as an unbiased, generic deep learning model which is shown to yield excellent performance, winning the first position in the BRATS 2017 competition among 50+ participating teams.
Employing Weak Annotations for Medical Image Analysis Problems
Aug 21, 2017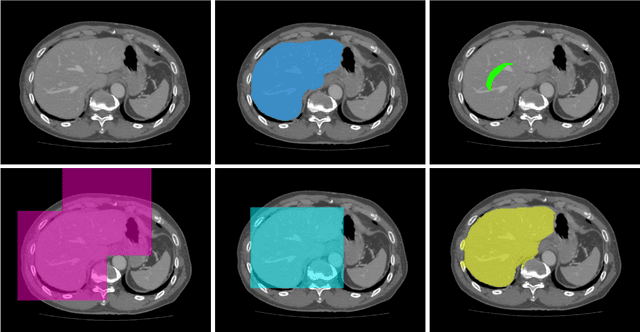
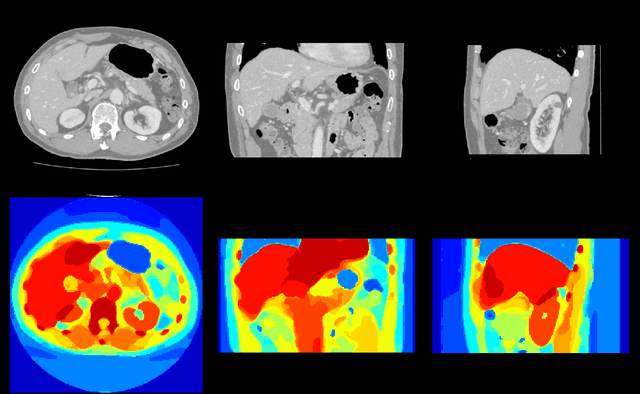
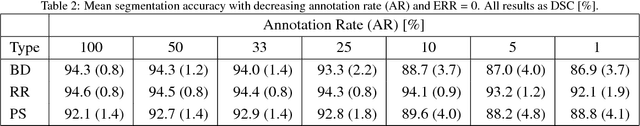
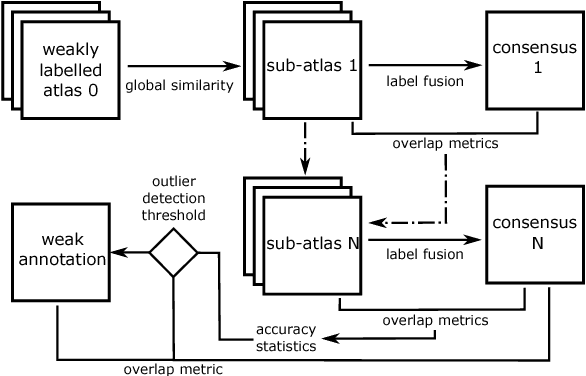
Abstract:To efficiently establish training databases for machine learning methods, collaborative and crowdsourcing platforms have been investigated to collectively tackle the annotation effort. However, when this concept is ported to the medical imaging domain, reading expertise will have a direct impact on the annotation accuracy. In this study, we examine the impact of expertise and the amount of available annotations on the accuracy outcome of a liver segmentation problem in an abdominal computed tomography (CT) image database. In controlled experiments, we study this impact for different types of weak annotations. To address the decrease in accuracy associated with lower expertise, we propose a method for outlier correction making use of a weakly labelled atlas. Using this approach, we demonstrate that weak annotations subject to high error rates can achieve a similarly high accuracy as state-of-the-art multi-atlas segmentation approaches relying on a large amount of expert manual segmentations. Annotations of this nature can realistically be obtained from a non-expert crowd and can potentially enable crowdsourcing of weak annotation tasks for medical image analysis.
Distance Metric Learning using Graph Convolutional Networks: Application to Functional Brain Networks
Jun 14, 2017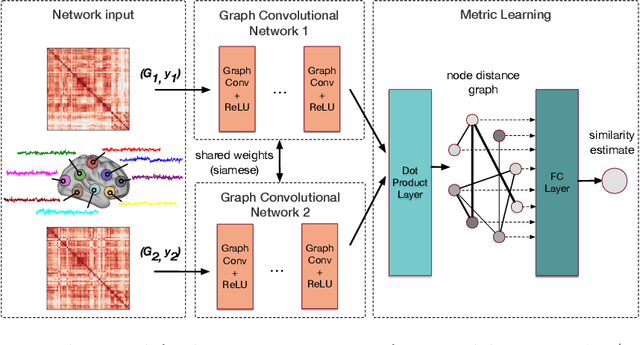
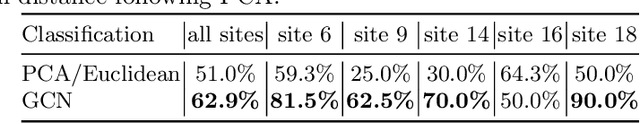
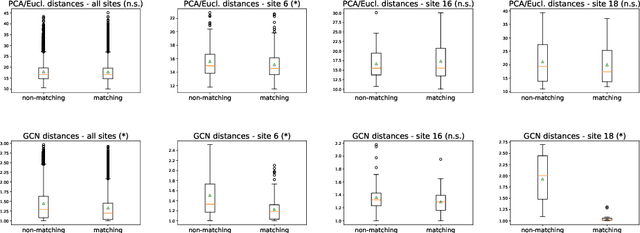
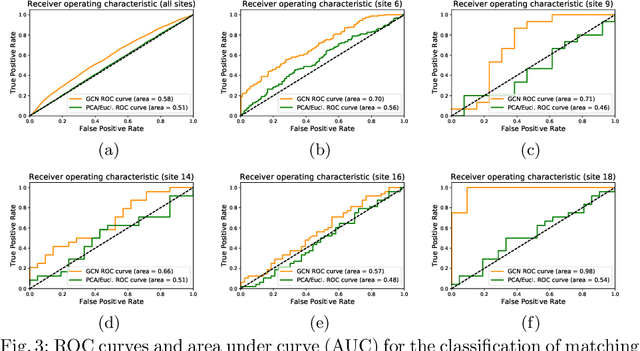
Abstract:Evaluating similarity between graphs is of major importance in several computer vision and pattern recognition problems, where graph representations are often used to model objects or interactions between elements. The choice of a distance or similarity metric is, however, not trivial and can be highly dependent on the application at hand. In this work, we propose a novel metric learning method to evaluate distance between graphs that leverages the power of convolutional neural networks, while exploiting concepts from spectral graph theory to allow these operations on irregular graphs. We demonstrate the potential of our method in the field of connectomics, where neuronal pathways or functional connections between brain regions are commonly modelled as graphs. In this problem, the definition of an appropriate graph similarity function is critical to unveil patterns of disruptions associated with certain brain disorders. Experimental results on the ABIDE dataset show that our method can learn a graph similarity metric tailored for a clinical application, improving the performance of a simple k-nn classifier by 11.9% compared to a traditional distance metric.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge