Nick Pawlowski
Probabilistic Temporal Prediction of Continuous Disease Trajectories and Treatment Effects Using Neural SDEs
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Personalized medicine based on medical images, including predicting future individualized clinical disease progression and treatment response, would have an enormous impact on healthcare and drug development, particularly for diseases (e.g. multiple sclerosis (MS)) with long term, complex, heterogeneous evolutions and no cure. In this work, we present the first stochastic causal temporal framework to model the continuous temporal evolution of disease progression via Neural Stochastic Differential Equations (NSDE). The proposed causal inference model takes as input the patient's high dimensional images (MRI) and tabular data, and predicts both factual and counterfactual progression trajectories on different treatments in latent space. The NSDE permits the estimation of high-confidence personalized trajectories and treatment effects. Extensive experiments were performed on a large, multi-centre, proprietary dataset of patient 3D MRI and clinical data acquired during several randomized clinical trials for MS treatments. Our results present the first successful uncertainty-based causal Deep Learning (DL) model to: (a) accurately predict future patient MS disability evolution (e.g. EDSS) and treatment effects leveraging baseline MRI, and (b) permit the discovery of subgroups of patients for which the model has high confidence in their response to treatment even in clinical trials which did not reach their clinical endpoints.
The Essential Role of Causality in Foundation World Models for Embodied AI
Feb 06, 2024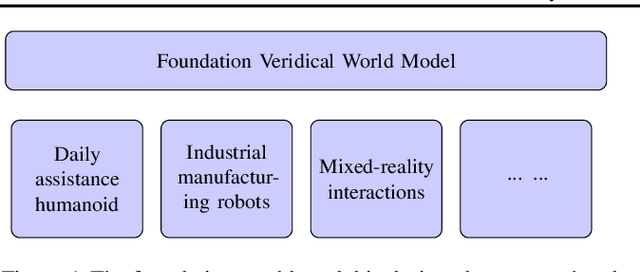
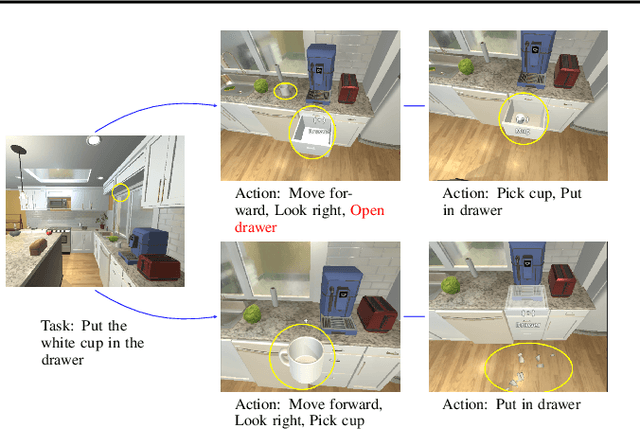
Abstract:Recent advances in foundation models, especially in large multi-modal models and conversational agents, have ignited interest in the potential of generally capable embodied agents. Such agents would require the ability to perform new tasks in many different real-world environments. However, current foundation models fail to accurately model physical interactions with the real world thus not sufficient for Embodied AI. The study of causality lends itself to the construction of veridical world models, which are crucial for accurately predicting the outcomes of possible interactions. This paper focuses on the prospects of building foundation world models for the upcoming generation of embodied agents and presents a novel viewpoint on the significance of causality within these. We posit that integrating causal considerations is vital to facilitate meaningful physical interactions with the world. Finally, we demystify misconceptions about causality in this context and present our outlook for future research.
BayesDAG: Gradient-Based Posterior Sampling for Causal Discovery
Jul 26, 2023Abstract:Bayesian causal discovery aims to infer the posterior distribution over causal models from observed data, quantifying epistemic uncertainty and benefiting downstream tasks. However, computational challenges arise due to joint inference over combinatorial space of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) and nonlinear functions. Despite recent progress towards efficient posterior inference over DAGs, existing methods are either limited to variational inference on node permutation matrices for linear causal models, leading to compromised inference accuracy, or continuous relaxation of adjacency matrices constrained by a DAG regularizer, which cannot ensure resulting graphs are DAGs. In this work, we introduce a scalable Bayesian causal discovery framework based on stochastic gradient Markov Chain Monte Carlo (SG-MCMC) that overcomes these limitations. Our approach directly samples DAGs from the posterior without requiring any DAG regularization, simultaneously draws function parameter samples and is applicable to both linear and nonlinear causal models. To enable our approach, we derive a novel equivalence to the permutation-based DAG learning, which opens up possibilities of using any relaxed gradient estimator defined over permutations. To our knowledge, this is the first framework applying gradient-based MCMC sampling for causal discovery. Empirical evaluations on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate our approach's effectiveness compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
High Fidelity Image Counterfactuals with Probabilistic Causal Models
Jul 18, 2023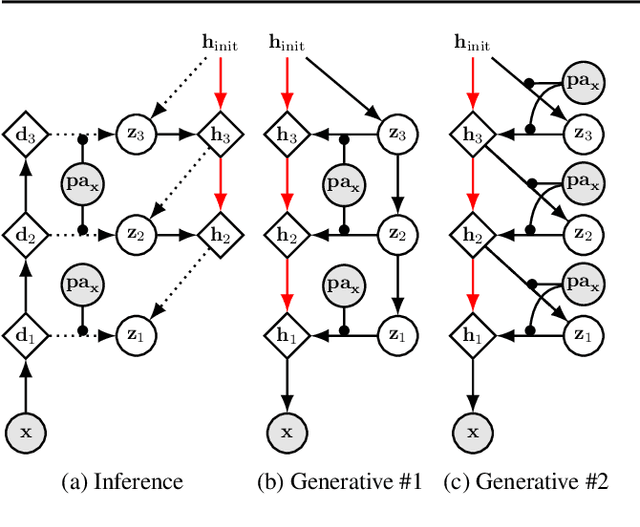
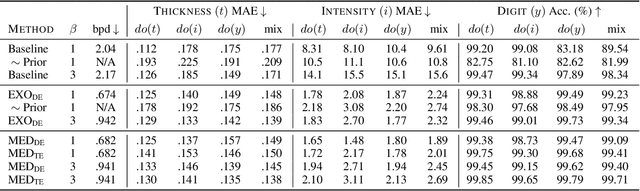
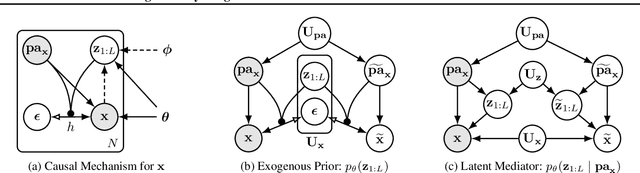
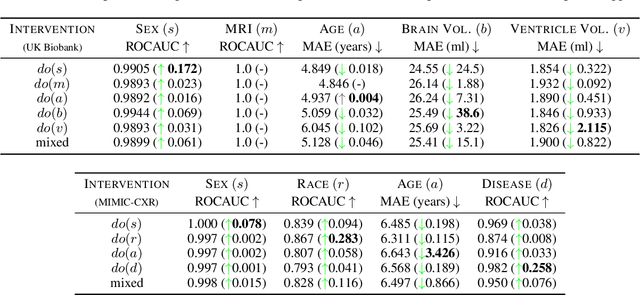
Abstract:We present a general causal generative modelling framework for accurate estimation of high fidelity image counterfactuals with deep structural causal models. Estimation of interventional and counterfactual queries for high-dimensional structured variables, such as images, remains a challenging task. We leverage ideas from causal mediation analysis and advances in generative modelling to design new deep causal mechanisms for structured variables in causal models. Our experiments demonstrate that our proposed mechanisms are capable of accurate abduction and estimation of direct, indirect and total effects as measured by axiomatic soundness of counterfactuals.
Improving Image-Based Precision Medicine with Uncertainty-Aware Causal Models
May 05, 2023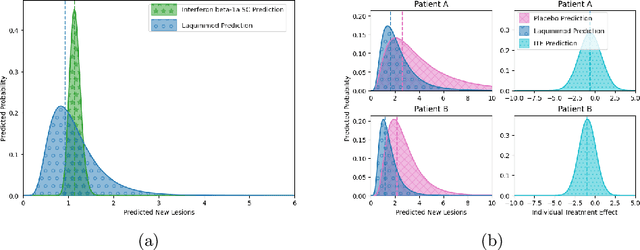
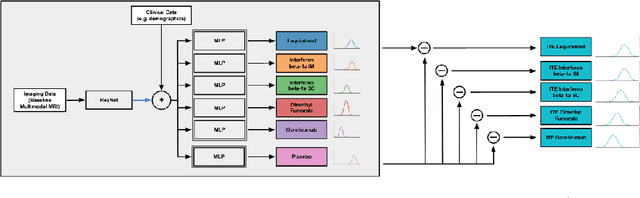
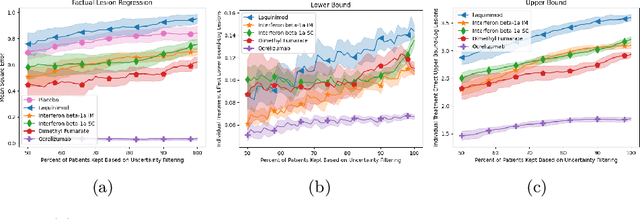
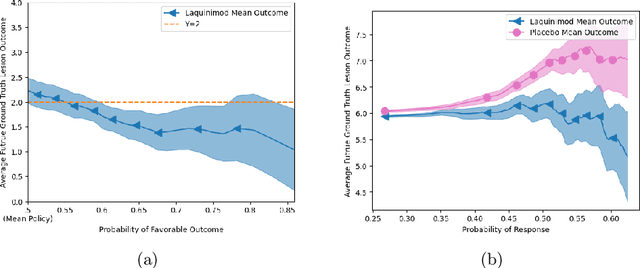
Abstract:Image-based precision medicine aims to personalize treatment decisions based on an individual's unique imaging features so as to improve their clinical outcome. Machine learning frameworks that integrate uncertainty estimation as part of their treatment recommendations would be safer and more reliable. However, little work has been done in adapting uncertainty estimation techniques and validation metrics for precision medicine. In this paper, we use Bayesian deep learning for estimating the posterior distribution over factual and counterfactual outcomes on several treatments. This allows for estimating the uncertainty for each treatment option and for the individual treatment effects (ITE) between any two treatments. We train and evaluate this model to predict future new and enlarging T2 lesion counts on a large, multi-center dataset of MR brain images of patients with multiple sclerosis, exposed to several treatments during randomized controlled trials. We evaluate the correlation of the uncertainty estimate with the factual error, and, given the lack of ground truth counterfactual outcomes, demonstrate how uncertainty for the ITE prediction relates to bounds on the ITE error. Lastly, we demonstrate how knowledge of uncertainty could modify clinical decision-making to improve individual patient and clinical trial outcomes.
Understanding Causality with Large Language Models: Feasibility and Opportunities
Apr 11, 2023
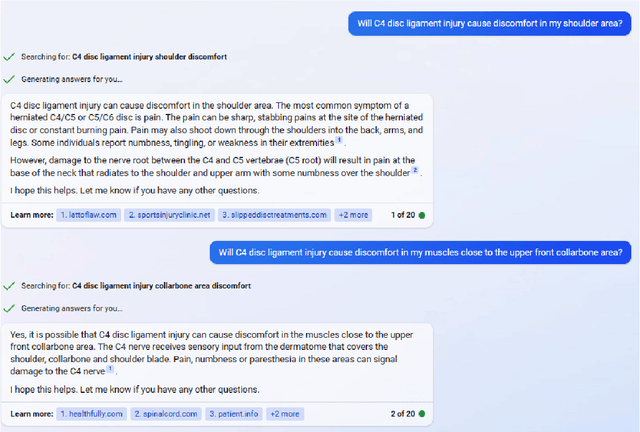
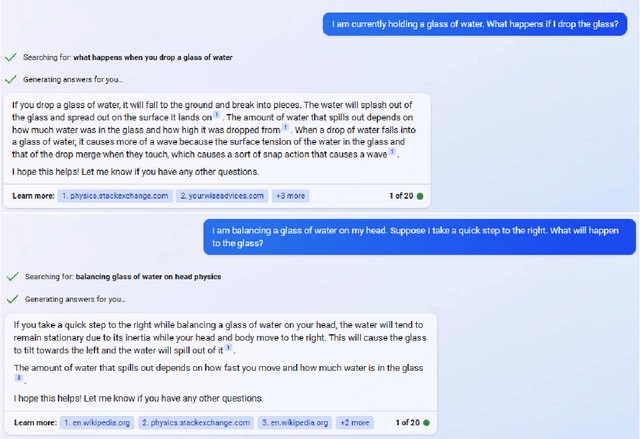
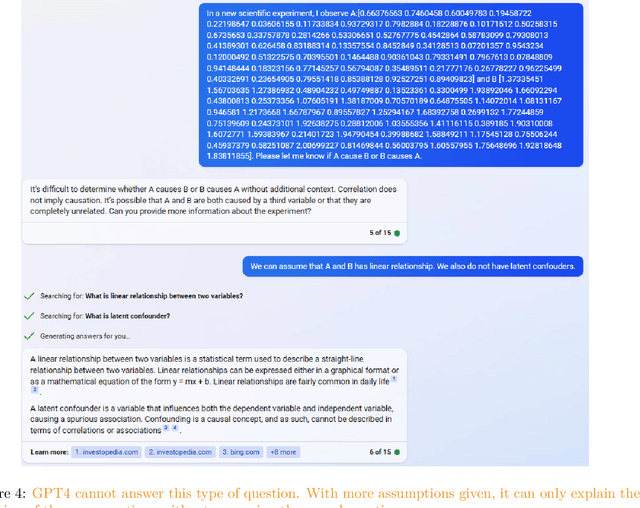
Abstract:We assess the ability of large language models (LLMs) to answer causal questions by analyzing their strengths and weaknesses against three types of causal question. We believe that current LLMs can answer causal questions with existing causal knowledge as combined domain experts. However, they are not yet able to provide satisfactory answers for discovering new knowledge or for high-stakes decision-making tasks with high precision. We discuss possible future directions and opportunities, such as enabling explicit and implicit causal modules as well as deep causal-aware LLMs. These will not only enable LLMs to answer many different types of causal questions for greater impact but also enable LLMs to be more trustworthy and efficient in general.
Measuring axiomatic soundness of counterfactual image models
Mar 02, 2023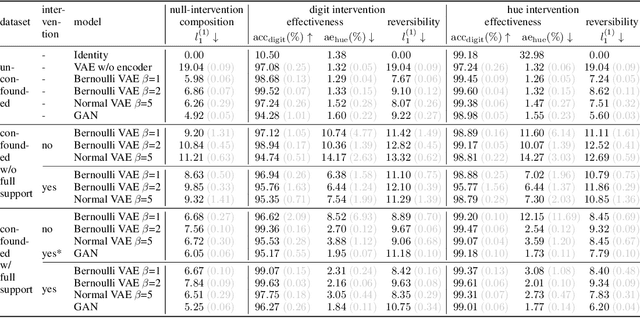
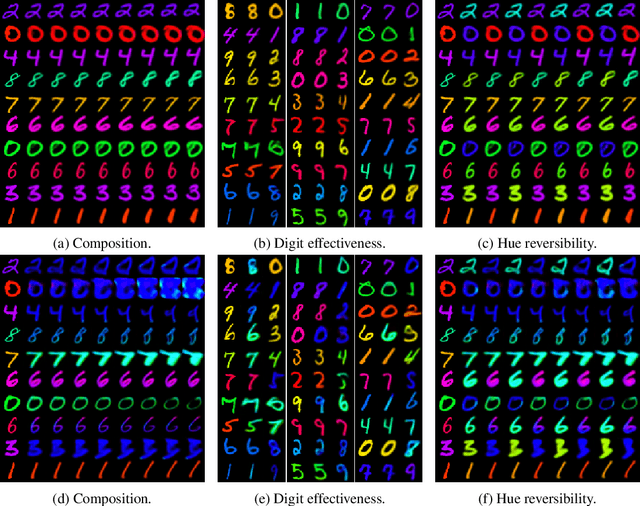
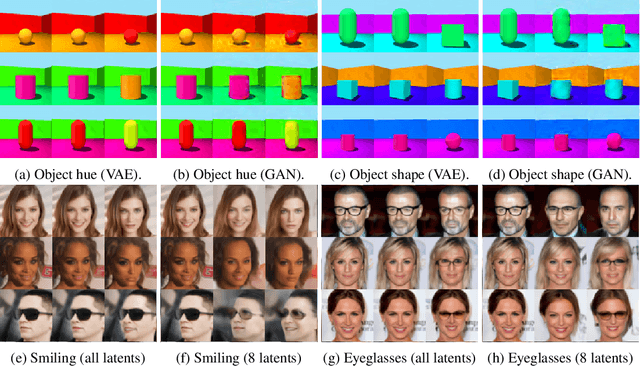
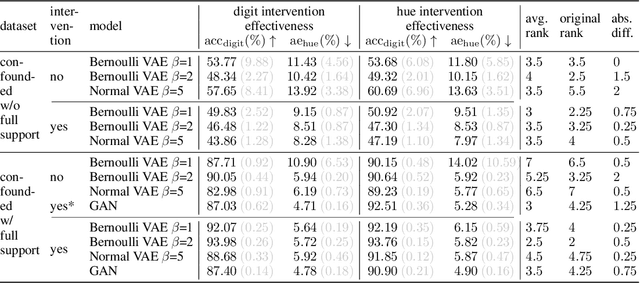
Abstract:We present a general framework for evaluating image counterfactuals. The power and flexibility of deep generative models make them valuable tools for learning mechanisms in structural causal models. However, their flexibility makes counterfactual identifiability impossible in the general case. Motivated by these issues, we revisit Pearl's axiomatic definition of counterfactuals to determine the necessary constraints of any counterfactual inference model: composition, reversibility, and effectiveness. We frame counterfactuals as functions of an input variable, its parents, and counterfactual parents and use the axiomatic constraints to restrict the set of functions that could represent the counterfactual, thus deriving distance metrics between the approximate and ideal functions. We demonstrate how these metrics can be used to compare and choose between different approximate counterfactual inference models and to provide insight into a model's shortcomings and trade-offs.
* Counterfactual inference, Generative Models, Computer Vision, Published in ICLR 2023
Rhino: Deep Causal Temporal Relationship Learning With History-dependent Noise
Oct 26, 2022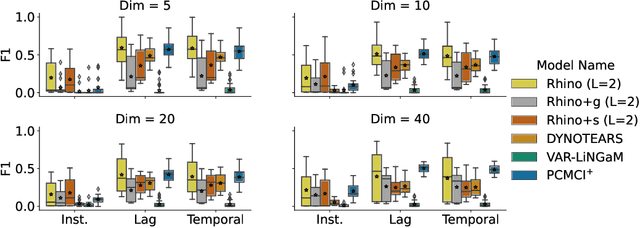

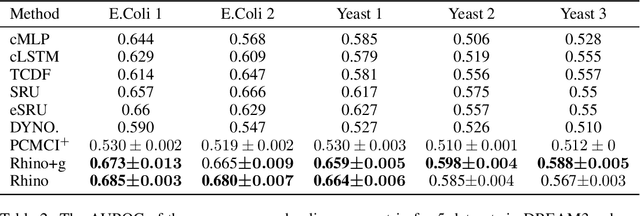
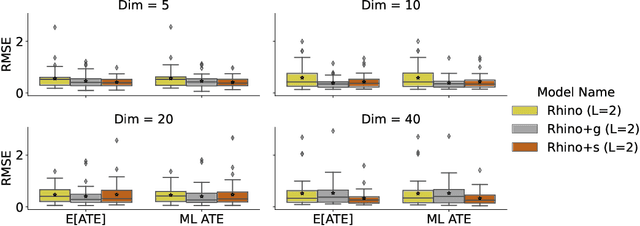
Abstract:Discovering causal relationships between different variables from time series data has been a long-standing challenge for many domains such as climate science, finance, and healthcare. Given the complexity of real-world relationships and the nature of observations in discrete time, causal discovery methods need to consider non-linear relations between variables, instantaneous effects and history-dependent noise (the change of noise distribution due to past actions). However, previous works do not offer a solution addressing all these problems together. In this paper, we propose a novel causal relationship learning framework for time-series data, called Rhino, which combines vector auto-regression, deep learning and variational inference to model non-linear relationships with instantaneous effects while allowing the noise distribution to be modulated by historical observations. Theoretically, we prove the structural identifiability of Rhino. Our empirical results from extensive synthetic experiments and two real-world benchmarks demonstrate better discovery performance compared to relevant baselines, with ablation studies revealing its robustness under model misspecification.
NeurIPS Competition Instructions and Guide: Causal Insights for Learning Paths in Education
Aug 31, 2022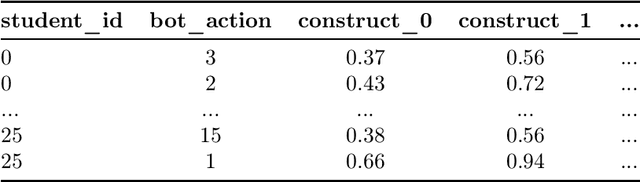
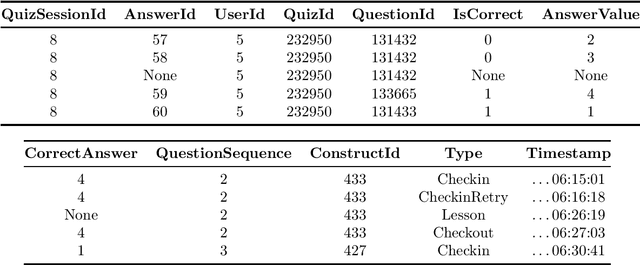
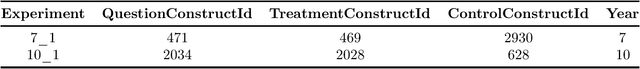
Abstract:In this competition, participants will address two fundamental causal challenges in machine learning in the context of education using time-series data. The first is to identify the causal relationships between different constructs, where a construct is defined as the smallest element of learning. The second challenge is to predict the impact of learning one construct on the ability to answer questions on other constructs. Addressing these challenges will enable optimisation of students' knowledge acquisition, which can be deployed in a real edtech solution impacting millions of students. Participants will run these tasks in an idealised environment with synthetic data and a real-world scenario with evaluation data collected from a series of A/B tests.
Deep Structural Causal Shape Models
Aug 23, 2022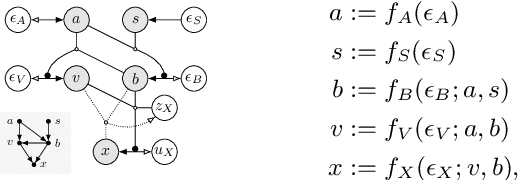

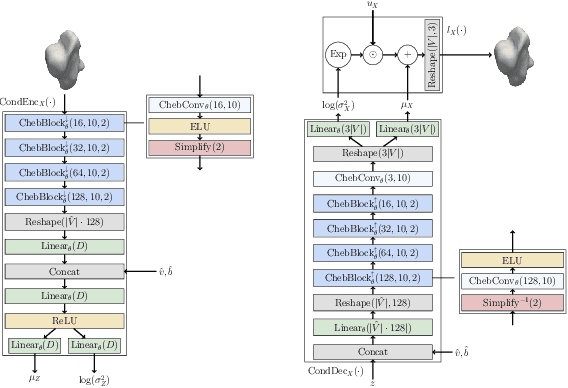

Abstract:Causal reasoning provides a language to ask important interventional and counterfactual questions beyond purely statistical association. In medical imaging, for example, we may want to study the causal effect of genetic, environmental, or lifestyle factors on the normal and pathological variation of anatomical phenotypes. However, while anatomical shape models of 3D surface meshes, extracted from automated image segmentation, can be reliably constructed, there is a lack of computational tooling to enable causal reasoning about morphological variations. To tackle this problem, we propose deep structural causal shape models (CSMs), which utilise high-quality mesh generation techniques, from geometric deep learning, within the expressive framework of deep structural causal models. CSMs enable subject-specific prognoses through counterfactual mesh generation ("How would this patient's brain structure change if they were ten years older?"), which is in contrast to most current works on purely population-level statistical shape modelling. We demonstrate the capabilities of CSMs at all levels of Pearl's causal hierarchy through a number of qualitative and quantitative experiments leveraging a large dataset of 3D brain structures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge