Douglas L. Arnold
Spatio-Temporal Conditional Diffusion Models for Forecasting Future Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Masks Conditioned on Treatments
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Image-based personalized medicine has the potential to transform healthcare, particularly for diseases that exhibit heterogeneous progression such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS). In this work, we introduce the first treatment-aware spatio-temporal diffusion model that is able to generate future masks demonstrating lesion evolution in MS. Our voxel-space approach incorporates multi-modal patient data, including MRI and treatment information, to forecast new and enlarging T2 (NET2) lesion masks at a future time point. Extensive experiments on a multi-centre dataset of 2131 patient 3D MRIs from randomized clinical trials for relapsing-remitting MS demonstrate that our generative model is able to accurately predict NET2 lesion masks for patients across six different treatments. Moreover, we demonstrate our model has the potential for real-world clinical applications through downstream tasks such as future lesion count and location estimation, binary lesion activity classification, and generating counterfactual future NET2 masks for several treatments with different efficacies. This work highlights the potential of causal, image-based generative models as powerful tools for advancing data-driven prognostics in MS.
Probabilistic Temporal Prediction of Continuous Disease Trajectories and Treatment Effects Using Neural SDEs
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Personalized medicine based on medical images, including predicting future individualized clinical disease progression and treatment response, would have an enormous impact on healthcare and drug development, particularly for diseases (e.g. multiple sclerosis (MS)) with long term, complex, heterogeneous evolutions and no cure. In this work, we present the first stochastic causal temporal framework to model the continuous temporal evolution of disease progression via Neural Stochastic Differential Equations (NSDE). The proposed causal inference model takes as input the patient's high dimensional images (MRI) and tabular data, and predicts both factual and counterfactual progression trajectories on different treatments in latent space. The NSDE permits the estimation of high-confidence personalized trajectories and treatment effects. Extensive experiments were performed on a large, multi-centre, proprietary dataset of patient 3D MRI and clinical data acquired during several randomized clinical trials for MS treatments. Our results present the first successful uncertainty-based causal Deep Learning (DL) model to: (a) accurately predict future patient MS disability evolution (e.g. EDSS) and treatment effects leveraging baseline MRI, and (b) permit the discovery of subgroups of patients for which the model has high confidence in their response to treatment even in clinical trials which did not reach their clinical endpoints.
Mitigating Calibration Bias Without Fixed Attribute Grouping for Improved Fairness in Medical Imaging Analysis
Jul 20, 2023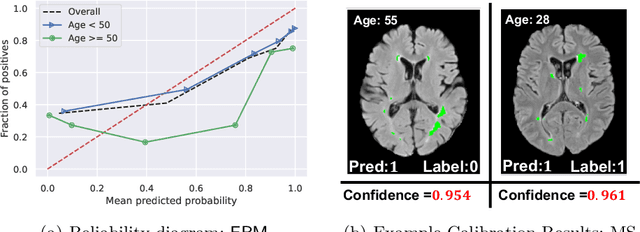
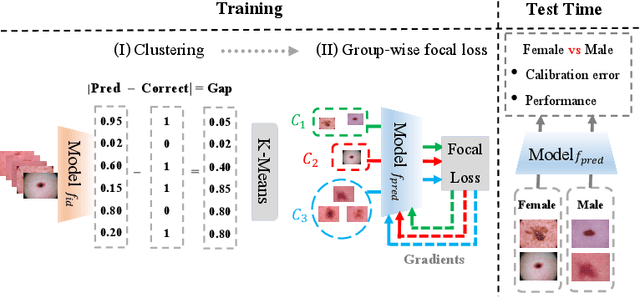

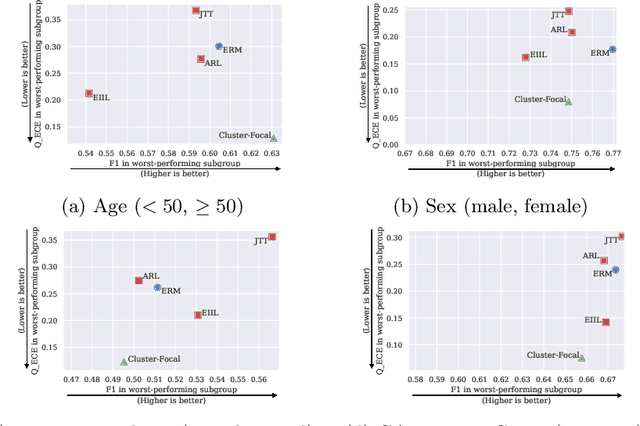
Abstract:Trustworthy deployment of deep learning medical imaging models into real-world clinical practice requires that they be calibrated. However, models that are well calibrated overall can still be poorly calibrated for a sub-population, potentially resulting in a clinician unwittingly making poor decisions for this group based on the recommendations of the model. Although methods have been shown to successfully mitigate biases across subgroups in terms of model accuracy, this work focuses on the open problem of mitigating calibration biases in the context of medical image analysis. Our method does not require subgroup attributes during training, permitting the flexibility to mitigate biases for different choices of sensitive attributes without re-training. To this end, we propose a novel two-stage method: Cluster-Focal to first identify poorly calibrated samples, cluster them into groups, and then introduce group-wise focal loss to improve calibration bias. We evaluate our method on skin lesion classification with the public HAM10000 dataset, and on predicting future lesional activity for multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. In addition to considering traditional sensitive attributes (e.g. age, sex) with demographic subgroups, we also consider biases among groups with different image-derived attributes, such as lesion load, which are required in medical image analysis. Our results demonstrate that our method effectively controls calibration error in the worst-performing subgroups while preserving prediction performance, and outperforming recent baselines.
Improving Image-Based Precision Medicine with Uncertainty-Aware Causal Models
May 05, 2023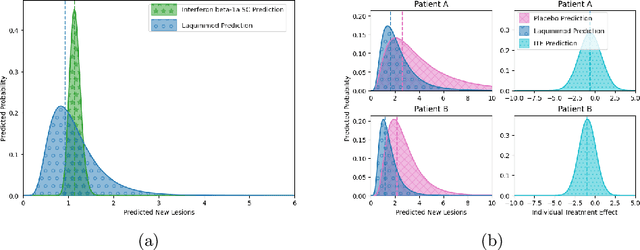
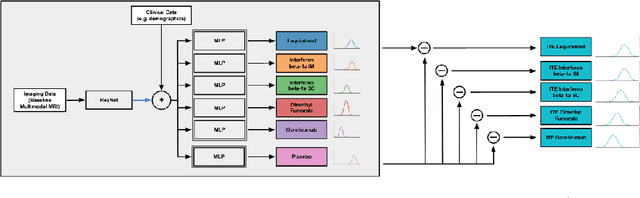
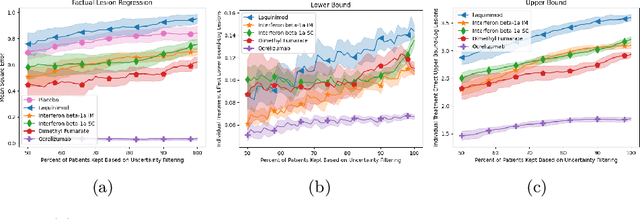
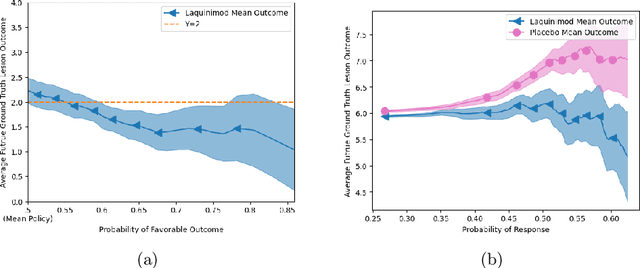
Abstract:Image-based precision medicine aims to personalize treatment decisions based on an individual's unique imaging features so as to improve their clinical outcome. Machine learning frameworks that integrate uncertainty estimation as part of their treatment recommendations would be safer and more reliable. However, little work has been done in adapting uncertainty estimation techniques and validation metrics for precision medicine. In this paper, we use Bayesian deep learning for estimating the posterior distribution over factual and counterfactual outcomes on several treatments. This allows for estimating the uncertainty for each treatment option and for the individual treatment effects (ITE) between any two treatments. We train and evaluate this model to predict future new and enlarging T2 lesion counts on a large, multi-center dataset of MR brain images of patients with multiple sclerosis, exposed to several treatments during randomized controlled trials. We evaluate the correlation of the uncertainty estimate with the factual error, and, given the lack of ground truth counterfactual outcomes, demonstrate how uncertainty for the ITE prediction relates to bounds on the ITE error. Lastly, we demonstrate how knowledge of uncertainty could modify clinical decision-making to improve individual patient and clinical trial outcomes.
Clinically Plausible Pathology-Anatomy Disentanglement in Patient Brain MRI with Structured Variational Priors
Nov 16, 2022


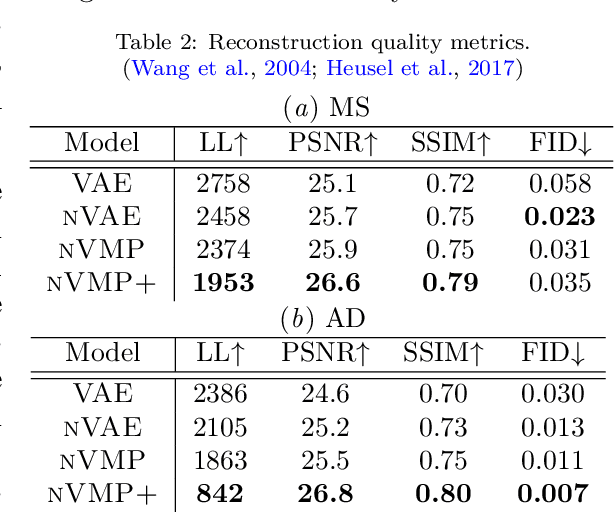
Abstract:We propose a hierarchically structured variational inference model for accurately disentangling observable evidence of disease (e.g. brain lesions or atrophy) from subject-specific anatomy in brain MRIs. With flexible, partially autoregressive priors, our model (1) addresses the subtle and fine-grained dependencies that typically exist between anatomical and pathological generating factors of an MRI to ensure the clinical validity of generated samples; (2) preserves and disentangles finer pathological details pertaining to a patient's disease state. Additionally, we experiment with an alternative training configuration where we provide supervision to a subset of latent units. It is shown that (1) a partially supervised latent space achieves a higher degree of disentanglement between evidence of disease and subject-specific anatomy; (2) when the prior is formulated with an autoregressive structure, knowledge from the supervision can propagate to the unsupervised latent units, resulting in more informative latent representations capable of modelling anatomy-pathology interdependencies.
Rethinking Generalization: The Impact of Annotation Style on Medical Image Segmentation
Oct 31, 2022Abstract:Generalization is an important attribute of machine learning models, particularly for those that are to be deployed in a medical context, where unreliable predictions can have real world consequences. While the failure of models to generalize across datasets is typically attributed to a mismatch in the data distributions, performance gaps are often a consequence of biases in the ``ground-truth" label annotations. This is particularly important in the context of medical image segmentation of pathological structures (e.g. lesions), where the annotation process is much more subjective, and affected by a number underlying factors, including the annotation protocol, rater education/experience, and clinical aims, among others. In this paper, we show that modeling annotation biases, rather than ignoring them, poses a promising way of accounting for differences in annotation style across datasets. To this end, we propose a generalized conditioning framework to (1) learn and account for different annotation styles across multiple datasets using a single model, (2) identify similar annotation styles across different datasets in order to permit their effective aggregation, and (3) fine-tune a fully trained model to a new annotation style with just a few samples. Next, we present an image-conditioning approach to model annotation styles that correlate with specific image features, potentially enabling detection biases to be more easily identified.
Heatmap Regression for Lesion Detection using Pointwise Annotations
Aug 11, 2022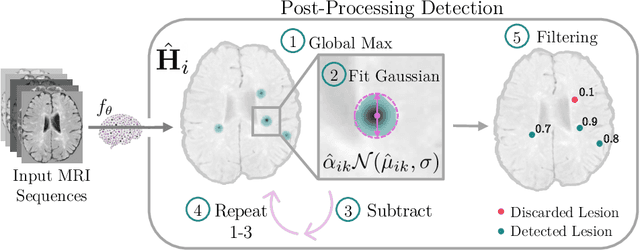

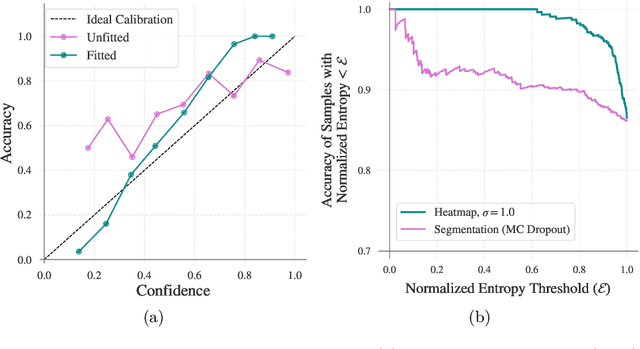
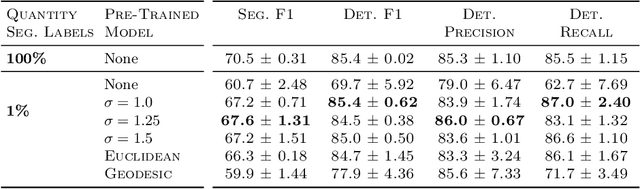
Abstract:In many clinical contexts, detecting all lesions is imperative for evaluating disease activity. Standard approaches pose lesion detection as a segmentation problem despite the time-consuming nature of acquiring segmentation labels. In this paper, we present a lesion detection method which relies only on point labels. Our model, which is trained via heatmap regression, can detect a variable number of lesions in a probabilistic manner. In fact, our proposed post-processing method offers a reliable way of directly estimating the lesion existence uncertainty. Experimental results on Gad lesion detection show our point-based method performs competitively compared to training on expensive segmentation labels. Finally, our detection model provides a suitable pre-training for segmentation. When fine-tuning on only 17 segmentation samples, we achieve comparable performance to training with the full dataset.
Counterfactual Image Synthesis for Discovery of Personalized Predictive Image Markers
Aug 03, 2022



Abstract:The discovery of patient-specific imaging markers that are predictive of future disease outcomes can help us better understand individual-level heterogeneity of disease evolution. In fact, deep learning models that can provide data-driven personalized markers are much more likely to be adopted in medical practice. In this work, we demonstrate that data-driven biomarker discovery can be achieved through a counterfactual synthesis process. We show how a deep conditional generative model can be used to perturb local imaging features in baseline images that are pertinent to subject-specific future disease evolution and result in a counterfactual image that is expected to have a different future outcome. Candidate biomarkers, therefore, result from examining the set of features that are perturbed in this process. Through several experiments on a large-scale, multi-scanner, multi-center multiple sclerosis (MS) clinical trial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) dataset of relapsing-remitting (RRMS) patients, we demonstrate that our model produces counterfactuals with changes in imaging features that reflect established clinical markers predictive of future MRI lesional activity at the population level. Additional qualitative results illustrate that our model has the potential to discover novel and subject-specific predictive markers of future activity.
Personalized Prediction of Future Lesion Activity and Treatment Effect in Multiple Sclerosis from Baseline MRI
Apr 01, 2022



Abstract:Precision medicine for chronic diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS) involves choosing a treatment which best balances efficacy and side effects/preferences for individual patients. Making this choice as early as possible is important, as delays in finding an effective therapy can lead to irreversible disability accrual. To this end, we present the first deep neural network model for individualized treatment decisions from baseline magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (with clinical information if available) for MS patients. Our model (a) predicts future new and enlarging T2 weighted (NE-T2) lesion counts on follow-up MRI on multiple treatments and (b) estimates the conditional average treatment effect (CATE), as defined by the predicted future suppression of NE-T2 lesions, between different treatment options relative to placebo. Our model is validated on a proprietary federated dataset of 1817 multi-sequence MRIs acquired from MS patients during four multi-centre randomized clinical trials. Our framework achieves high average precision in the binarized regression of future NE-T2 lesions on five different treatments, identifies heterogeneous treatment effects, and provides a personalized treatment recommendation that accounts for treatment-associated risk (e.g. side effects, patient preference, administration difficulties).
Cohort Bias Adaptation in Aggregated Datasets for Lesion Segmentation
Aug 02, 2021



Abstract:Many automatic machine learning models developed for focal pathology (e.g. lesions, tumours) detection and segmentation perform well, but do not generalize as well to new patient cohorts, impeding their widespread adoption into real clinical contexts. One strategy to create a more diverse, generalizable training set is to naively pool datasets from different cohorts. Surprisingly, training on this \it{big data} does not necessarily increase, and may even reduce, overall performance and model generalizability, due to the existence of cohort biases that affect label distributions. In this paper, we propose a generalized affine conditioning framework to learn and account for cohort biases across multi-source datasets, which we call Source-Conditioned Instance Normalization (SCIN). Through extensive experimentation on three different, large scale, multi-scanner, multi-centre Multiple Sclerosis (MS) clinical trial MRI datasets, we show that our cohort bias adaptation method (1) improves performance of the network on pooled datasets relative to naively pooling datasets and (2) can quickly adapt to a new cohort by fine-tuning the instance normalization parameters, thus learning the new cohort bias with only 10 labelled samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge