Clinically Plausible Pathology-Anatomy Disentanglement in Patient Brain MRI with Structured Variational Priors
Paper and Code
Nov 16, 2022


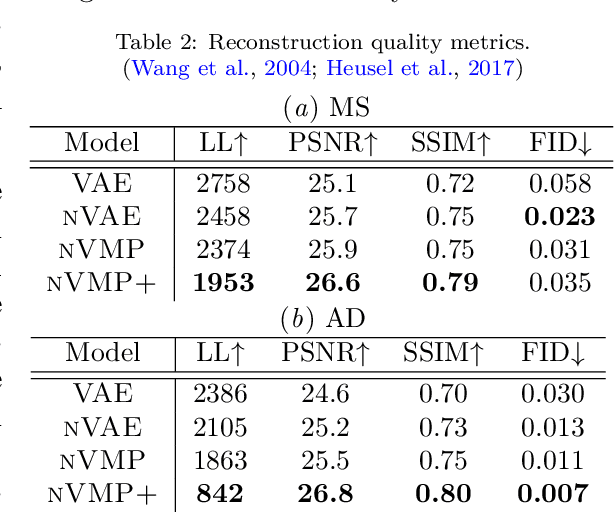
We propose a hierarchically structured variational inference model for accurately disentangling observable evidence of disease (e.g. brain lesions or atrophy) from subject-specific anatomy in brain MRIs. With flexible, partially autoregressive priors, our model (1) addresses the subtle and fine-grained dependencies that typically exist between anatomical and pathological generating factors of an MRI to ensure the clinical validity of generated samples; (2) preserves and disentangles finer pathological details pertaining to a patient's disease state. Additionally, we experiment with an alternative training configuration where we provide supervision to a subset of latent units. It is shown that (1) a partially supervised latent space achieves a higher degree of disentanglement between evidence of disease and subject-specific anatomy; (2) when the prior is formulated with an autoregressive structure, knowledge from the supervision can propagate to the unsupervised latent units, resulting in more informative latent representations capable of modelling anatomy-pathology interdependencies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge