James Housden
Mechanically Powered Motion Imaging Phantoms: Proof of Concept
May 17, 2019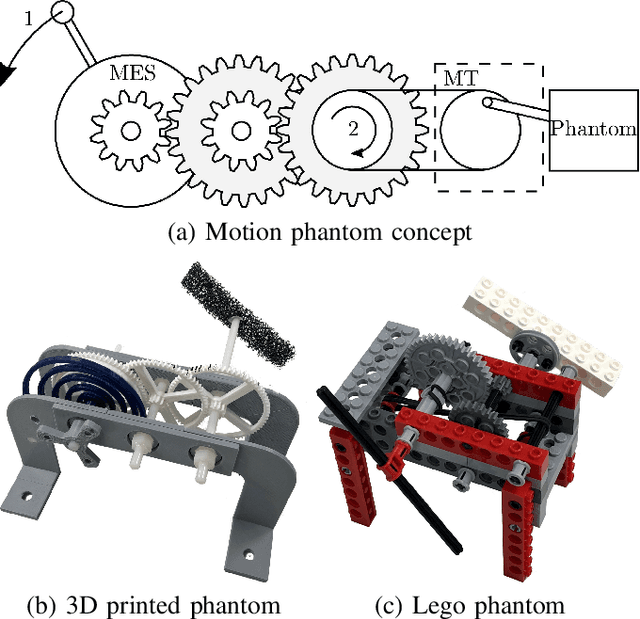
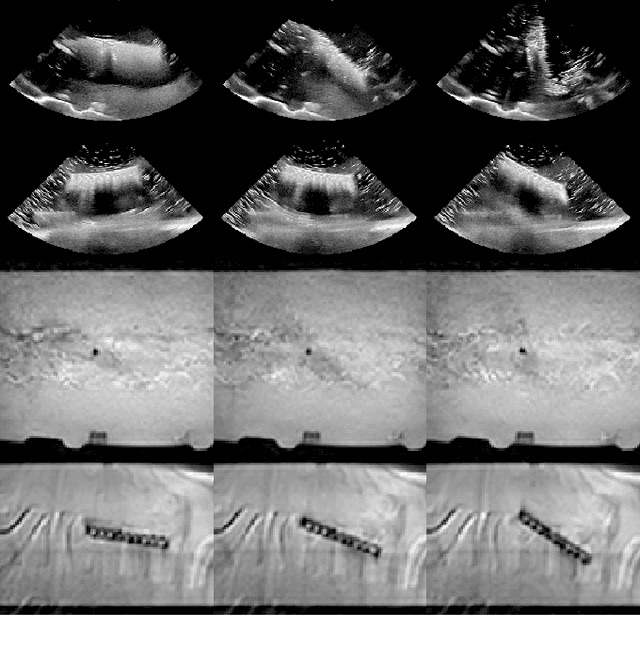
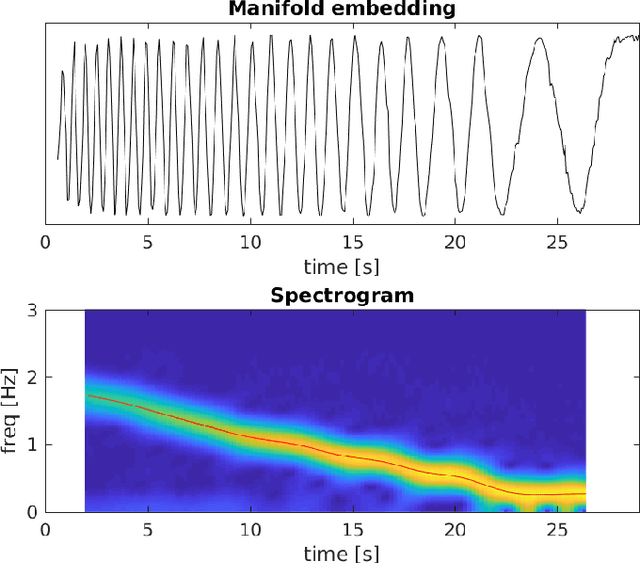
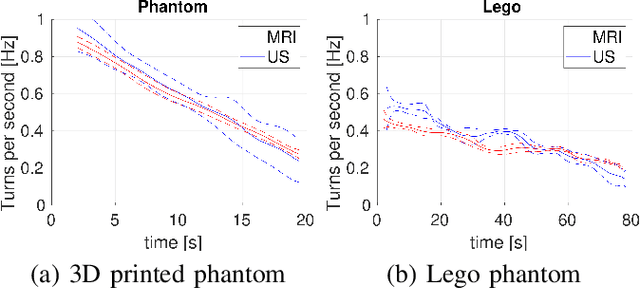
Abstract:Motion imaging phantoms are expensive, bulky and difficult to transport and set-up. The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate a simple approach to the design of multi-modality motion imaging phantoms that use mechanically stored energy to produce motion. We propose two phantom designs that use mainsprings and elastic bands to store energy. A rectangular piece was attached to an axle at the end of the transmission chain of each phantom, and underwent a rotary motion upon release of the mechanical motor. The phantoms were imaged with MRI and US, and the image sequences were embedded in a 1D non linear manifold (Laplacian Eigenmap) and the spectrogram of the embedding was used to derive the angular velocity over time. The derived velocities were consistent and reproducible within a small error. The proposed motion phantom concept showed great potential for the construction of simple and affordable motion phantoms
Robotic-assisted Ultrasound for Fetal Imaging: Evolution from Single-arm to Dual-arm System
Apr 10, 2019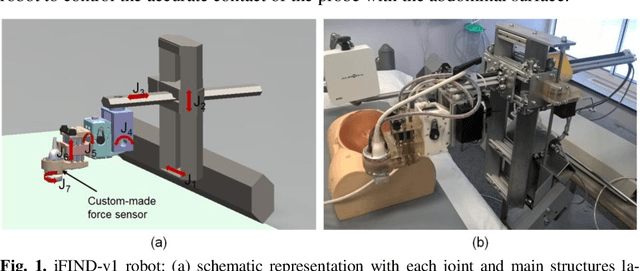
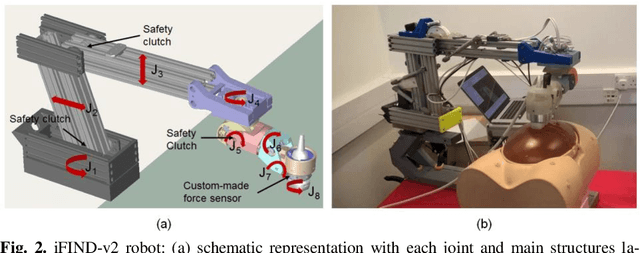
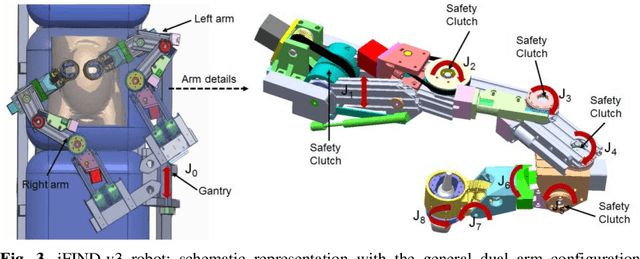
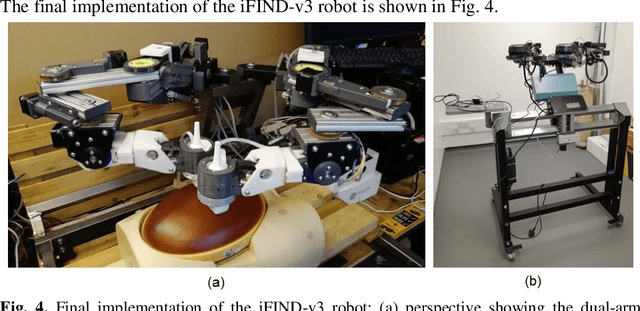
Abstract:The development of robotic-assisted extracorporeal ultrasound systems has a long history and a number of projects have been proposed since the 1990s focusing on different technical aspects. These aim to resolve the deficiencies of on-site manual manipulation of hand-held ultrasound probes. This paper presents the recent ongoing developments of a series of bespoke robotic systems, including both single-arm and dual-arm versions, for a project known as intelligent Fetal Imaging and Diagnosis (iFIND). After a brief review of the development history of the extracorporeal ultrasound robotic system used for fetal and abdominal examinations, the specific aim of the iFIND robots, the design evolution, the implementation details of each version, and the initial clinical feedback of the iFIND robot series are presented. Based on the preliminary testing of these newly-proposed robots on 42 volunteers, the successful and re-liable working of the mechatronic systems were validated. Analysis of a participant questionnaire indicates a comfortable scanning experience for the volunteers and a good acceptance rate to being scanned by the robots.
Weakly Supervised Estimation of Shadow Confidence Maps in Ultrasound Imaging
Nov 21, 2018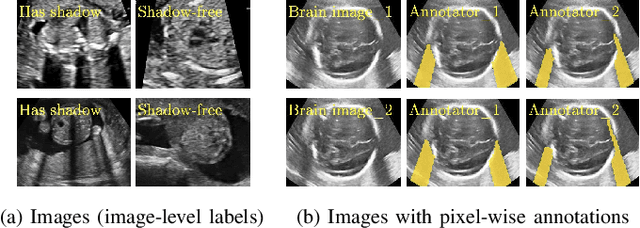

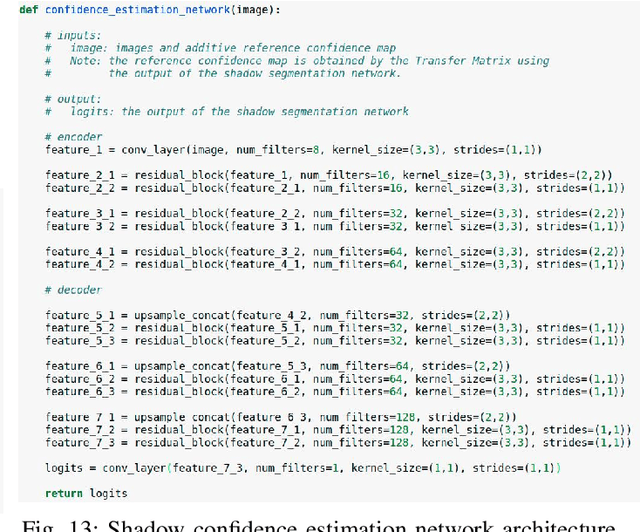
Abstract:Detecting acoustic shadows in ultrasound images is important in many clinical and engineering applications. Real-time feedback of acoustic shadows can guide sonographers to a standardized diagnostic viewing plane with minimal artifacts and can provide additional information for other automatic image analysis algorithms. However, automatically detecting shadow regions is challenging because pixel-wise annotation of acoustic shadows is subjective and time consuming. In this paper we propose a weakly supervised method for automatic confidence estimation of acoustic shadow regions, which is able to generate a dense shadow-focused confidence map. During training, a multi-task module for shadow segmentation is built to learn general shadow features according based image-level annotations as well as a small number of coarse pixel-wise shadow annotations. A transfer function is then established to extend the binary shadow segmentation to a reference confidence map. In addition, a confidence estimation network is proposed to learn the mapping between input images and the reference confidence maps. This confidence estimation network is able to predict shadow confidence maps directly from input images during inference. We evaluate DICE, soft DICE, recall, precision, mean squared error and inter-class correlation to verify the effectiveness of our method. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art qualitatively and quantitatively. We further demonstrate the applicability of our method by integrating shadow confidence maps into tasks such as ultrasound image classification, multi-view image fusion and automated biometric measurements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge