Steven McDonagh
GaussianHeadTalk: Wobble-Free 3D Talking Heads with Audio Driven Gaussian Splatting
Dec 11, 2025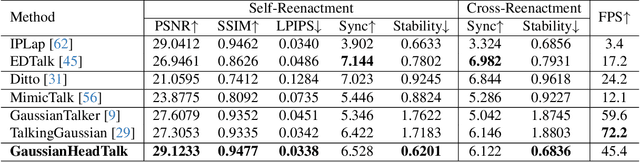
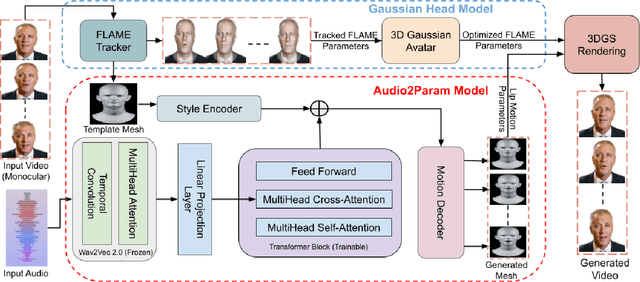
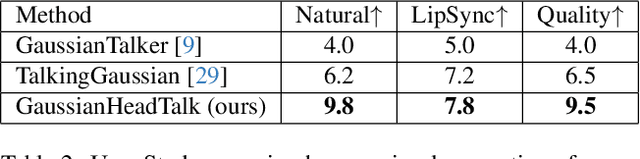
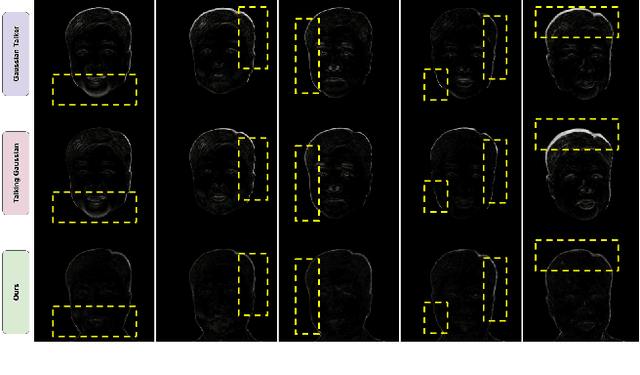
Abstract:Speech-driven talking heads have recently emerged and enable interactive avatars. However, real-world applications are limited, as current methods achieve high visual fidelity but slow or fast yet temporally unstable. Diffusion methods provide realistic image generation, yet struggle with oneshot settings. Gaussian Splatting approaches are real-time, yet inaccuracies in facial tracking, or inconsistent Gaussian mappings, lead to unstable outputs and video artifacts that are detrimental to realistic use cases. We address this problem by mapping Gaussian Splatting using 3D Morphable Models to generate person-specific avatars. We introduce transformer-based prediction of model parameters, directly from audio, to drive temporal consistency. From monocular video and independent audio speech inputs, our method enables generation of real-time talking head videos where we report competitive quantitative and qualitative performance.
SWiFT: Soft-Mask Weight Fine-tuning for Bias Mitigation
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have shown that Machine Learning (ML) models can exhibit bias in real-world scenarios, posing significant challenges in ethically sensitive domains such as healthcare. Such bias can negatively affect model fairness, model generalization abilities and further risks amplifying social discrimination. There is a need to remove biases from trained models. Existing debiasing approaches often necessitate access to original training data and need extensive model retraining; they also typically exhibit trade-offs between model fairness and discriminative performance. To address these challenges, we propose Soft-Mask Weight Fine-Tuning (SWiFT), a debiasing framework that efficiently improves fairness while preserving discriminative performance with much less debiasing costs. Notably, SWiFT requires only a small external dataset and only a few epochs of model fine-tuning. The idea behind SWiFT is to first find the relative, and yet distinct, contributions of model parameters to both bias and predictive performance. Then, a two-step fine-tuning process updates each parameter with different gradient flows defined by its contribution. Extensive experiments with three bias sensitive attributes (gender, skin tone, and age) across four dermatological and two chest X-ray datasets demonstrate that SWiFT can consistently reduce model bias while achieving competitive or even superior diagnostic accuracy under common fairness and accuracy metrics, compared to the state-of-the-art. Specifically, we demonstrate improved model generalization ability as evidenced by superior performance on several out-of-distribution (OOD) datasets.
* Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://melba-journal.org/2025:015
No time to train! Training-Free Reference-Based Instance Segmentation
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:The performance of image segmentation models has historically been constrained by the high cost of collecting large-scale annotated data. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) alleviates this original problem through a promptable, semantics-agnostic, segmentation paradigm and yet still requires manual visual-prompts or complex domain-dependent prompt-generation rules to process a new image. Towards reducing this new burden, our work investigates the task of object segmentation when provided with, alternatively, only a small set of reference images. Our key insight is to leverage strong semantic priors, as learned by foundation models, to identify corresponding regions between a reference and a target image. We find that correspondences enable automatic generation of instance-level segmentation masks for downstream tasks and instantiate our ideas via a multi-stage, training-free method incorporating (1) memory bank construction; (2) representation aggregation and (3) semantic-aware feature matching. Our experiments show significant improvements on segmentation metrics, leading to state-of-the-art performance on COCO FSOD (36.8% nAP), PASCAL VOC Few-Shot (71.2% nAP50) and outperforming existing training-free approaches on the Cross-Domain FSOD benchmark (22.4% nAP).
CheXGenBench: A Unified Benchmark For Fidelity, Privacy and Utility of Synthetic Chest Radiographs
May 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce CheXGenBench, a rigorous and multifaceted evaluation framework for synthetic chest radiograph generation that simultaneously assesses fidelity, privacy risks, and clinical utility across state-of-the-art text-to-image generative models. Despite rapid advancements in generative AI for real-world imagery, medical domain evaluations have been hindered by methodological inconsistencies, outdated architectural comparisons, and disconnected assessment criteria that rarely address the practical clinical value of synthetic samples. CheXGenBench overcomes these limitations through standardised data partitioning and a unified evaluation protocol comprising over 20 quantitative metrics that systematically analyse generation quality, potential privacy vulnerabilities, and downstream clinical applicability across 11 leading text-to-image architectures. Our results reveal critical inefficiencies in the existing evaluation protocols, particularly in assessing generative fidelity, leading to inconsistent and uninformative comparisons. Our framework establishes a standardised benchmark for the medical AI community, enabling objective and reproducible comparisons while facilitating seamless integration of both existing and future generative models. Additionally, we release a high-quality, synthetic dataset, SynthCheX-75K, comprising 75K radiographs generated by the top-performing model (Sana 0.6B) in our benchmark to support further research in this critical domain. Through CheXGenBench, we establish a new state-of-the-art and release our framework, models, and SynthCheX-75K dataset at https://raman1121.github.io/CheXGenBench/
Exploiting Mixture-of-Experts Redundancy Unlocks Multimodal Generative Abilities
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:In this work, we undertake the challenge of augmenting the existing generative capabilities of pre-trained text-only large language models (LLMs) with multi-modal generation capability while satisfying two core constraints: C1 preserving the preservation of original language generative capabilities with negligible performance degradation, and C2 adhering to a small parameter budget to learn the new modality, ensuring scalability and efficiency. In contrast to current approaches that add dedicated modules, thereby significantly increasing the parameter count, we propose a method that leverages the underutilized capacity inherent in deep models. Specifically, we exploit the parameter redundancy within Mixture-of-Experts (MoEs) as a source of additional capacity for learning a new modality, enabling better parameter efficiency (C1). Moreover, we preserve the original language generation capabilities by applying low-rank adaptation exclusively to the tokens of the new modality (C2). Furthermore, we introduce a novel parameter initialization scheme based on the Gromov-Wasserstein distance to improve convergence and training stability. Through an extensive analysis of the routing mechanism, we uncover the emergence of modality-specific pathways and decreased redundancy within the experts that can efficiently unlock multi-modal generative capabilities. Overall, our method can be seamlessly applied to a wide range of contemporary LLMs, providing a new pathway for transitioning from uni-modal to multi-modal architectures.
Mind the Gap: Benchmarking Spatial Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have recently emerged as powerful tools, excelling in tasks that integrate visual and textual comprehension, such as image captioning, visual question answering, and image-text retrieval. However, existing benchmarks for VLMs include spatial components, which often fail to isolate spatial reasoning from related tasks such as object detection or semantic comprehension. In this paper, we address these deficiencies with a multi-faceted approach towards understanding spatial reasoning. Informed by the diverse and multi-dimensional nature of human spatial reasoning abilities, we present a detailed analysis that first delineates the core elements of spatial reasoning: spatial relations, orientation and navigation, mental rotation, and spatial visualization, and then assesses the performance of these models in both synthetic and real-world images, bridging controlled and naturalistic contexts. We analyze 13 state-of-the-art Vision-Language Models, uncovering pivotal insights into their spatial reasoning performance. Our results reveal profound shortcomings in current VLMs, with average accuracy across the 13 models approximating random chance, highlighting spatial reasoning as a persistent obstacle. This work not only exposes the pressing need to advance spatial reasoning within VLMs but also establishes a solid platform for future exploration. Code available on GitHub (https://github.com/stogiannidis/srbench) and dataset available on HuggingFace (https://huggingface.co/datasets/stogiannidis/srbench).
CRCE: Coreference-Retention Concept Erasure in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Text-to-Image diffusion models can produce undesirable content that necessitates concept erasure techniques. However, existing methods struggle with under-erasure, leaving residual traces of targeted concepts, or over-erasure, mistakenly eliminating unrelated but visually similar concepts. To address these limitations, we introduce CRCE, a novel concept erasure framework that leverages Large Language Models to identify both semantically related concepts that should be erased alongside the target and distinct concepts that should be preserved. By explicitly modeling coreferential and retained concepts semantically, CRCE enables more precise concept removal, without unintended erasure. Experiments demonstrate that CRCE outperforms existing methods on diverse erasure tasks.
Unlocking the Potential of Weakly Labeled Data: A Co-Evolutionary Learning Framework for Abnormality Detection and Report Generation
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Anatomical abnormality detection and report generation of chest X-ray (CXR) are two essential tasks in clinical practice. The former aims at localizing and characterizing cardiopulmonary radiological findings in CXRs, while the latter summarizes the findings in a detailed report for further diagnosis and treatment. Existing methods often focused on either task separately, ignoring their correlation. This work proposes a co-evolutionary abnormality detection and report generation (CoE-DG) framework. The framework utilizes both fully labeled (with bounding box annotations and clinical reports) and weakly labeled (with reports only) data to achieve mutual promotion between the abnormality detection and report generation tasks. Specifically, we introduce a bi-directional information interaction strategy with generator-guided information propagation (GIP) and detector-guided information propagation (DIP). For semi-supervised abnormality detection, GIP takes the informative feature extracted by the generator as an auxiliary input to the detector and uses the generator's prediction to refine the detector's pseudo labels. We further propose an intra-image-modal self-adaptive non-maximum suppression module (SA-NMS). This module dynamically rectifies pseudo detection labels generated by the teacher detection model with high-confidence predictions by the student.Inversely, for report generation, DIP takes the abnormalities' categories and locations predicted by the detector as input and guidance for the generator to improve the generated reports.
There is no SAMantics! Exploring SAM as a Backbone for Visual Understanding Tasks
Nov 22, 2024Abstract:The Segment Anything Model (SAM) was originally designed for label-agnostic mask generation. Does this model also possess inherent semantic understanding, of value to broader visual tasks? In this work we follow a multi-staged approach towards exploring this question. We firstly quantify SAM's semantic capabilities by comparing base image encoder efficacy under classification tasks, in comparison with established models (CLIP and DINOv2). Our findings reveal a significant lack of semantic discriminability in SAM feature representations, limiting potential for tasks that require class differentiation. This initial result motivates our exploratory study that attempts to enable semantic information via in-context learning with lightweight fine-tuning where we observe that generalisability to unseen classes remains limited. Our observations culminate in the proposal of a training-free approach that leverages DINOv2 features, towards better endowing SAM with semantic understanding and achieving instance-level class differentiation through feature-based similarity. Our study suggests that incorporation of external semantic sources provides a promising direction for the enhancement of SAM's utility with respect to complex visual tasks that require semantic understanding.
Improving Object Detection via Local-global Contrastive Learning
Oct 07, 2024
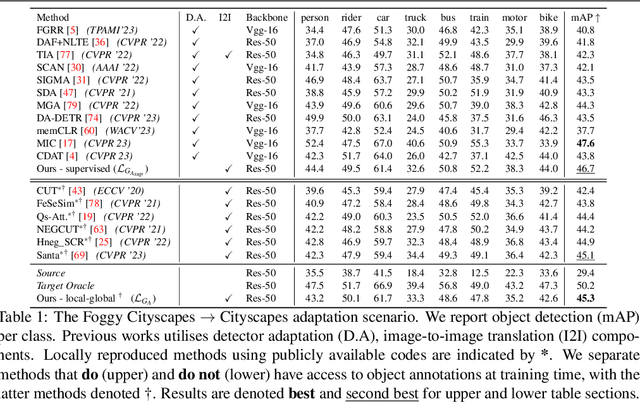
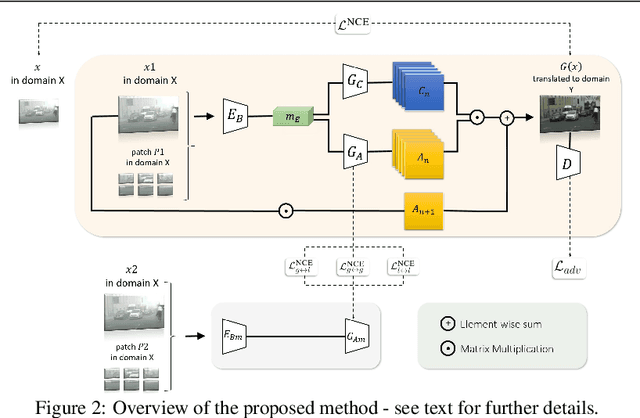
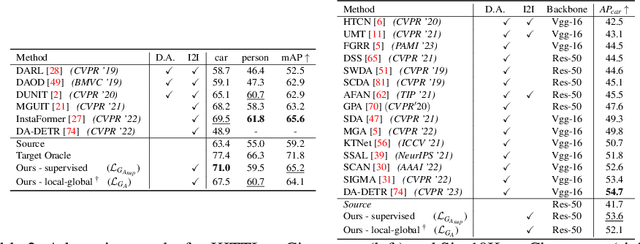
Abstract:Visual domain gaps often impact object detection performance. Image-to-image translation can mitigate this effect, where contrastive approaches enable learning of the image-to-image mapping under unsupervised regimes. However, existing methods often fail to handle content-rich scenes with multiple object instances, which manifests in unsatisfactory detection performance. Sensitivity to such instance-level content is typically only gained through object annotations, which can be expensive to obtain. Towards addressing this issue, we present a novel image-to-image translation method that specifically targets cross-domain object detection. We formulate our approach as a contrastive learning framework with an inductive prior that optimises the appearance of object instances through spatial attention masks, implicitly delineating the scene into foreground regions associated with the target object instances and background non-object regions. Instead of relying on object annotations to explicitly account for object instances during translation, our approach learns to represent objects by contrasting local-global information. This affords investigation of an under-explored challenge: obtaining performant detection, under domain shifts, without relying on object annotations nor detector model fine-tuning. We experiment with multiple cross-domain object detection settings across three challenging benchmarks and report state-of-the-art performance. Project page: https://local-global-detection.github.io
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge