Ilias Stogiannidis
Anatomy-Grounded Weakly Supervised Prompt Tuning for Chest X-ray Latent Diffusion Models
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Latent Diffusion Models have shown remarkable results in text-guided image synthesis in recent years. In the domain of natural (RGB) images, recent works have shown that such models can be adapted to various vision-language downstream tasks with little to no supervision involved. On the contrary, text-to-image Latent Diffusion Models remain relatively underexplored in the field of medical imaging, primarily due to limited data availability (e.g., due to privacy concerns). In this work, focusing on the chest X-ray modality, we first demonstrate that a standard text-conditioned Latent Diffusion Model has not learned to align clinically relevant information in free-text radiology reports with the corresponding areas of the given scan. Then, to alleviate this issue, we propose a fine-tuning framework to improve multi-modal alignment in a pre-trained model such that it can be efficiently repurposed for downstream tasks such as phrase grounding. Our method sets a new state-of-the-art on a standard benchmark dataset (MS-CXR), while also exhibiting robust performance on out-of-distribution data (VinDr-CXR). Our code will be made publicly available.
PhenoAssistant: A Conversational Multi-Agent AI System for Automated Plant Phenotyping
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Plant phenotyping increasingly relies on (semi-)automated image-based analysis workflows to improve its accuracy and scalability. However, many existing solutions remain overly complex, difficult to reimplement and maintain, and pose high barriers for users without substantial computational expertise. To address these challenges, we introduce PhenoAssistant: a pioneering AI-driven system that streamlines plant phenotyping via intuitive natural language interaction. PhenoAssistant leverages a large language model to orchestrate a curated toolkit supporting tasks including automated phenotype extraction, data visualisation and automated model training. We validate PhenoAssistant through several representative case studies and a set of evaluation tasks. By significantly lowering technical hurdles, PhenoAssistant underscores the promise of AI-driven methodologies to democratising AI adoption in plant biology.
Mind the Gap: Benchmarking Spatial Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have recently emerged as powerful tools, excelling in tasks that integrate visual and textual comprehension, such as image captioning, visual question answering, and image-text retrieval. However, existing benchmarks for VLMs include spatial components, which often fail to isolate spatial reasoning from related tasks such as object detection or semantic comprehension. In this paper, we address these deficiencies with a multi-faceted approach towards understanding spatial reasoning. Informed by the diverse and multi-dimensional nature of human spatial reasoning abilities, we present a detailed analysis that first delineates the core elements of spatial reasoning: spatial relations, orientation and navigation, mental rotation, and spatial visualization, and then assesses the performance of these models in both synthetic and real-world images, bridging controlled and naturalistic contexts. We analyze 13 state-of-the-art Vision-Language Models, uncovering pivotal insights into their spatial reasoning performance. Our results reveal profound shortcomings in current VLMs, with average accuracy across the 13 models approximating random chance, highlighting spatial reasoning as a persistent obstacle. This work not only exposes the pressing need to advance spatial reasoning within VLMs but also establishes a solid platform for future exploration. Code available on GitHub (https://github.com/stogiannidis/srbench) and dataset available on HuggingFace (https://huggingface.co/datasets/stogiannidis/srbench).
Making LLMs Worth Every Penny: Resource-Limited Text Classification in Banking
Nov 10, 2023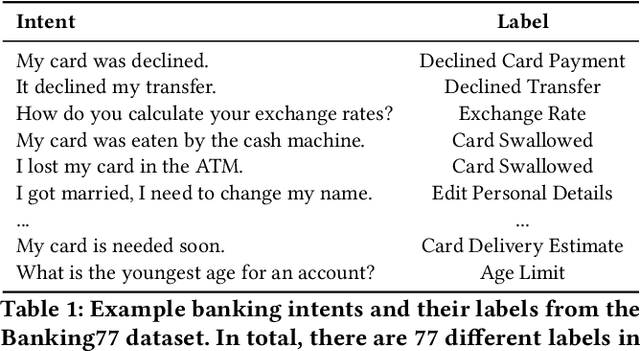
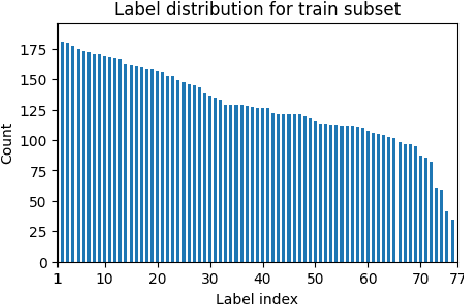
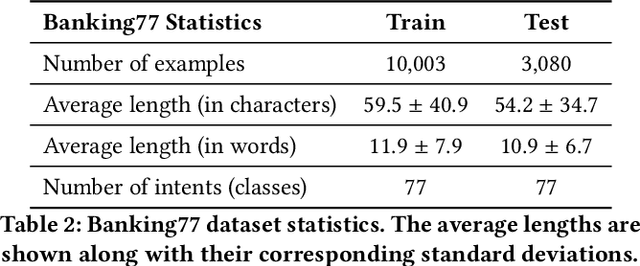

Abstract:Standard Full-Data classifiers in NLP demand thousands of labeled examples, which is impractical in data-limited domains. Few-shot methods offer an alternative, utilizing contrastive learning techniques that can be effective with as little as 20 examples per class. Similarly, Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 can perform effectively with just 1-5 examples per class. However, the performance-cost trade-offs of these methods remain underexplored, a critical concern for budget-limited organizations. Our work addresses this gap by studying the aforementioned approaches over the Banking77 financial intent detection dataset, including the evaluation of cutting-edge LLMs by OpenAI, Cohere, and Anthropic in a comprehensive set of few-shot scenarios. We complete the picture with two additional methods: first, a cost-effective querying method for LLMs based on retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), able to reduce operational costs multiple times compared to classic few-shot approaches, and second, a data augmentation method using GPT-4, able to improve performance in data-limited scenarios. Finally, to inspire future research, we provide a human expert's curated subset of Banking77, along with extensive error analysis.
Cache me if you Can: an Online Cost-aware Teacher-Student framework to Reduce the Calls to Large Language Models
Oct 20, 2023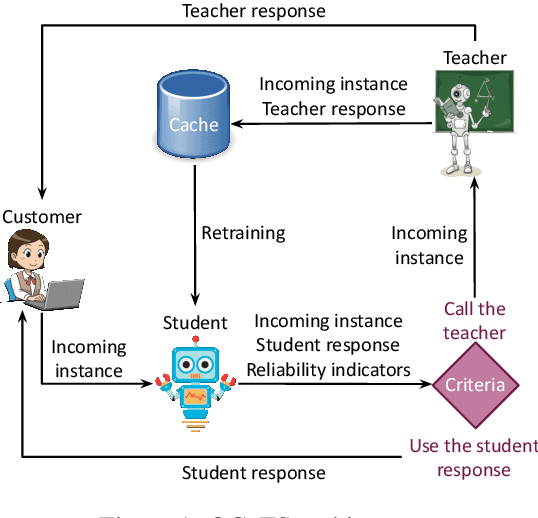
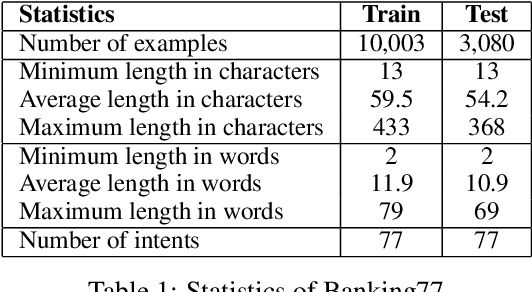
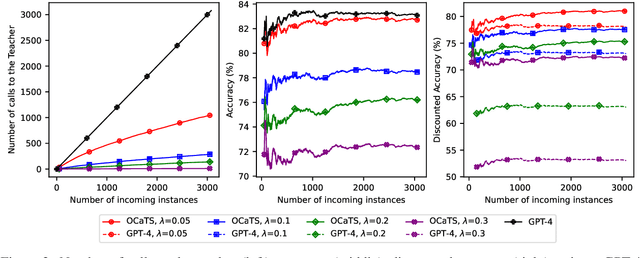
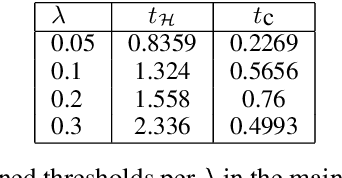
Abstract:Prompting Large Language Models (LLMs) performs impressively in zero- and few-shot settings. Hence, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that cannot afford the cost of creating large task-specific training datasets, but also the cost of pretraining their own LLMs, are increasingly turning to third-party services that allow them to prompt LLMs. However, such services currently require a payment per call, which becomes a significant operating expense (OpEx). Furthermore, customer inputs are often very similar over time, hence SMEs end-up prompting LLMs with very similar instances. We propose a framework that allows reducing the calls to LLMs by caching previous LLM responses and using them to train a local inexpensive model on the SME side. The framework includes criteria for deciding when to trust the local model or call the LLM, and a methodology to tune the criteria and measure the tradeoff between performance and cost. For experimental purposes, we instantiate our framework with two LLMs, GPT-3.5 or GPT-4, and two inexpensive students, a k-NN classifier or a Multi-Layer Perceptron, using two common business tasks, intent recognition and sentiment analysis. Experimental results indicate that significant OpEx savings can be obtained with only slightly lower performance.
Breaking the Bank with ChatGPT: Few-Shot Text Classification for Finance
Aug 28, 2023
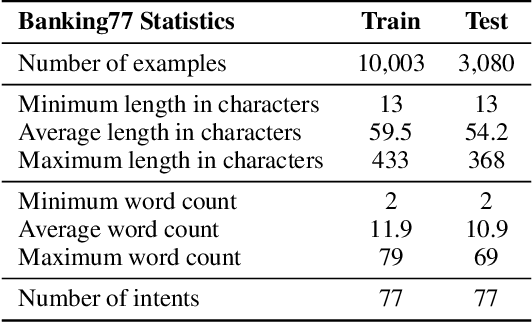

Abstract:We propose the use of conversational GPT models for easy and quick few-shot text classification in the financial domain using the Banking77 dataset. Our approach involves in-context learning with GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, which minimizes the technical expertise required and eliminates the need for expensive GPU computing while yielding quick and accurate results. Additionally, we fine-tune other pre-trained, masked language models with SetFit, a recent contrastive learning technique, to achieve state-of-the-art results both in full-data and few-shot settings. Our findings show that querying GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 can outperform fine-tuned, non-generative models even with fewer examples. However, subscription fees associated with these solutions may be considered costly for small organizations. Lastly, we find that generative models perform better on the given task when shown representative samples selected by a human expert rather than when shown random ones. We conclude that a) our proposed methods offer a practical solution for few-shot tasks in datasets with limited label availability, and b) our state-of-the-art results can inspire future work in the area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge