Paul M. Matthews
Division of Brain Sciences, Dept. of Medicine, Imperial College London, UK Dementia Research Institute, Imperial College London
SegHeD: Segmentation of Heterogeneous Data for Multiple Sclerosis Lesions with Anatomical Constraints
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Assessment of lesions and their longitudinal progression from brain magnetic resonance (MR) images plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring multiple sclerosis (MS). Machine learning models have demonstrated a great potential for automated MS lesion segmentation. Training such models typically requires large-scale high-quality datasets that are consistently annotated. However, MS imaging datasets are often small, segregated across multiple sites, with different formats (cross-sectional or longitudinal), and diverse annotation styles. This poses a significant challenge to train a unified MS lesion segmentation model. To tackle this challenge, we present SegHeD, a novel multi-dataset multi-task segmentation model that can incorporate heterogeneous data as input and perform all-lesion, new-lesion, as well as vanishing-lesion segmentation. Furthermore, we account for domain knowledge about MS lesions, incorporating longitudinal, spatial, and volumetric constraints into the segmentation model. SegHeD is assessed on five MS datasets and achieves a high performance in all, new, and vanishing-lesion segmentation, outperforming several state-of-the-art methods in this field.
A Personalised 3D+t Mesh Generative Model for Unveiling Normal Heart Dynamics
Sep 20, 2024



Abstract:Understanding the structure and motion of the heart is crucial for diagnosing and managing cardiovascular diseases, the leading cause of global death. There is wide variation in cardiac shape and motion patterns, that are influenced by demographic, anthropometric and disease factors. Unravelling the normal patterns of shape and motion, as well as understanding how each individual deviates from the norm, would facilitate accurate diagnosis and personalised treatment strategies. To this end, we developed a novel conditional generative model, MeshHeart, to learn the distribution of cardiac shape and motion patterns. MeshHeart is capable of generating 3D+t cardiac mesh sequences, taking into account clinical factors such as age, sex, weight and height. To model the high-dimensional and complex spatio-temporal mesh data, MeshHeart employs a geometric encoder to represent cardiac meshes in a latent space, followed by a temporal Transformer to model the motion dynamics of latent representations. Based on MeshHeart, we investigate the latent space of 3D+t cardiac mesh sequences and propose a novel distance metric termed latent delta, which quantifies the deviation of a real heart from its personalised normative pattern in the latent space. In experiments using a large dataset of 38,309 subjects, MeshHeart demonstrates a high performance in cardiac mesh sequence reconstruction and generation. Features defined in the latent space are highly discriminative for cardiac disease classification, whereas the latent delta exhibits strong correlation with clinical phenotypes in phenome-wide association studies. The codes and models of this study will be released to benefit further research on digital heart modelling.
LesionMix: A Lesion-Level Data Augmentation Method for Medical Image Segmentation
Aug 17, 2023



Abstract:Data augmentation has become a de facto component of deep learning-based medical image segmentation methods. Most data augmentation techniques used in medical imaging focus on spatial and intensity transformations to improve the diversity of training images. They are often designed at the image level, augmenting the full image, and do not pay attention to specific abnormalities within the image. Here, we present LesionMix, a novel and simple lesion-aware data augmentation method. It performs augmentation at the lesion level, increasing the diversity of lesion shape, location, intensity and load distribution, and allowing both lesion populating and inpainting. Experiments on different modalities and different lesion datasets, including four brain MR lesion datasets and one liver CT lesion dataset, demonstrate that LesionMix achieves promising performance in lesion image segmentation, outperforming several recent Mix-based data augmentation methods. The code will be released at https://github.com/dogabasaran/lesionmix.
Generative Modelling of the Ageing Heart with Cross-Sectional Imaging and Clinical Data
Aug 28, 2022


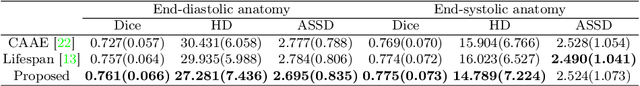
Abstract:Cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death globally, is an age-related disease. Understanding the morphological and functional changes of the heart during ageing is a key scientific question, the answer to which will help us define important risk factors of cardiovascular disease and monitor disease progression. In this work, we propose a novel conditional generative model to describe the changes of 3D anatomy of the heart during ageing. The proposed model is flexible and allows integration of multiple clinical factors (e.g. age, gender) into the generating process. We train the model on a large-scale cross-sectional dataset of cardiac anatomies and evaluate on both cross-sectional and longitudinal datasets. The model demonstrates excellent performance in predicting the longitudinal evolution of the ageing heart and modelling its data distribution.
Subject-Specific Lesion Generation and Pseudo-Healthy Synthesis for Multiple Sclerosis Brain Images
Aug 03, 2022



Abstract:Understanding the intensity characteristics of brain lesions is key for defining image-based biomarkers in neurological studies and for predicting disease burden and outcome. In this work, we present a novel foreground-based generative method for modelling the local lesion characteristics that can both generate synthetic lesions on healthy images and synthesize subject-specific pseudo-healthy images from pathological images. Furthermore, the proposed method can be used as a data augmentation module to generate synthetic images for training brain image segmentation networks. Experiments on multiple sclerosis (MS) brain images acquired on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrate that the proposed method can generate highly realistic pseudo-healthy and pseudo-pathological brain images. Data augmentation using the synthetic images improves the brain image segmentation performance compared to traditional data augmentation methods as well as a recent lesion-aware data augmentation technique, CarveMix. The code will be released at https://github.com/dogabasaran/lesion-synthesis.
Self-Supervised Learning for Cardiac MR Image Segmentation by Anatomical Position Prediction
Jul 05, 2019



Abstract:In the recent years, convolutional neural networks have transformed the field of medical image analysis due to their capacity to learn discriminative image features for a variety of classification and regression tasks. However, successfully learning these features requires a large amount of manually annotated data, which is expensive to acquire and limited by the available resources of expert image analysts. Therefore, unsupervised, weakly-supervised and self-supervised feature learning techniques receive a lot of attention, which aim to utilise the vast amount of available data, while at the same time avoid or substantially reduce the effort of manual annotation. In this paper, we propose a novel way for training a cardiac MR image segmentation network, in which features are learnt in a self-supervised manner by predicting anatomical positions. The anatomical positions serve as a supervisory signal and do not require extra manual annotation. We demonstrate that this seemingly simple task provides a strong signal for feature learning and with self-supervised learning, we achieve a high segmentation accuracy that is better than or comparable to a U-net trained from scratch, especially at a small data setting. When only five annotated subjects are available, the proposed method improves the mean Dice metric from 0.811 to 0.852 for short-axis image segmentation, compared to the baseline U-net.
Automated Quality Control in Image Segmentation: Application to the UK Biobank Cardiac MR Imaging Study
Jan 27, 2019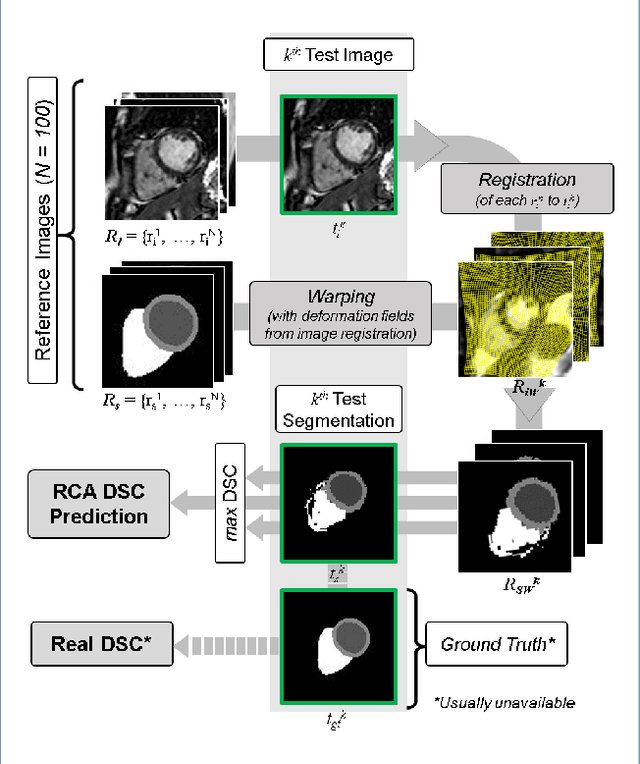
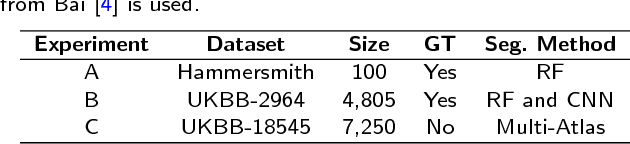
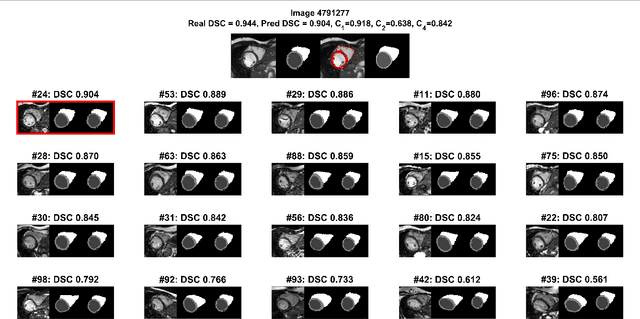
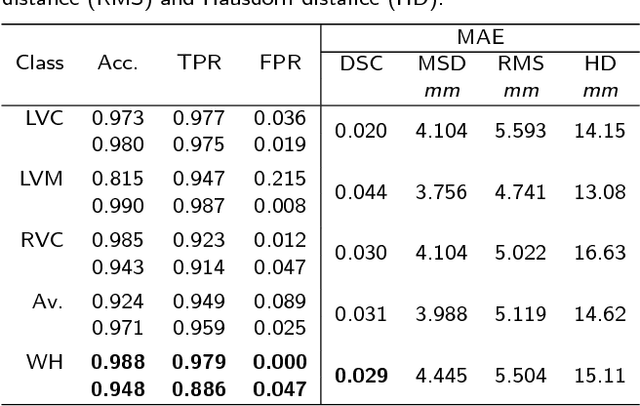
Abstract:Background: The trend towards large-scale studies including population imaging poses new challenges in terms of quality control (QC). This is a particular issue when automatic processing tools, e.g. image segmentation methods, are employed to derive quantitative measures or biomarkers for later analyses. Manual inspection and visual QC of each segmentation isn't feasible at large scale. However, it's important to be able to automatically detect when a segmentation method fails so as to avoid inclusion of wrong measurements into subsequent analyses which could lead to incorrect conclusions. Methods: To overcome this challenge, we explore an approach for predicting segmentation quality based on Reverse Classification Accuracy, which enables us to discriminate between successful and failed segmentations on a per-cases basis. We validate this approach on a new, large-scale manually-annotated set of 4,800 cardiac magnetic resonance scans. We then apply our method to a large cohort of 7,250 cardiac MRI on which we have performed manual QC. Results: We report results used for predicting segmentation quality metrics including Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and surface-distance measures. As initial validation, we present data for 400 scans demonstrating 99% accuracy for classifying low and high quality segmentations using predicted DSC scores. As further validation we show high correlation between real and predicted scores and 95% classification accuracy on 4,800 scans for which manual segmentations were available. We mimic real-world application of the method on 7,250 cardiac MRI where we show good agreement between predicted quality metrics and manual visual QC scores. Conclusions: We show that RCA has the potential for accurate and fully automatic segmentation QC on a per-case basis in the context of large-scale population imaging as in the UK Biobank Imaging Study.
Learning-Based Quality Control for Cardiac MR Images
Sep 15, 2018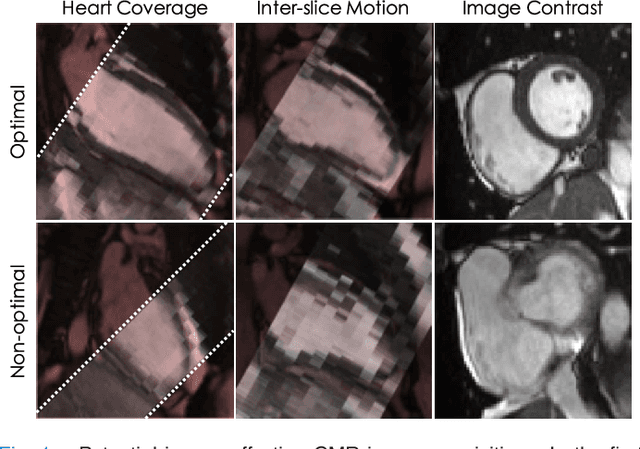
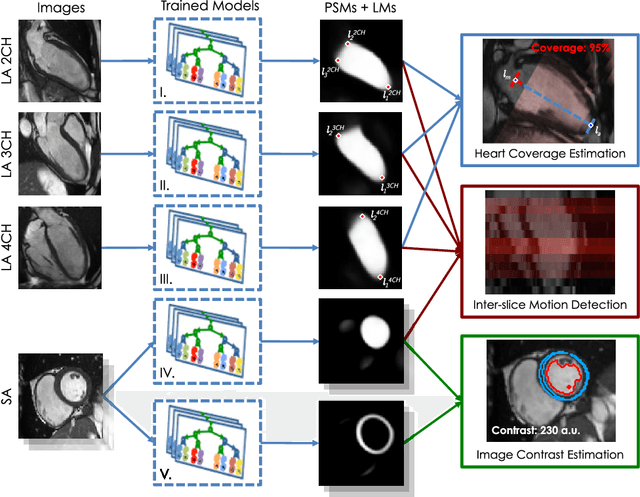
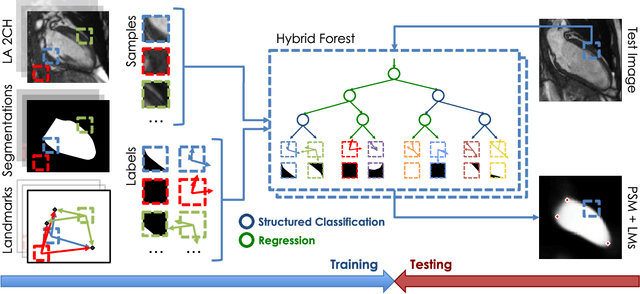
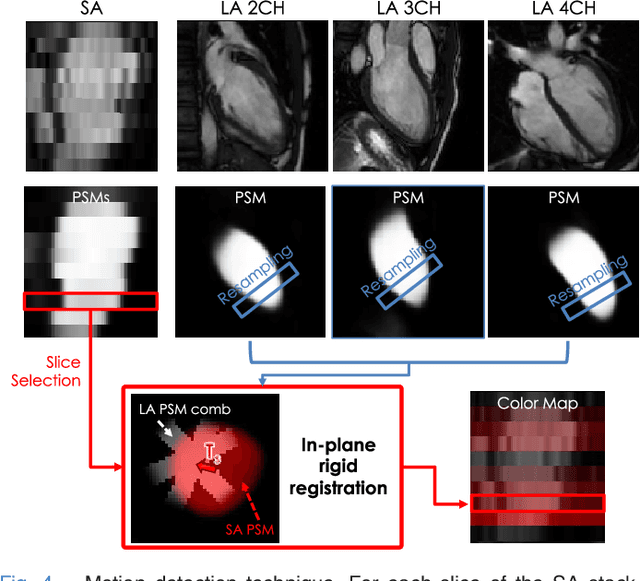
Abstract:The effectiveness of a cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) scan depends on the ability of the operator to correctly tune the acquisition parameters to the subject being scanned and on the potential occurrence of imaging artefacts such as cardiac and respiratory motion. In the clinical practice, a quality control step is performed by visual assessment of the acquired images: however, this procedure is strongly operator-dependent, cumbersome and sometimes incompatible with the time constraints in clinical settings and large-scale studies. We propose a fast, fully-automated, learning-based quality control pipeline for CMR images, specifically for short-axis image stacks. Our pipeline performs three important quality checks: 1) heart coverage estimation, 2) inter-slice motion detection, 3) image contrast estimation in the cardiac region. The pipeline uses a hybrid decision forest method - integrating both regression and structured classification models - to extract landmarks as well as probabilistic segmentation maps from both long- and short-axis images as a basis to perform the quality checks. The technique was tested on up to 3000 cases from the UK Biobank as well as on 100 cases from the UK Digital Heart Project, and validated against manual annotations and visual inspections performed by expert interpreters. The results show the capability of the proposed pipeline to correctly detect incomplete or corrupted scans (e.g. on UK Biobank, sensitivity and specificity respectively 88% and 99% for heart coverage estimation, 85% and 95% for motion detection), allowing their exclusion from the analysed dataset or the triggering of a new acquisition.
Recurrent neural networks for aortic image sequence segmentation with sparse annotations
Aug 01, 2018



Abstract:Segmentation of image sequences is an important task in medical image analysis, which enables clinicians to assess the anatomy and function of moving organs. However, direct application of a segmentation algorithm to each time frame of a sequence may ignore the temporal continuity inherent in the sequence. In this work, we propose an image sequence segmentation algorithm by combining a fully convolutional network with a recurrent neural network, which incorporates both spatial and temporal information into the segmentation task. A key challenge in training this network is that the available manual annotations are temporally sparse, which forbids end-to-end training. We address this challenge by performing non-rigid label propagation on the annotations and introducing an exponentially weighted loss function for training. Experiments on aortic MR image sequences demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves both accuracy and temporal smoothness of segmentation, compared to a baseline method that utilises spatial information only. It achieves an average Dice metric of 0.960 for the ascending aorta and 0.953 for the descending aorta.
NeuroNet: Fast and Robust Reproduction of Multiple Brain Image Segmentation Pipelines
Jun 11, 2018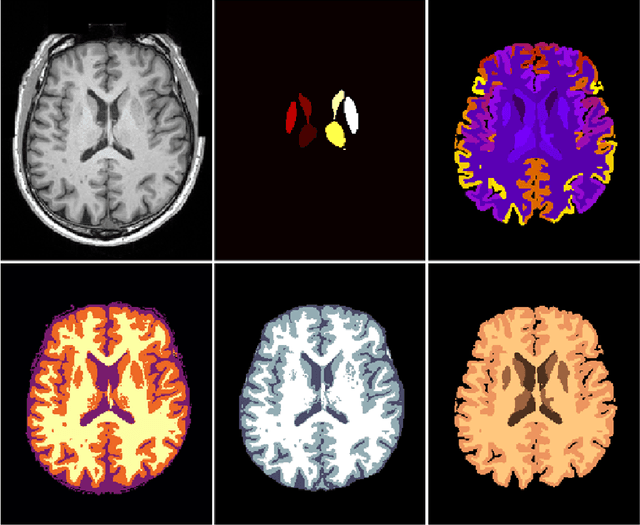
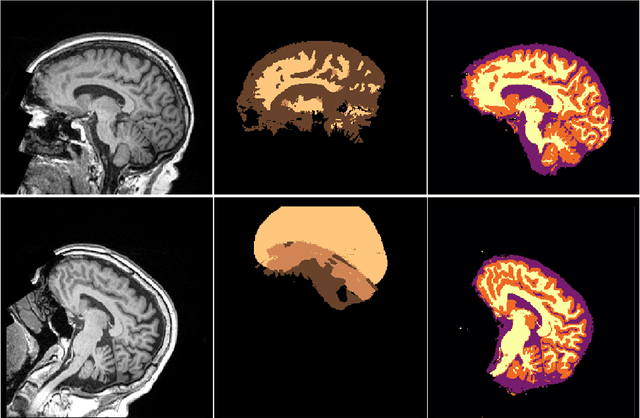
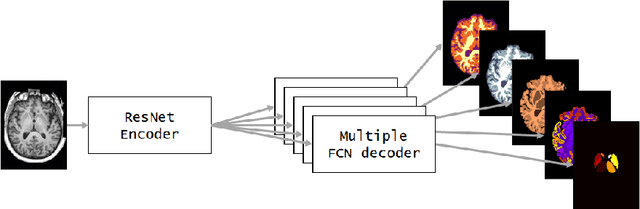
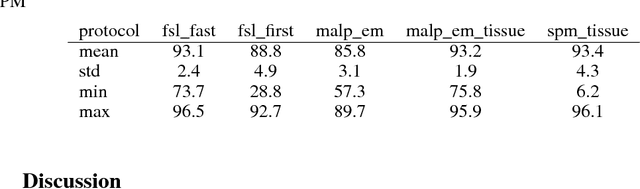
Abstract:NeuroNet is a deep convolutional neural network mimicking multiple popular and state-of-the-art brain segmentation tools including FSL, SPM, and MALPEM. The network is trained on 5,000 T1-weighted brain MRI scans from the UK Biobank Imaging Study that have been automatically segmented into brain tissue and cortical and sub-cortical structures using the standard neuroimaging pipelines. Training a single model from these complementary and partially overlapping label maps yields a new powerful "all-in-one", multi-output segmentation tool. The processing time for a single subject is reduced by an order of magnitude compared to running each individual software package. We demonstrate very good reproducibility of the original outputs while increasing robustness to variations in the input data. We believe NeuroNet could be an important tool in large-scale population imaging studies and serve as a new standard in neuroscience by reducing the risk of introducing bias when choosing a specific software package.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge