Louis Castricato
Results of the NeurIPS 2023 Neural MMO Competition on Multi-task Reinforcement Learning
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:We present the results of the NeurIPS 2023 Neural MMO Competition, which attracted over 200 participants and submissions. Participants trained goal-conditional policies that generalize to tasks, maps, and opponents never seen during training. The top solution achieved a score 4x higher than our baseline within 8 hours of training on a single 4090 GPU. We open-source everything relating to Neural MMO and the competition under the MIT license, including the policy weights and training code for our baseline and for the top submissions.
Big-Math: A Large-Scale, High-Quality Math Dataset for Reinforcement Learning in Language Models
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Increasing interest in reasoning models has led math to become a prominent testing ground for algorithmic and methodological improvements. However, existing open math datasets either contain a small collection of high-quality, human-written problems or a large corpus of machine-generated problems of uncertain quality, forcing researchers to choose between quality and quantity. In this work, we present Big-Math, a dataset of over 250,000 high-quality math questions with verifiable answers, purposefully made for reinforcement learning (RL). To create Big-Math, we rigorously filter, clean, and curate openly available datasets, extracting questions that satisfy our three desiderata: (1) problems with uniquely verifiable solutions, (2) problems that are open-ended, (3) and problems with a closed-form solution. To ensure the quality of Big-Math, we manually verify each step in our filtering process. Based on the findings from our filtering process, we introduce 47,000 new questions with verified answers, Big-Math-Reformulated: closed-ended questions (i.e. multiple choice questions) that have been reformulated as open-ended questions through a systematic reformulation algorithm. Compared to the most commonly used existing open-source datasets for math reasoning, GSM8k and MATH, Big-Math is an order of magnitude larger, while our rigorous filtering ensures that we maintain the questions most suitable for RL. We also provide a rigorous analysis of the dataset, finding that Big-Math contains a high degree of diversity across problem domains, and incorporates a wide range of problem difficulties, enabling a wide range of downstream uses for models of varying capabilities and training requirements. By bridging the gap between data quality and quantity, Big-Math establish a robust foundation for advancing reasoning in LLMs.
Towards System 2 Reasoning in LLMs: Learning How to Think With Meta Chain-of-Thought
Jan 08, 2025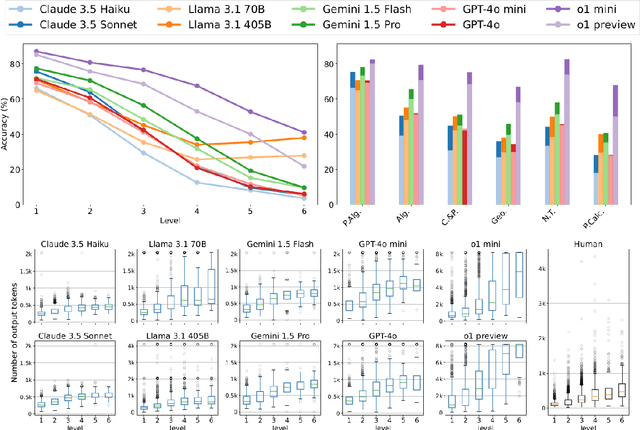
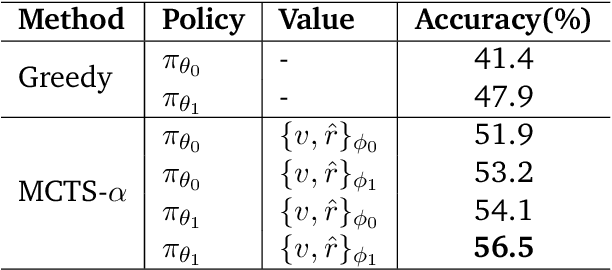
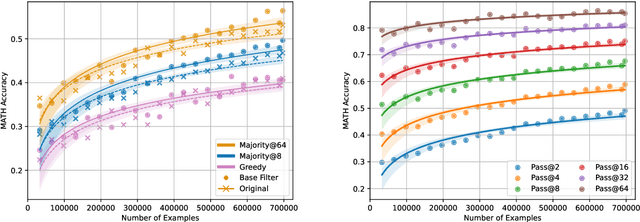
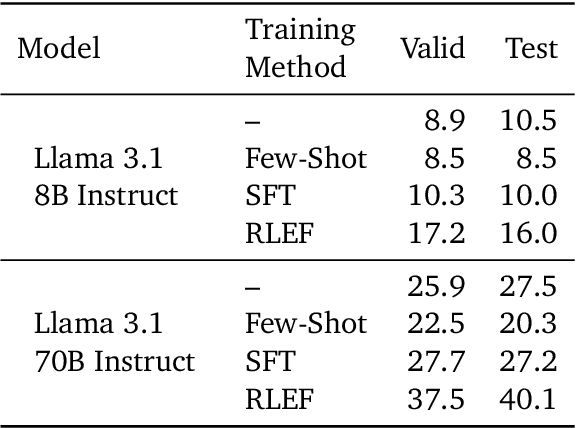
Abstract:We propose a novel framework, Meta Chain-of-Thought (Meta-CoT), which extends traditional Chain-of-Thought (CoT) by explicitly modeling the underlying reasoning required to arrive at a particular CoT. We present empirical evidence from state-of-the-art models exhibiting behaviors consistent with in-context search, and explore methods for producing Meta-CoT via process supervision, synthetic data generation, and search algorithms. Finally, we outline a concrete pipeline for training a model to produce Meta-CoTs, incorporating instruction tuning with linearized search traces and reinforcement learning post-training. Finally, we discuss open research questions, including scaling laws, verifier roles, and the potential for discovering novel reasoning algorithms. This work provides a theoretical and practical roadmap to enable Meta-CoT in LLMs, paving the way for more powerful and human-like reasoning in artificial intelligence.
Self-Directed Synthetic Dialogues and Revisions Technical Report
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:Synthetic data has become an important tool in the fine-tuning of language models to follow instructions and solve complex problems. Nevertheless, the majority of open data to date is often lacking multi-turn data and collected on closed models, limiting progress on advancing open fine-tuning methods. We introduce Self Directed Synthetic Dialogues (SDSD), an experimental dataset consisting of guided conversations of language models talking to themselves. The dataset consists of multi-turn conversations generated with DBRX, Llama 2 70B, and Mistral Large, all instructed to follow a conversation plan generated prior to the conversation. We also explore including principles from Constitutional AI and other related works to create synthetic preference data via revisions to the final conversation turn. We hope this work encourages further exploration in multi-turn data and the use of open models for expanding the impact of synthetic data.
PERSONA: A Reproducible Testbed for Pluralistic Alignment
Jul 24, 2024Abstract:The rapid advancement of language models (LMs) necessitates robust alignment with diverse user values. However, current preference optimization approaches often fail to capture the plurality of user opinions, instead reinforcing majority viewpoints and marginalizing minority perspectives. We introduce PERSONA, a reproducible test bed designed to evaluate and improve pluralistic alignment of LMs. We procedurally generate diverse user profiles from US census data, resulting in 1,586 synthetic personas with varied demographic and idiosyncratic attributes. We then generate a large-scale evaluation dataset containing 3,868 prompts and 317,200 feedback pairs obtained from our synthetic personas. Leveraging this dataset, we systematically evaluate LM capabilities in role-playing diverse users, verified through human judges, and the establishment of both a benchmark, PERSONA Bench, for pluralistic alignment approaches as well as an extensive dataset to create new and future benchmarks. The full dataset and benchmarks are available here: https://www.synthlabs.ai/research/persona.
Suppressing Pink Elephants with Direct Principle Feedback
Feb 13, 2024Abstract:Existing methods for controlling language models, such as RLHF and Constitutional AI, involve determining which LLM behaviors are desirable and training them into a language model. However, in many cases, it is desirable for LLMs to be controllable at inference time, so that they can be used in multiple contexts with diverse needs. We illustrate this with the Pink Elephant Problem: instructing an LLM to avoid discussing a certain entity (a ``Pink Elephant''), and instead discuss a preferred entity (``Grey Elephant''). We apply a novel simplification of Constitutional AI, Direct Principle Feedback, which skips the ranking of responses and uses DPO directly on critiques and revisions. Our results show that after DPF fine-tuning on our synthetic Pink Elephants dataset, our 13B fine-tuned LLaMA 2 model significantly outperforms Llama-2-13B-Chat and a prompted baseline, and performs as well as GPT-4 in on our curated test set assessing the Pink Elephant Problem.
Neural MMO 2.0: A Massively Multi-task Addition to Massively Multi-agent Learning
Nov 07, 2023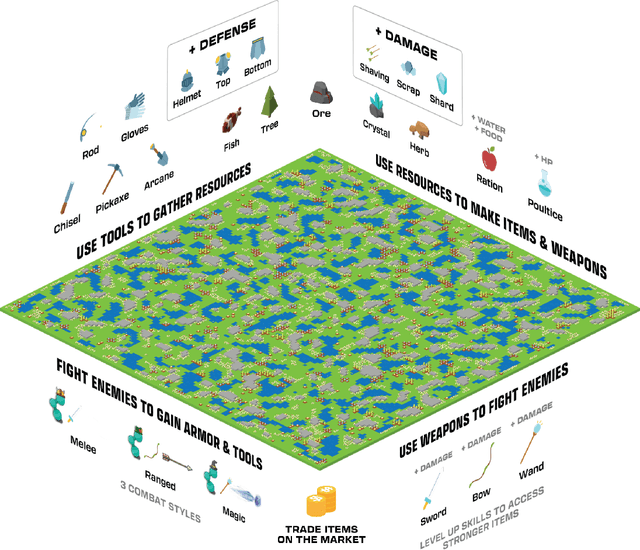
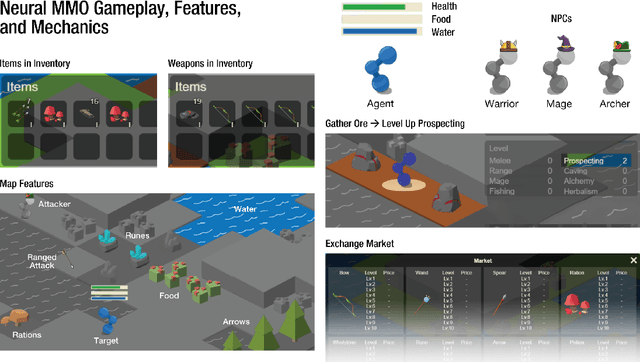
Abstract:Neural MMO 2.0 is a massively multi-agent environment for reinforcement learning research. The key feature of this new version is a flexible task system that allows users to define a broad range of objectives and reward signals. We challenge researchers to train agents capable of generalizing to tasks, maps, and opponents never seen during training. Neural MMO features procedurally generated maps with 128 agents in the standard setting and support for up to. Version 2.0 is a complete rewrite of its predecessor with three-fold improved performance and compatibility with CleanRL. We release the platform as free and open-source software with comprehensive documentation available at neuralmmo.github.io and an active community Discord. To spark initial research on this new platform, we are concurrently running a competition at NeurIPS 2023.
Robust Preference Learning for Storytelling via Contrastive Reinforcement Learning
Oct 14, 2022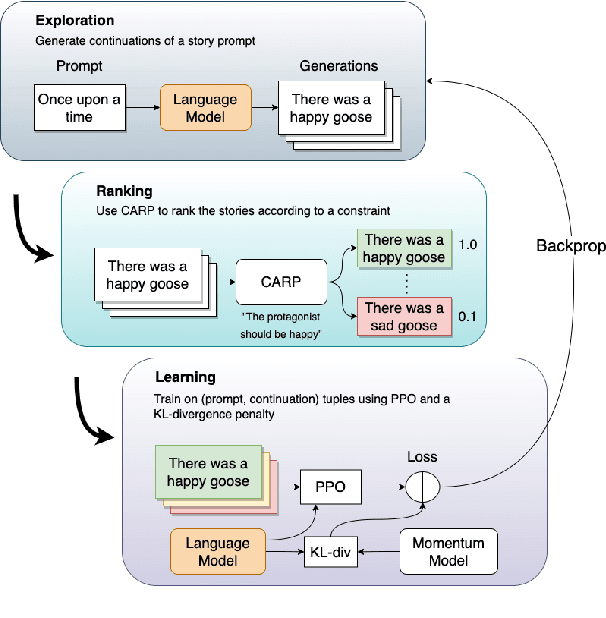

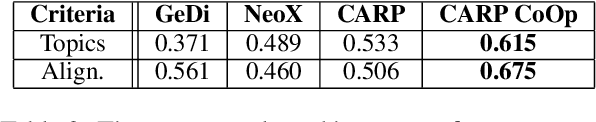
Abstract:Controlled automated story generation seeks to generate natural language stories satisfying constraints from natural language critiques or preferences. Existing methods to control for story preference utilize prompt engineering which is labor intensive and often inconsistent. They may also use logit-manipulation methods which require annotated datasets to exist for the desired attributes. To address these issues, we first train a contrastive bi-encoder model to align stories with corresponding human critiques, named CARP, building a general purpose preference model. This is subsequently used as a reward function to fine-tune a generative language model via reinforcement learning. However, simply fine-tuning a generative language model with a contrastive reward model does not always reliably result in a story generation system capable of generating stories that meet user preferences. To increase story generation robustness we further fine-tune the contrastive reward model using a prompt-learning technique. A human participant study is then conducted comparing generations from our full system, ablations, and two baselines. We show that the full fine-tuning pipeline results in a story generator preferred over a LLM 20x as large as well as logit-based methods. This motivates the use of contrastive learning for general purpose human preference modeling.
EleutherAI: Going Beyond "Open Science" to "Science in the Open"
Oct 12, 2022Abstract:Over the past two years, EleutherAI has established itself as a radically novel initiative aimed at both promoting open-source research and conducting research in a transparent, openly accessible and collaborative manner. EleutherAI's approach to research goes beyond transparency: by doing research entirely in public, anyone in the world can observe and contribute at every stage. Our work has been received positively and has resulted in several high-impact projects in Natural Language Processing and other fields. In this paper, we describe our experience doing public-facing machine learning research, the benefits we believe this approach brings, and the pitfalls we have encountered.
Linearly Mapping from Image to Text Space
Sep 30, 2022
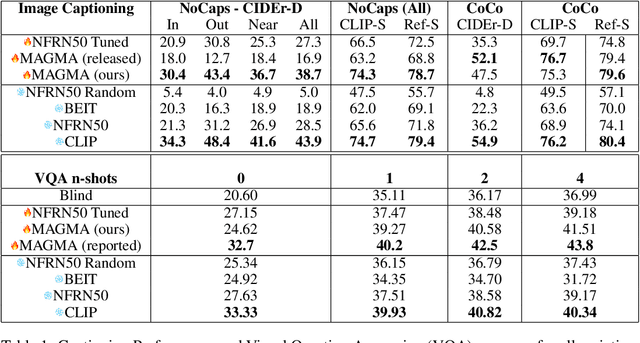

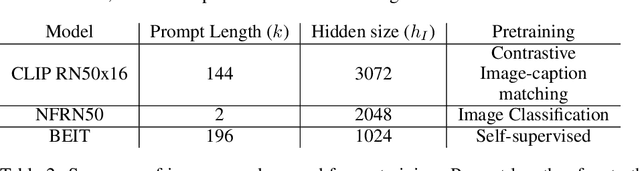
Abstract:The extent to which text-only language models (LMs) learn to represent the physical, non-linguistic world is an open question. Prior work has shown that pretrained LMs can be taught to ``understand'' visual inputs when the models' parameters are updated on image captioning tasks. We test a stronger hypothesis: that the conceptual representations learned by text-only models are functionally equivalent (up to a linear transformation) to those learned by models trained on vision tasks. Specifically, we show that the image representations from vision models can be transferred as continuous prompts to frozen LMs by training only a single linear projection. Using these to prompt the LM achieves competitive performance on captioning and visual question answering tasks compared to models that tune both the image encoder and text decoder (such as the MAGMA model). We compare three image encoders with increasing amounts of linguistic supervision seen during pretraining: BEIT (no linguistic information), NF-ResNET (lexical category information), and CLIP (full natural language descriptions). We find that all three encoders perform equally well at transferring visual property information to the language model (e.g., whether an animal is large or small), but that image encoders pretrained with linguistic supervision more saliently encode category information (e.g., distinguishing hippo vs.\ elephant) and thus perform significantly better on benchmark language-and-vision tasks. Our results indicate that LMs encode conceptual information structurally similarly to vision-based models, even those that are solely trained on images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge