Hao Xiang Li
Learning Resilient Elections with Adversarial GNNs
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:In the face of adverse motives, it is indispensable to achieve a consensus. Elections have been the canonical way by which modern democracy has operated since the 17th century. Nowadays, they regulate markets, provide an engine for modern recommender systems or peer-to-peer networks, and remain the main approach to represent democracy. However, a desirable universal voting rule that satisfies all hypothetical scenarios is still a challenging topic, and the design of these systems is at the forefront of mechanism design research. Automated mechanism design is a promising approach, and recent works have demonstrated that set-invariant architectures are uniquely suited to modelling electoral systems. However, various concerns prevent the direct application to real-world settings, such as robustness to strategic voting. In this paper, we generalise the expressive capability of learned voting rules, and combine improvements in neural network architecture with adversarial training to improve the resilience of voting rules while maximizing social welfare. We evaluate the effectiveness of our methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets. Our method resolves critical limitations of prior work regarding learning voting rules by representing elections using bipartite graphs, and learning such voting rules using graph neural networks. We believe this opens new frontiers for applying machine learning to real-world elections.
Results of the NeurIPS 2023 Neural MMO Competition on Multi-task Reinforcement Learning
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:We present the results of the NeurIPS 2023 Neural MMO Competition, which attracted over 200 participants and submissions. Participants trained goal-conditional policies that generalize to tasks, maps, and opponents never seen during training. The top solution achieved a score 4x higher than our baseline within 8 hours of training on a single 4090 GPU. We open-source everything relating to Neural MMO and the competition under the MIT license, including the policy weights and training code for our baseline and for the top submissions.
Neural MMO 2.0: A Massively Multi-task Addition to Massively Multi-agent Learning
Nov 07, 2023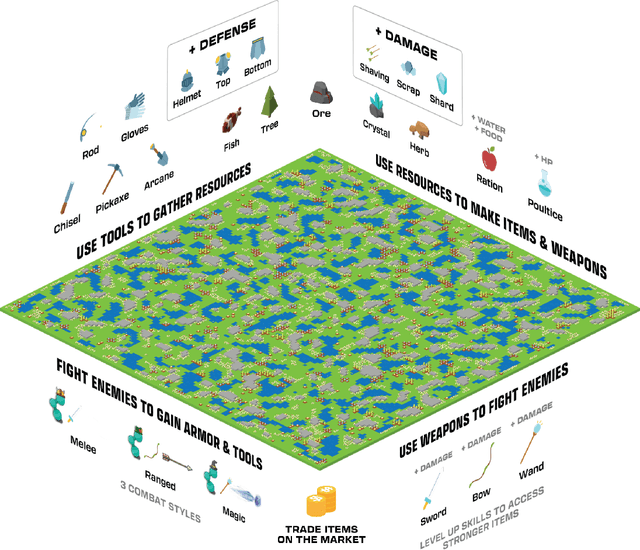
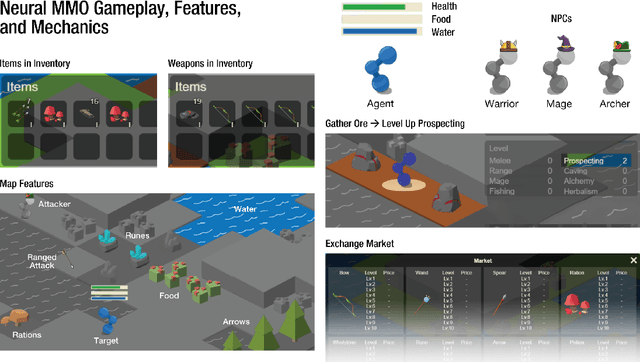
Abstract:Neural MMO 2.0 is a massively multi-agent environment for reinforcement learning research. The key feature of this new version is a flexible task system that allows users to define a broad range of objectives and reward signals. We challenge researchers to train agents capable of generalizing to tasks, maps, and opponents never seen during training. Neural MMO features procedurally generated maps with 128 agents in the standard setting and support for up to. Version 2.0 is a complete rewrite of its predecessor with three-fold improved performance and compatibility with CleanRL. We release the platform as free and open-source software with comprehensive documentation available at neuralmmo.github.io and an active community Discord. To spark initial research on this new platform, we are concurrently running a competition at NeurIPS 2023.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge