Long Zeng
APEX: Academic Poster Editing Agentic Expert
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Designing academic posters is a labor-intensive process requiring the precise balance of high-density content and sophisticated layout. While existing paper-to-poster generation methods automate initial drafting, they are typically single-pass and non-interactive, often fail to align with complex, subjective user intent. To bridge this gap, we propose APEX (Academic Poster Editing agentic eXpert), the first agentic framework for interactive academic poster editing, supporting fine-grained control with robust multi-level API-based editing and a review-and-adjustment Mechanism. In addition, we introduce APEX-Bench, the first systematic benchmark comprising 514 academic poster editing instructions, categorized by a multi-dimensional taxonomy including operation type, difficulty, and abstraction level, constructed via reference-guided and reference-free strategies to ensure realism and diversity. We further establish a multi-dimensional VLM-as-a-judge evaluation protocol to assess instruction fulfillment, modification scope, and visual consistency & harmony. Experimental results demonstrate that APEX significantly outperforms baseline methods. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/Breesiu/APEX.
SculptDrug : A Spatial Condition-Aware Bayesian Flow Model for Structure-based Drug Design
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Structure-Based drug design (SBDD) has emerged as a popular approach in drug discovery, leveraging three-dimensional protein structures to generate drug ligands. However, existing generative models encounter several key challenges: (1) incorporating boundary condition constraints, (2) integrating hierarchical structural conditions, and (3) ensuring spatial modeling fidelity. To address these limitations, we propose SculptDrug, a spatial condition-aware generative model based on Bayesian flow networks (BFNs). First, SculptDrug follows a BFN-based framework and employs a progressive denoising strategy to ensure spatial modeling fidelity, iteratively refining atom positions while enhancing local interactions for precise spatial alignment. Second, we introduce a Boundary Awareness Block that incorporates protein surface constraints into the generative process to ensure that generated ligands are geometrically compatible with the target protein. Third, we design a Hierarchical Encoder that captures global structural context while preserving fine-grained molecular interactions, ensuring overall consistency and accurate ligand-protein conformations. We evaluate SculptDrug on the CrossDocked dataset, and experimental results demonstrate that SculptDrug outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, highlighting the effectiveness of spatial condition-aware modeling.
GTR-Bench: Evaluating Geo-Temporal Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Oct 09, 2025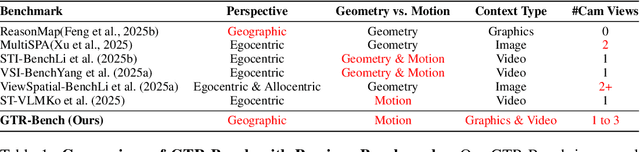
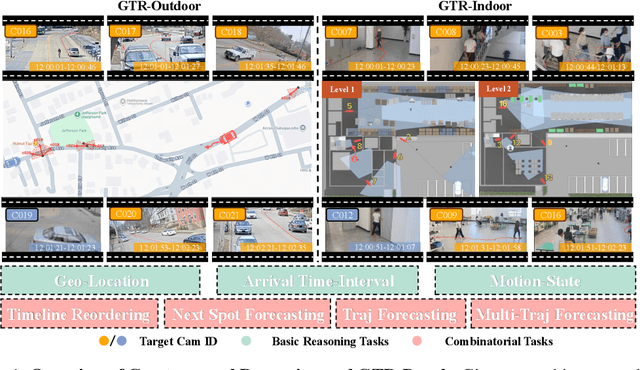
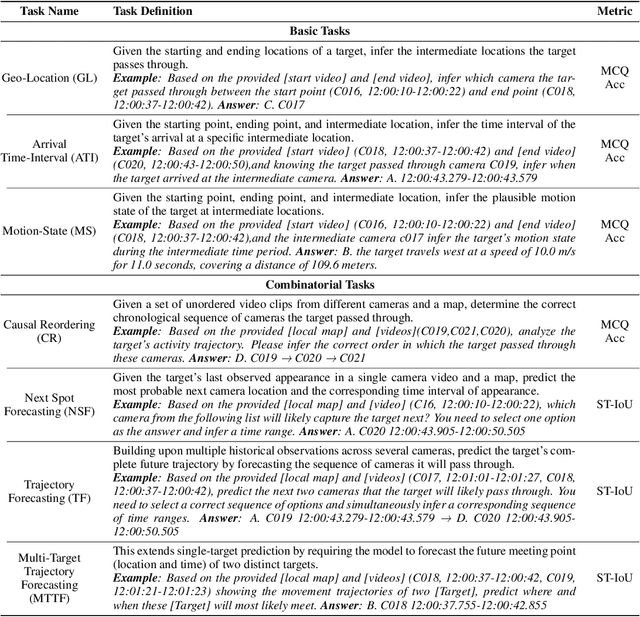
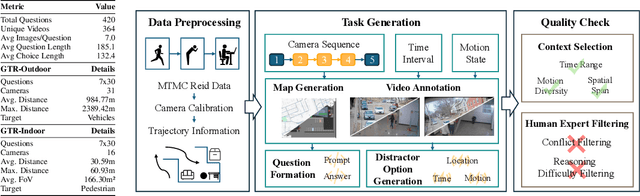
Abstract:Recently spatial-temporal intelligence of Visual-Language Models (VLMs) has attracted much attention due to its importance for Autonomous Driving, Embodied AI and General Artificial Intelligence. Existing spatial-temporal benchmarks mainly focus on egocentric perspective reasoning with images/video context, or geographic perspective reasoning with graphics context (eg. a map), thus fail to assess VLMs' geographic spatial-temporal intelligence with both images/video and graphics context, which is important for areas like traffic management and emergency response. To address the gaps, we introduce Geo-Temporal Reasoning benchmark (GTR-Bench), a novel challenge for geographic temporal reasoning of moving targets in a large-scale camera network. GTR-Bench is more challenging as it requires multiple perspective switches between maps and videos, joint reasoning across multiple videos with non-overlapping fields of view, and inference over spatial-temporal regions that are unobserved by any video context. Evaluations of more than 10 popular VLMs on GTR-Bench demonstrate that even the best proprietary model, Gemini-2.5-Pro (34.9%), significantly lags behind human performance (78.61%) on geo-temporal reasoning. Moreover, our comprehensive analysis on GTR-Bench reveals three primary deficiencies of current models for geo-temporal reasoning. (1) VLMs' reasoning is impaired by an imbalanced utilization of spatial-temporal context. (2) VLMs are weak in temporal forecasting, which leads to worse performance on temporal-emphasized tasks than on spatial-emphasized tasks. (3) VLMs lack the proficiency to comprehend or align the map data with multi-view video inputs. We believe GTR-Bench offers valuable insights and opens up new opportunities for research and applications in spatial-temporal intelligence. Benchmark and code will be released at https://github.com/X-Luffy/GTR-Bench.
MUSE: MCTS-Driven Red Teaming Framework for Enhanced Multi-Turn Dialogue Safety in Large Language Models
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:As large language models~(LLMs) become widely adopted, ensuring their alignment with human values is crucial to prevent jailbreaks where adversaries manipulate models to produce harmful content. While most defenses target single-turn attacks, real-world usage often involves multi-turn dialogues, exposing models to attacks that exploit conversational context to bypass safety measures. We introduce MUSE, a comprehensive framework tackling multi-turn jailbreaks from both attack and defense angles. For attacks, we propose MUSE-A, a method that uses frame semantics and heuristic tree search to explore diverse semantic trajectories. For defense, we present MUSE-D, a fine-grained safety alignment approach that intervenes early in dialogues to reduce vulnerabilities. Extensive experiments on various models show that MUSE effectively identifies and mitigates multi-turn vulnerabilities. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/yansiyu02/MUSE}{https://github.com/yansiyu02/MUSE}.
Perception Before Reasoning: Two-Stage Reinforcement Learning for Visual Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has proven highly effective in eliciting the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Inspired by this success, recent studies have explored applying similar techniques to vision-language models (VLMs), aiming to enhance their reasoning performance. However, directly transplanting RL methods from LLMs to VLMs is suboptimal, as the tasks faced by VLMs are inherently more complex. Specifically, VLMs must first accurately perceive and understand visual inputs before reasoning can be effectively performed. To address this challenge, we propose a two-stage reinforcement learning framework designed to jointly enhance both the perceptual and reasoning capabilities of VLMs. To mitigate the vanishing advantage issue commonly observed in RL training, we first perform dataset-level sampling to selectively strengthen specific capabilities using distinct data sources. During training, the first stage focuses on improving the model's visual perception through coarse- and fine-grained visual understanding, while the second stage targets the enhancement of reasoning abilities. After the proposed two-stage reinforcement learning process, we obtain PeBR-R1, a vision-language model with significantly enhanced perceptual and reasoning capabilities. Experimental results on seven benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach and validate the superior performance of PeBR-R1 across diverse visual reasoning tasks.
$S^3$LAM: Surfel Splatting SLAM for Geometrically Accurate Tracking and Mapping
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:We propose $S^3$LAM, a novel RGB-D SLAM system that leverages 2D surfel splatting to achieve highly accurate geometric representations for simultaneous tracking and mapping. Unlike existing 3DGS-based SLAM approaches that rely on 3D Gaussian ellipsoids, we utilize 2D Gaussian surfels as primitives for more efficient scene representation. By focusing on the surfaces of objects in the scene, this design enables $S^3$LAM to reconstruct high-quality geometry, benefiting both mapping and tracking. To address inherent SLAM challenges including real-time optimization under limited viewpoints, we introduce a novel adaptive surface rendering strategy that improves mapping accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency. We further derive camera pose Jacobians directly from 2D surfel splatting formulation, highlighting the importance of our geometrically accurate representation that improves tracking convergence. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets validate that $S^3$LAM achieves state-of-the-art performance. Code will be made publicly available.
Embodied Intelligent Industrial Robotics: Concepts and Techniques
May 15, 2025Abstract:In recent years, embodied intelligent robotics (EIR) has made significant progress in multi-modal perception, autonomous decision-making, and physical interaction. Some robots have already been tested in general-purpose scenarios such as homes and shopping malls. We aim to advance the research and application of embodied intelligence in industrial scenes. However, current EIR lacks a deep understanding of industrial environment semantics and the normative constraints between industrial operating objects. To address this gap, this paper first reviews the history of industrial robotics and the mainstream EIR frameworks. We then introduce the concept of the embodied intelligent industrial robotics (EIIR) and propose a knowledge-driven EIIR technology framework for industrial environments. The framework includes four main modules: world model, high-level task planner, low-level skill controller, and simulator. We also review the current development of technologies related to each module and highlight recent progress in adapting them to industrial applications. Finally, we summarize the key challenges EIIR faces in industrial scenarios and suggest future research directions. We believe that EIIR technology will shape the next generation of industrial robotics. Industrial systems based on embodied intelligent industrial robots offer strong potential for enabling intelligent manufacturing. We will continue to track and summarize new research in this area and hope this review will serve as a valuable reference for scholars and engineers interested in industrial embodied intelligence. Together, we can help drive the rapid advancement and application of this technology. The associated project can be found at https://github.com/jackyzengl/EIIR.
Demonstrating DVS: Dynamic Virtual-Real Simulation Platform for Mobile Robotic Tasks
Apr 26, 2025Abstract:With the development of embodied artificial intelligence, robotic research has increasingly focused on complex tasks. Existing simulation platforms, however, are often limited to idealized environments, simple task scenarios and lack data interoperability. This restricts task decomposition and multi-task learning. Additionally, current simulation platforms face challenges in dynamic pedestrian modeling, scene editability, and synchronization between virtual and real assets. These limitations hinder real world robot deployment and feedback. To address these challenges, we propose DVS (Dynamic Virtual-Real Simulation Platform), a platform for dynamic virtual-real synchronization in mobile robotic tasks. DVS integrates a random pedestrian behavior modeling plugin and large-scale, customizable indoor scenes for generating annotated training datasets. It features an optical motion capture system, synchronizing object poses and coordinates between virtual and real world to support dynamic task benchmarking. Experimental validation shows that DVS supports tasks such as pedestrian trajectory prediction, robot path planning, and robotic arm grasping, with potential for both simulation and real world deployment. In this way, DVS represents more than just a versatile robotic platform; it paves the way for research in human intervention in robot execution tasks and real-time feedback algorithms in virtual-real fusion environments. More information about the simulation platform is available on https://immvlab.github.io/DVS/.
Hierarchical Vector Quantized Graph Autoencoder with Annealing-Based Code Selection
Apr 17, 2025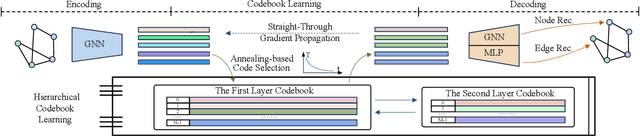
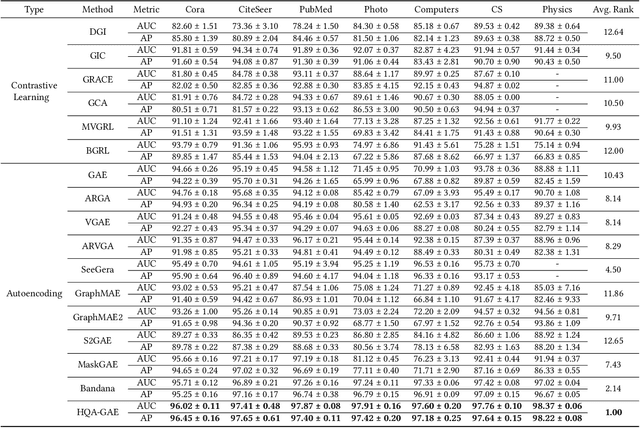
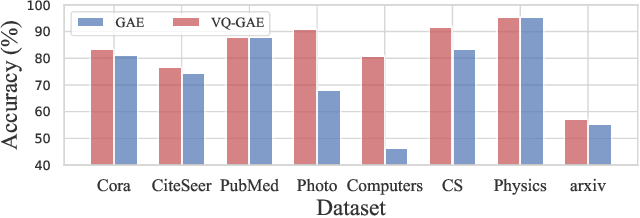
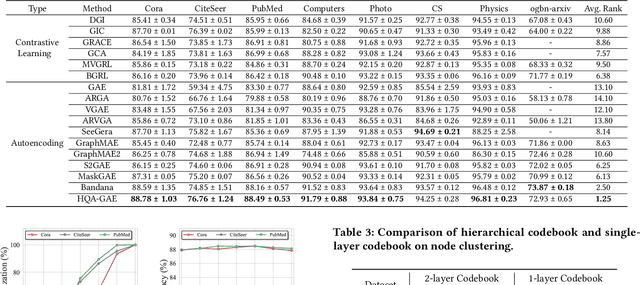
Abstract:Graph self-supervised learning has gained significant attention recently. However, many existing approaches heavily depend on perturbations, and inappropriate perturbations may corrupt the graph's inherent information. The Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE) is a powerful autoencoder extensively used in fields such as computer vision; however, its application to graph data remains underexplored. In this paper, we provide an empirical analysis of vector quantization in the context of graph autoencoders, demonstrating its significant enhancement of the model's capacity to capture graph topology. Furthermore, we identify two key challenges associated with vector quantization when applying in graph data: codebook underutilization and codebook space sparsity. For the first challenge, we propose an annealing-based encoding strategy that promotes broad code utilization in the early stages of training, gradually shifting focus toward the most effective codes as training progresses. For the second challenge, we introduce a hierarchical two-layer codebook that captures relationships between embeddings through clustering. The second layer codebook links similar codes, encouraging the model to learn closer embeddings for nodes with similar features and structural topology in the graph. Our proposed model outperforms 16 representative baseline methods in self-supervised link prediction and node classification tasks across multiple datasets.
DSM: Building A Diverse Semantic Map for 3D Visual Grounding
Apr 11, 2025



Abstract:In recent years, with the growing research and application of multimodal large language models (VLMs) in robotics, there has been an increasing trend of utilizing VLMs for robotic scene understanding tasks. Existing approaches that use VLMs for 3D Visual Grounding tasks often focus on obtaining scene information through geometric and visual information, overlooking the extraction of diverse semantic information from the scene and the understanding of rich implicit semantic attributes, such as appearance, physics, and affordance. The 3D scene graph, which combines geometry and language, is an ideal representation method for environmental perception and is an effective carrier for language models in 3D Visual Grounding tasks. To address these issues, we propose a diverse semantic map construction method specifically designed for robotic agents performing 3D Visual Grounding tasks. This method leverages VLMs to capture the latent semantic attributes and relations of objects within the scene and creates a Diverse Semantic Map (DSM) through a geometry sliding-window map construction strategy. We enhance the understanding of grounding information based on DSM and introduce a novel approach named DSM-Grounding. Experimental results show that our method outperforms current approaches in tasks like semantic segmentation and 3D Visual Grounding, particularly excelling in overall metrics compared to the state-of-the-art. In addition, we have deployed this method on robots to validate its effectiveness in navigation and grasping tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge