Keith Anderson
Dj
Heterogenous graph neural networks for species distribution modeling
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Species distribution models (SDMs) are necessary for measuring and predicting occurrences and habitat suitability of species and their relationship with environmental factors. We introduce a novel presence-only SDM with graph neural networks (GNN). In our model, species and locations are treated as two distinct node sets, and the learning task is predicting detection records as the edges that connect locations to species. Using GNN for SDM allows us to model fine-grained interactions between species and the environment. We evaluate the potential of this methodology on the six-region dataset compiled by National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis (NCEAS) for benchmarking SDMs. For each of the regions, the heterogeneous GNN model is comparable to or outperforms previously-benchmarked single-species SDMs as well as a feed-forward neural network baseline model.
Using Unity to Help Solve Intelligence
Nov 18, 2020
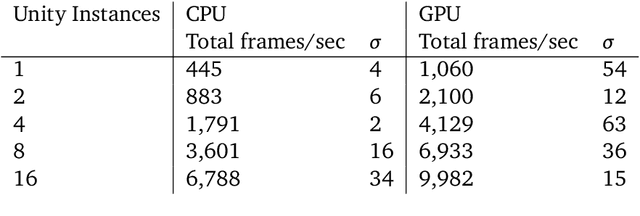
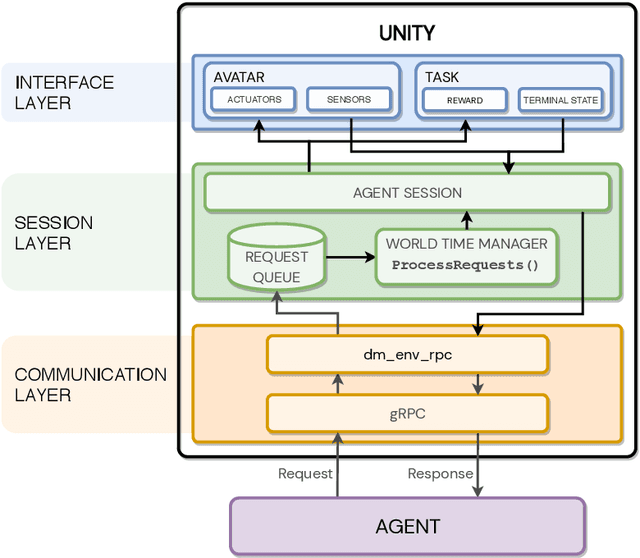
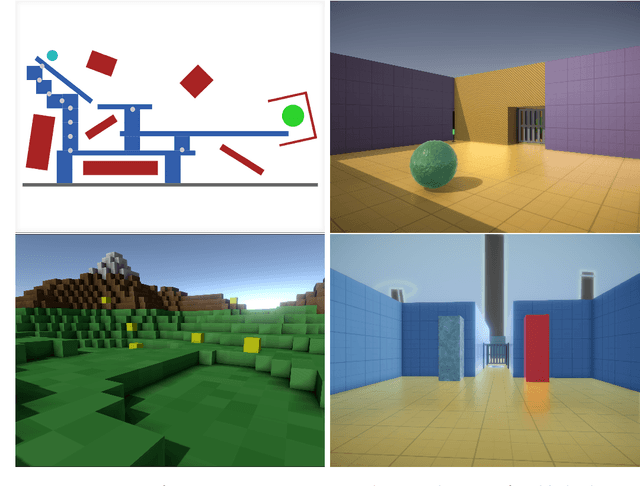
Abstract:In the pursuit of artificial general intelligence, our most significant measurement of progress is an agent's ability to achieve goals in a wide range of environments. Existing platforms for constructing such environments are typically constrained by the technologies they are founded on, and are therefore only able to provide a subset of scenarios necessary to evaluate progress. To overcome these shortcomings, we present our use of Unity, a widely recognized and comprehensive game engine, to create more diverse, complex, virtual simulations. We describe the concepts and components developed to simplify the authoring of these environments, intended for use predominantly in the field of reinforcement learning. We also introduce a practical approach to packaging and re-distributing environments in a way that attempts to improve the robustness and reproducibility of experiment results. To illustrate the versatility of our use of Unity compared to other solutions, we highlight environments already created using our approach from published papers. We hope that others can draw inspiration from how we adapted Unity to our needs, and anticipate increasingly varied and complex environments to emerge from our approach as familiarity grows.
The StreetLearn Environment and Dataset
Mar 04, 2019



Abstract:Navigation is a rich and well-grounded problem domain that drives progress in many different areas of research: perception, planning, memory, exploration, and optimisation in particular. Historically these challenges have been separately considered and solutions built that rely on stationary datasets - for example, recorded trajectories through an environment. These datasets cannot be used for decision-making and reinforcement learning, however, and in general the perspective of navigation as an interactive learning task, where the actions and behaviours of a learning agent are learned simultaneously with the perception and planning, is relatively unsupported. Thus, existing navigation benchmarks generally rely on static datasets (Geiger et al., 2013; Kendall et al., 2015) or simulators (Beattie et al., 2016; Shah et al., 2018). To support and validate research in end-to-end navigation, we present StreetLearn: an interactive, first-person, partially-observed visual environment that uses Google Street View for its photographic content and broad coverage, and give performance baselines for a challenging goal-driven navigation task. The environment code, baseline agent code, and the dataset are available at http://streetlearn.cc
Learning To Follow Directions in Street View
Mar 01, 2019



Abstract:Navigating and understanding the real world remains a key challenge in machine learning and inspires a great variety of research in areas such as language grounding, planning, navigation and computer vision. We propose an instruction-following task that requires all of the above, and which combines the practicality of simulated environments with the challenges of ambiguous, noisy real world data. StreetNav is built on top of Google Street View and provides visually accurate environments representing real places. Agents are given driving instructions which they must learn to interpret in order to successfully navigate in this environment. Since humans equipped with driving instructions can readily navigate in previously unseen cities, we set a high bar and test our trained agents for similar cognitive capabilities. Although deep reinforcement learning (RL) methods are frequently evaluated only on data that closely follow the training distribution, our dataset extends to multiple cities and has a clean train/test separation. This allows for thorough testing of generalisation ability. This paper presents the StreetNav environment and tasks, a set of novel models that establish strong baselines, and analysis of the task and the trained agents.
Rigorous Agent Evaluation: An Adversarial Approach to Uncover Catastrophic Failures
Dec 04, 2018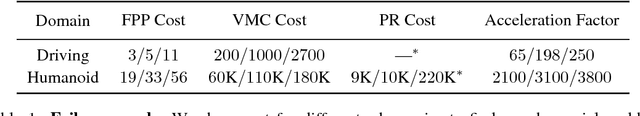
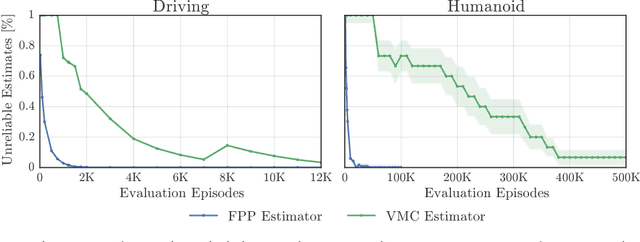
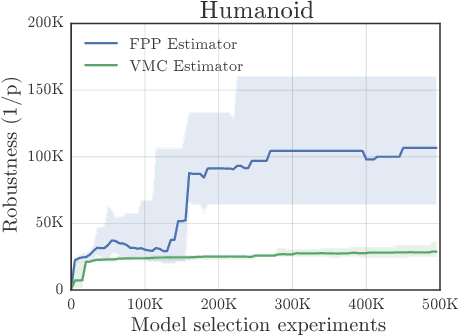
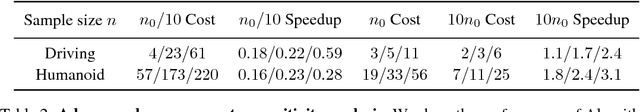
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of evaluating learning systems in safety critical domains such as autonomous driving, where failures can have catastrophic consequences. We focus on two problems: searching for scenarios when learned agents fail and assessing their probability of failure. The standard method for agent evaluation in reinforcement learning, Vanilla Monte Carlo, can miss failures entirely, leading to the deployment of unsafe agents. We demonstrate this is an issue for current agents, where even matching the compute used for training is sometimes insufficient for evaluation. To address this shortcoming, we draw upon the rare event probability estimation literature and propose an adversarial evaluation approach. Our approach focuses evaluation on adversarially chosen situations, while still providing unbiased estimates of failure probabilities. The key difficulty is in identifying these adversarial situations -- since failures are rare there is little signal to drive optimization. To solve this we propose a continuation approach that learns failure modes in related but less robust agents. Our approach also allows reuse of data already collected for training the agent. We demonstrate the efficacy of adversarial evaluation on two standard domains: humanoid control and simulated driving. Experimental results show that our methods can find catastrophic failures and estimate failures rates of agents multiple orders of magnitude faster than standard evaluation schemes, in minutes to hours rather than days.
Learning to Navigate in Cities Without a Map
Apr 17, 2018



Abstract:Navigating through unstructured environments is a basic capability of intelligent creatures, and thus is of fundamental interest in the study and development of artificial intelligence. Long-range navigation is a complex cognitive task that relies on developing an internal representation of space, grounded by recognisable landmarks and robust visual processing, that can simultaneously support continuous self-localisation ("I am here") and a representation of the goal ("I am going there"). Building upon recent research that applies deep reinforcement learning to maze navigation problems, we present an end-to-end deep reinforcement learning approach that can be applied on a city scale. Recognising that successful navigation relies on integration of general policies with locale-specific knowledge, we propose a dual pathway architecture that allows locale-specific features to be encapsulated, while still enabling transfer to multiple cities. We present an interactive navigation environment that uses Google StreetView for its photographic content and worldwide coverage, and demonstrate that our learning method allows agents to learn to navigate multiple cities and to traverse to target destinations that may be kilometres away. A video summarizing our research and showing the trained agent in diverse city environments as well as on the transfer task is available at: https://sites.google.com/view/streetlearn.
Psychlab: A Psychology Laboratory for Deep Reinforcement Learning Agents
Feb 04, 2018


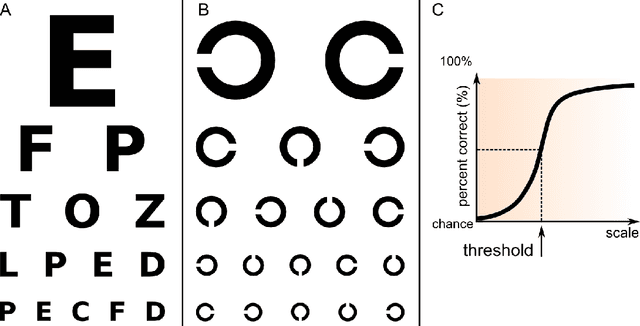
Abstract:Psychlab is a simulated psychology laboratory inside the first-person 3D game world of DeepMind Lab (Beattie et al. 2016). Psychlab enables implementations of classical laboratory psychological experiments so that they work with both human and artificial agents. Psychlab has a simple and flexible API that enables users to easily create their own tasks. As examples, we are releasing Psychlab implementations of several classical experimental paradigms including visual search, change detection, random dot motion discrimination, and multiple object tracking. We also contribute a study of the visual psychophysics of a specific state-of-the-art deep reinforcement learning agent: UNREAL (Jaderberg et al. 2016). This study leads to the surprising conclusion that UNREAL learns more quickly about larger target stimuli than it does about smaller stimuli. In turn, this insight motivates a specific improvement in the form of a simple model of foveal vision that turns out to significantly boost UNREAL's performance, both on Psychlab tasks, and on standard DeepMind Lab tasks. By open-sourcing Psychlab we hope to facilitate a range of future such studies that simultaneously advance deep reinforcement learning and improve its links with cognitive science.
DeepMind Lab
Dec 13, 2016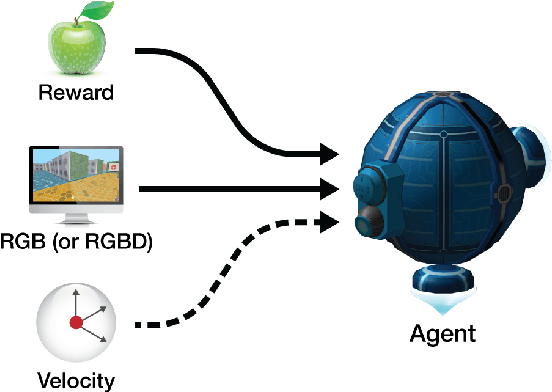
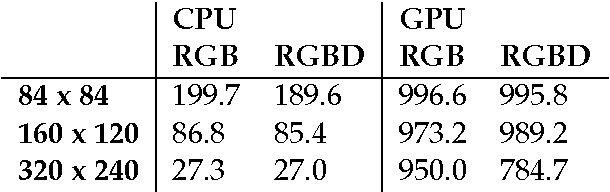
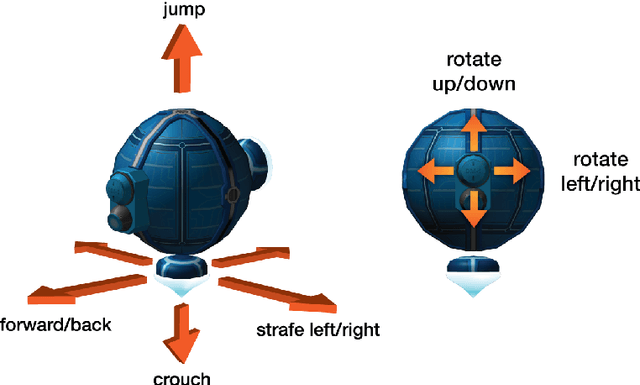

Abstract:DeepMind Lab is a first-person 3D game platform designed for research and development of general artificial intelligence and machine learning systems. DeepMind Lab can be used to study how autonomous artificial agents may learn complex tasks in large, partially observed, and visually diverse worlds. DeepMind Lab has a simple and flexible API enabling creative task-designs and novel AI-designs to be explored and quickly iterated upon. It is powered by a fast and widely recognised game engine, and tailored for effective use by the research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge