Marcus Wainwright
Grounded Language Learning in a Simulated 3D World
Jun 26, 2017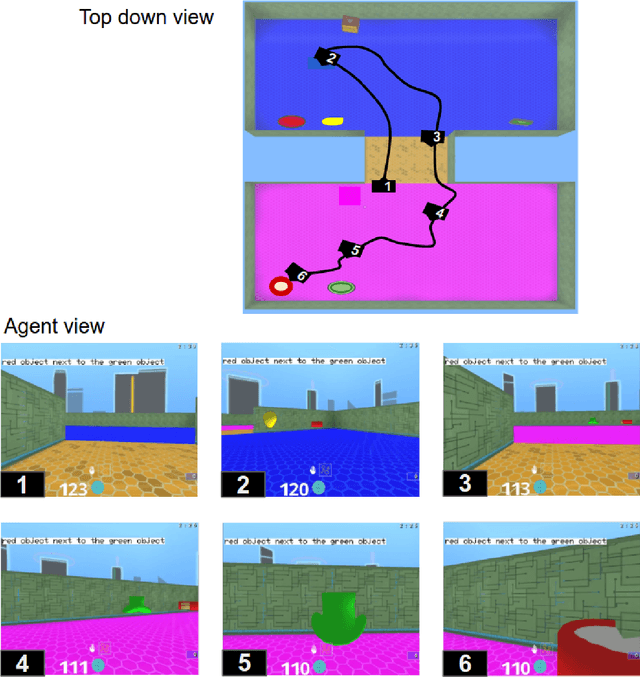
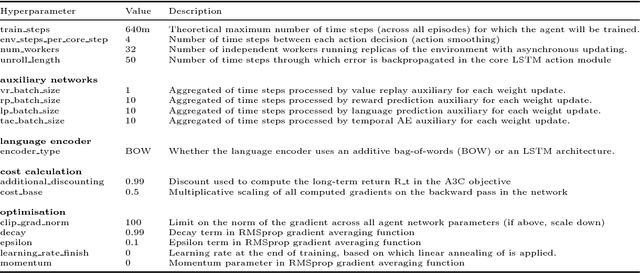
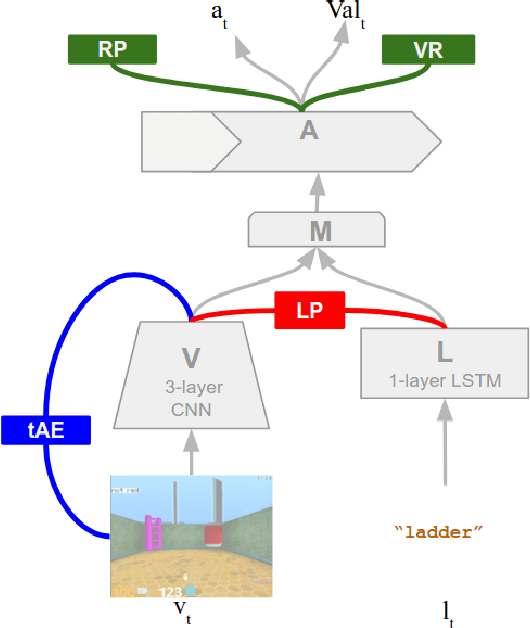
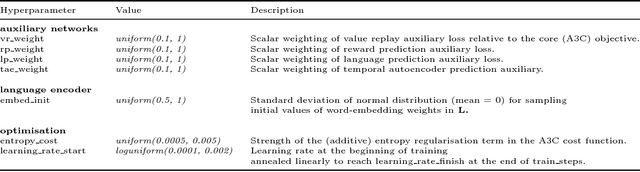
Abstract:We are increasingly surrounded by artificially intelligent technology that takes decisions and executes actions on our behalf. This creates a pressing need for general means to communicate with, instruct and guide artificial agents, with human language the most compelling means for such communication. To achieve this in a scalable fashion, agents must be able to relate language to the world and to actions; that is, their understanding of language must be grounded and embodied. However, learning grounded language is a notoriously challenging problem in artificial intelligence research. Here we present an agent that learns to interpret language in a simulated 3D environment where it is rewarded for the successful execution of written instructions. Trained via a combination of reinforcement and unsupervised learning, and beginning with minimal prior knowledge, the agent learns to relate linguistic symbols to emergent perceptual representations of its physical surroundings and to pertinent sequences of actions. The agent's comprehension of language extends beyond its prior experience, enabling it to apply familiar language to unfamiliar situations and to interpret entirely novel instructions. Moreover, the speed with which this agent learns new words increases as its semantic knowledge grows. This facility for generalising and bootstrapping semantic knowledge indicates the potential of the present approach for reconciling ambiguous natural language with the complexity of the physical world.
DeepMind Lab
Dec 13, 2016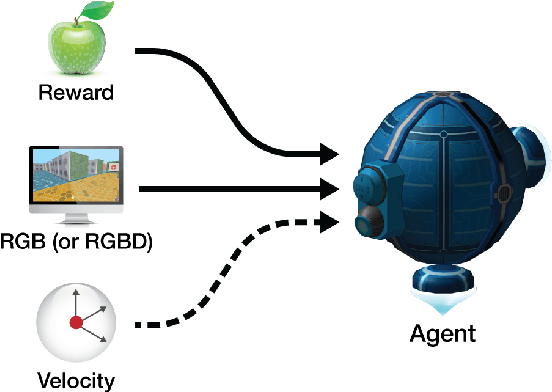
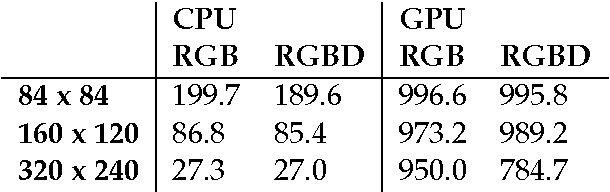
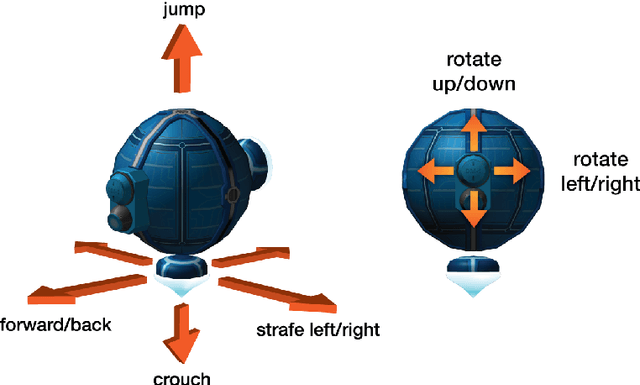

Abstract:DeepMind Lab is a first-person 3D game platform designed for research and development of general artificial intelligence and machine learning systems. DeepMind Lab can be used to study how autonomous artificial agents may learn complex tasks in large, partially observed, and visually diverse worlds. DeepMind Lab has a simple and flexible API enabling creative task-designs and novel AI-designs to be explored and quickly iterated upon. It is powered by a fast and widely recognised game engine, and tailored for effective use by the research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge