Maxim Neumann
Not Every Tree Is a Forest: Benchmarking Forest Types from Satellite Remote Sensing
May 03, 2025Abstract:Developing accurate and reliable models for forest types mapping is critical to support efforts for halting deforestation and for biodiversity conservation (such as European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR)). This work introduces ForTy, a benchmark for global-scale FORest TYpes mapping using multi-temporal satellite data1. The benchmark comprises 200,000 time series of image patches, each consisting of Sentinel-2, Sentinel-1, climate, and elevation data. Each time series captures variations at monthly or seasonal cadence. Per-pixel annotations, including forest types and other land use classes, support image segmentation tasks. Unlike most existing land use products that often categorize all forest areas into a single class, our benchmark differentiates between three forest types classes: natural forest, planted forest, and tree crops. By leveraging multiple public data sources, we achieve global coverage with this benchmark. We evaluate the forest types dataset using several baseline models, including convolution neural networks and transformer-based models. Additionally, we propose a novel transformer-based model specifically designed to handle multi-modal, multi-temporal satellite data for forest types mapping. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model surpasses the baseline models in performance.
Heterogenous graph neural networks for species distribution modeling
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Species distribution models (SDMs) are necessary for measuring and predicting occurrences and habitat suitability of species and their relationship with environmental factors. We introduce a novel presence-only SDM with graph neural networks (GNN). In our model, species and locations are treated as two distinct node sets, and the learning task is predicting detection records as the edges that connect locations to species. Using GNN for SDM allows us to model fine-grained interactions between species and the environment. We evaluate the potential of this methodology on the six-region dataset compiled by National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis (NCEAS) for benchmarking SDMs. For each of the regions, the heterogeneous GNN model is comparable to or outperforms previously-benchmarked single-species SDMs as well as a feed-forward neural network baseline model.
PaliGemma: A versatile 3B VLM for transfer
Jul 10, 2024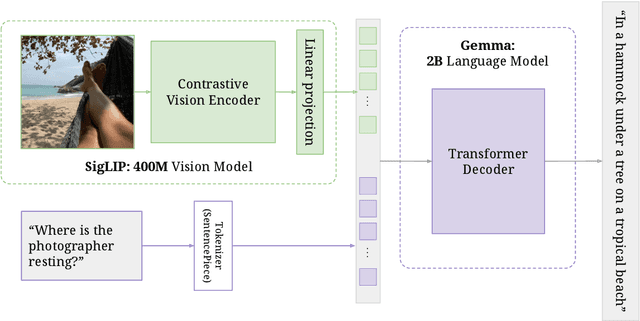
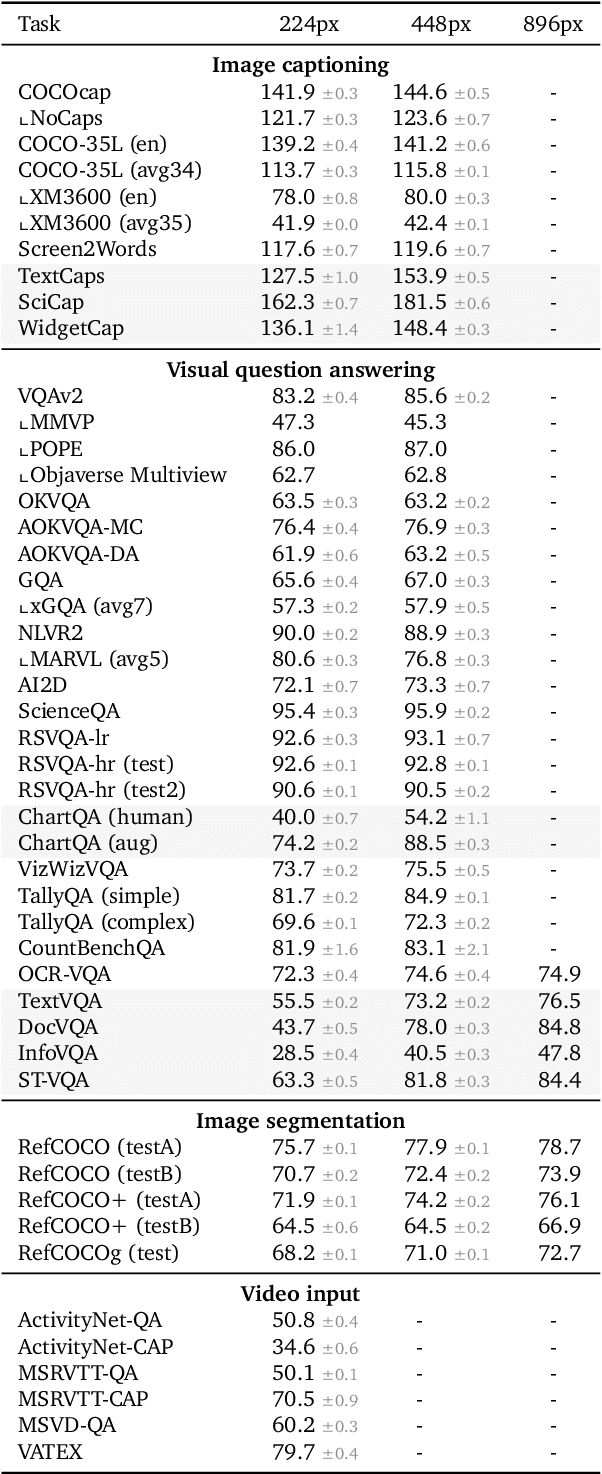
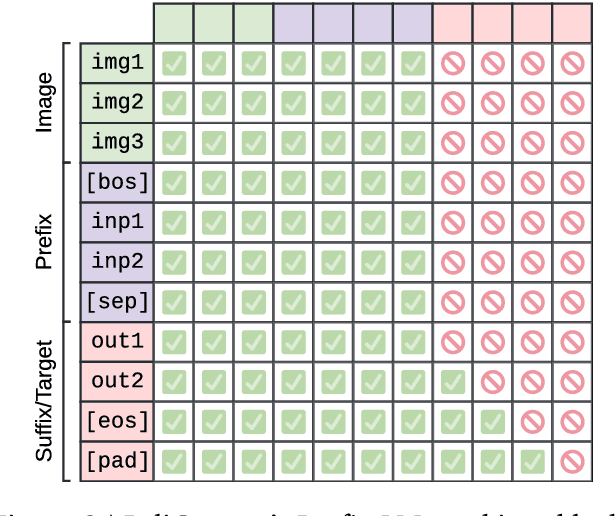
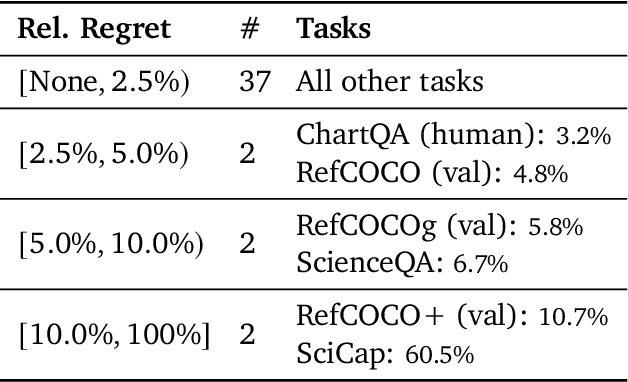
Abstract:PaliGemma is an open Vision-Language Model (VLM) that is based on the SigLIP-So400m vision encoder and the Gemma-2B language model. It is trained to be a versatile and broadly knowledgeable base model that is effective to transfer. It achieves strong performance on a wide variety of open-world tasks. We evaluate PaliGemma on almost 40 diverse tasks including standard VLM benchmarks, but also more specialized tasks such as remote-sensing and segmentation.
Simple Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision Transformers
May 12, 2022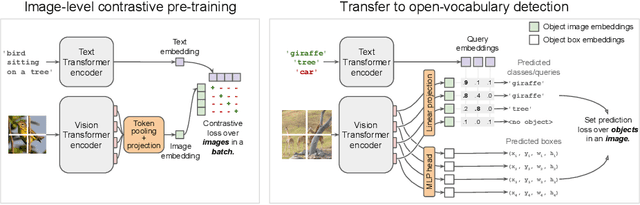
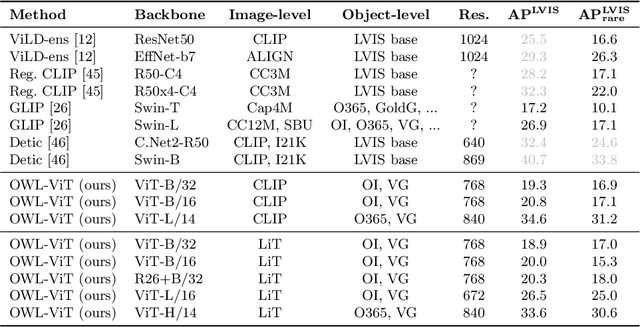
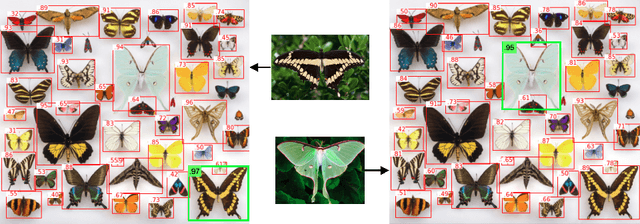
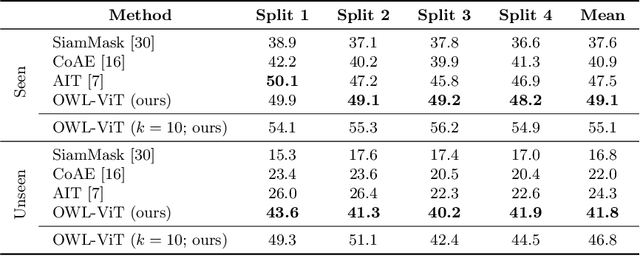
Abstract:Combining simple architectures with large-scale pre-training has led to massive improvements in image classification. For object detection, pre-training and scaling approaches are less well established, especially in the long-tailed and open-vocabulary setting, where training data is relatively scarce. In this paper, we propose a strong recipe for transferring image-text models to open-vocabulary object detection. We use a standard Vision Transformer architecture with minimal modifications, contrastive image-text pre-training, and end-to-end detection fine-tuning. Our analysis of the scaling properties of this setup shows that increasing image-level pre-training and model size yield consistent improvements on the downstream detection task. We provide the adaptation strategies and regularizations needed to attain very strong performance on zero-shot text-conditioned and one-shot image-conditioned object detection. Code and models are available on GitHub.
Continental-Scale Building Detection from High Resolution Satellite Imagery
Jul 29, 2021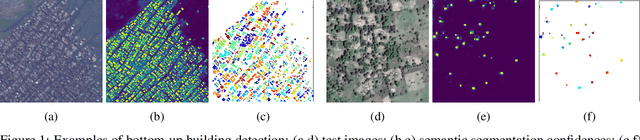
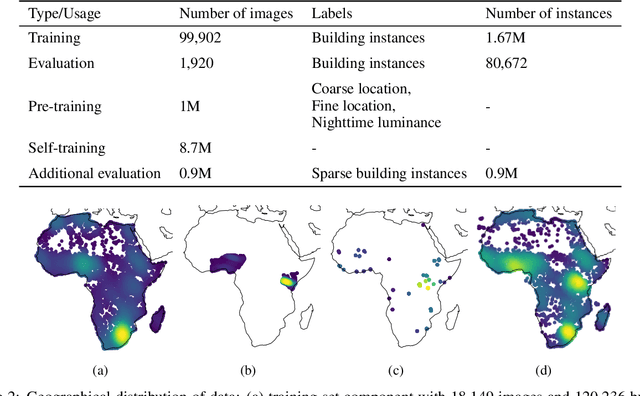

Abstract:Identifying the locations and footprints of buildings is vital for many practical and scientific purposes. Such information can be particularly useful in developing regions where alternative data sources may be scarce. In this work, we describe a model training pipeline for detecting buildings across the entire continent of Africa, using 50 cm satellite imagery. Starting with the U-Net model, widely used in satellite image analysis, we study variations in architecture, loss functions, regularization, pre-training, self-training and post-processing that increase instance segmentation performance. Experiments were carried out using a dataset of 100k satellite images across Africa containing 1.75M manually labelled building instances, and further datasets for pre-training and self-training. We report novel methods for improving performance of building detection with this type of model, including the use of mixup (mAP +0.12) and self-training with soft KL loss (mAP +0.06). The resulting pipeline obtains good results even on a wide variety of challenging rural and urban contexts, and was used to create the Open Buildings dataset of 516M Africa-wide detected footprints.
Scaling Vision with Sparse Mixture of Experts
Jun 10, 2021



Abstract:Sparsely-gated Mixture of Experts networks (MoEs) have demonstrated excellent scalability in Natural Language Processing. In Computer Vision, however, almost all performant networks are "dense", that is, every input is processed by every parameter. We present a Vision MoE (V-MoE), a sparse version of the Vision Transformer, that is scalable and competitive with the largest dense networks. When applied to image recognition, V-MoE matches the performance of state-of-the-art networks, while requiring as little as half of the compute at inference time. Further, we propose an extension to the routing algorithm that can prioritize subsets of each input across the entire batch, leading to adaptive per-image compute. This allows V-MoE to trade-off performance and compute smoothly at test-time. Finally, we demonstrate the potential of V-MoE to scale vision models, and train a 15B parameter model that attains 90.35% on ImageNet.
Training general representations for remote sensing using in-domain knowledge
Sep 30, 2020
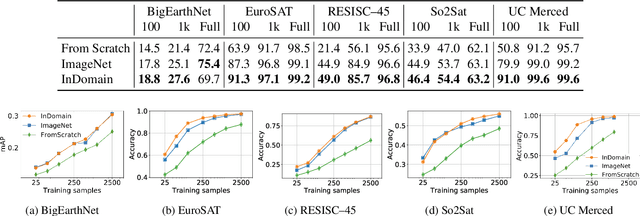


Abstract:Automatically finding good and general remote sensing representations allows to perform transfer learning on a wide range of applications - improving the accuracy and reducing the required number of training samples. This paper investigates development of generic remote sensing representations, and explores which characteristics are important for a dataset to be a good source for representation learning. For this analysis, five diverse remote sensing datasets are selected and used for both, disjoint upstream representation learning and downstream model training and evaluation. A common evaluation protocol is used to establish baselines for these datasets that achieve state-of-the-art performance. As the results indicate, especially with a low number of available training samples a significant performance enhancement can be observed when including additionally in-domain data in comparison to training models from scratch or fine-tuning only on ImageNet (up to 11% and 40%, respectively, at 100 training samples). All datasets and pretrained representation models are published online.
AttentionNAS: Spatiotemporal Attention Cell Search for Video Classification
Jul 31, 2020



Abstract:Convolutional operations have two limitations: (1) do not explicitly model where to focus as the same filter is applied to all the positions, and (2) are unsuitable for modeling long-range dependencies as they only operate on a small neighborhood. While both limitations can be alleviated by attention operations, many design choices remain to be determined to use attention, especially when applying attention to videos. Towards a principled way of applying attention to videos, we address the task of spatiotemporal attention cell search. We propose a novel search space for spatiotemporal attention cells, which allows the search algorithm to flexibly explore various design choices in the cell. The discovered attention cells can be seamlessly inserted into existing backbone networks, e.g., I3D or S3D, and improve video classification accuracy by more than 2% on both Kinetics-600 and MiT datasets. The discovered attention cells outperform non-local blocks on both datasets, and demonstrate strong generalization across different modalities, backbones, and datasets. Inserting our attention cells into I3D-R50 yields state-of-the-art performance on both datasets.
In-domain representation learning for remote sensing
Nov 15, 2019



Abstract:Given the importance of remote sensing, surprisingly little attention has been paid to it by the representation learning community. To address it and to establish baselines and a common evaluation protocol in this domain, we provide simplified access to 5 diverse remote sensing datasets in a standardized form. Specifically, we investigate in-domain representation learning to develop generic remote sensing representations and explore which characteristics are important for a dataset to be a good source for remote sensing representation learning. The established baselines achieve state-of-the-art performance on these datasets.
The Visual Task Adaptation Benchmark
Oct 01, 2019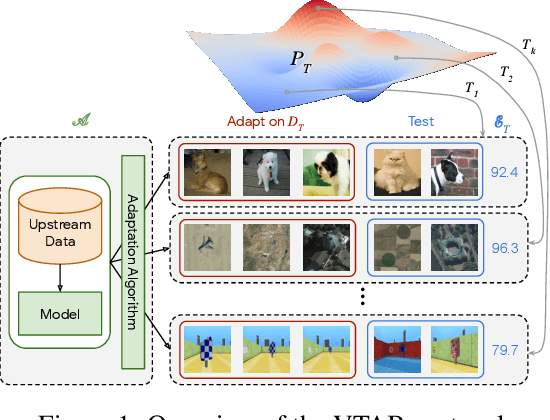
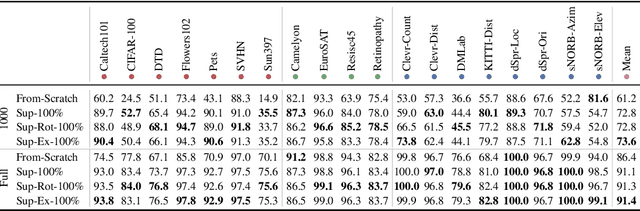
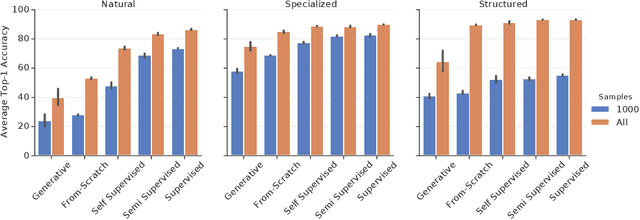
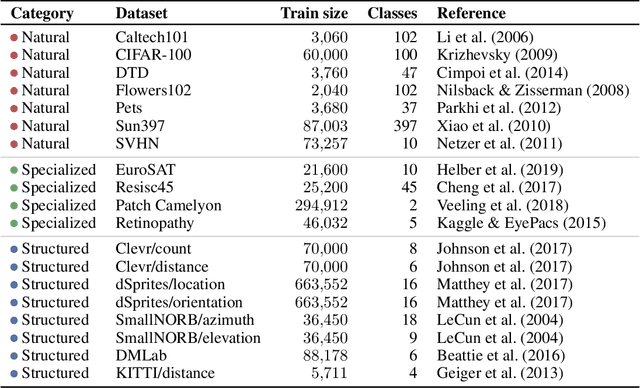
Abstract:Representation learning promises to unlock deep learning for the long tail of vision tasks without expansive labelled datasets. Yet, the absence of a unified yardstick to evaluate general visual representations hinders progress. Many sub-fields promise representations, but each has different evaluation protocols that are either too constrained (linear classification), limited in scope (ImageNet, CIFAR, Pascal-VOC), or only loosely related to representation quality (generation). We present the Visual Task Adaptation Benchmark (VTAB): a diverse, realistic, and challenging benchmark to evaluate representations. VTAB embodies one principle: good representations adapt to unseen tasks with few examples. We run a large VTAB study of popular algorithms, answering questions like: How effective are ImageNet representation on non-standard datasets? Are generative models competitive? Is self-supervision useful if one already has labels?
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge