Kaer Huang
SEA: Self-Evolution Agent with Step-wise Reward for Computer Use
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Computer use agent is an emerging area in artificial intelligence that aims to operate the computers to achieve the user's tasks, which attracts a lot of attention from both industry and academia. However, the present agents' performance is far from being used. In this paper, we propose the Self-Evolution Agent (SEA) for computer use, and to develop this agent, we propose creative methods in data generation, reinforcement learning, and model enhancement. Specifically, we first propose an automatic pipeline to generate the verifiable trajectory for training. And then, we propose efficient step-wise reinforcement learning to alleviate the significant computational requirements for long-horizon training. In the end, we propose the enhancement method to merge the grounding and planning ability into one model without any extra training. Accordingly, based on our proposed innovation of data generation, training strategy, and enhancement, we get the Selfevolution Agent (SEA) for computer use with only 7B parameters, which outperforms models with the same number of parameters and has comparable performance to larger ones. We will make the models' weight and related codes open-source in the future.
A Summary on GUI Agents with Foundation Models Enhanced by Reinforcement Learning
Apr 29, 2025

Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents, driven by Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), have emerged as a promising paradigm for enabling intelligent interaction with digital systems. This paper provides a structured summary of recent advances in GUI agents, focusing on architectures enhanced by Reinforcement Learning (RL). We first formalize GUI agent tasks as Markov Decision Processes and discuss typical execution environments and evaluation metrics. We then review the modular architecture of (M)LLM-based GUI agents, covering Perception, Planning, and Acting modules, and trace their evolution through representative works. Furthermore, we categorize GUI agent training methodologies into Prompt-based, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT)-based, and RL-based approaches, highlighting the progression from simple prompt engineering to dynamic policy learning via RL. Our summary illustrates how recent innovations in multimodal perception, decision reasoning, and adaptive action generation have significantly improved the generalization and robustness of GUI agents in complex real-world environments. We conclude by identifying key challenges and future directions for building more capable and reliable GUI agents.
EffOWT: Transfer Visual Language Models to Open-World Tracking Efficiently and Effectively
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Open-World Tracking (OWT) aims to track every object of any category, which requires the model to have strong generalization capabilities. Trackers can improve their generalization ability by leveraging Visual Language Models (VLMs). However, challenges arise with the fine-tuning strategies when VLMs are transferred to OWT: full fine-tuning results in excessive parameter and memory costs, while the zero-shot strategy leads to sub-optimal performance. To solve the problem, EffOWT is proposed for efficiently transferring VLMs to OWT. Specifically, we build a small and independent learnable side network outside the VLM backbone. By freezing the backbone and only executing backpropagation on the side network, the model's efficiency requirements can be met. In addition, EffOWT enhances the side network by proposing a hybrid structure of Transformer and CNN to improve the model's performance in the OWT field. Finally, we implement sparse interactions on the MLP, thus reducing parameter updates and memory costs significantly. Thanks to the proposed methods, EffOWT achieves an absolute gain of 5.5% on the tracking metric OWTA for unknown categories, while only updating 1.3% of the parameters compared to full fine-tuning, with a 36.4% memory saving. Other metrics also demonstrate obvious improvement.
ArtCrafter: Text-Image Aligning Style Transfer via Embedding Reframing
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in text-guided style transfer, primarily attributed to innovations in diffusion models. These models excel in conditional guidance, utilizing text or images to direct the sampling process. However, despite their capabilities, direct conditional guidance approaches often face challenges in balancing the expressiveness of textual semantics with the diversity of output results while capturing stylistic features. To address these challenges, we introduce ArtCrafter, a novel framework for text-to-image style transfer. Specifically, we introduce an attention-based style extraction module, meticulously engineered to capture the subtle stylistic elements within an image. This module features a multi-layer architecture that leverages the capabilities of perceiver attention mechanisms to integrate fine-grained information. Additionally, we present a novel text-image aligning augmentation component that adeptly balances control over both modalities, enabling the model to efficiently map image and text embeddings into a shared feature space. We achieve this through attention operations that enable smooth information flow between modalities. Lastly, we incorporate an explicit modulation that seamlessly blends multimodal enhanced embeddings with original embeddings through an embedding reframing design, empowering the model to generate diverse outputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ArtCrafter yields impressive results in visual stylization, exhibiting exceptional levels of stylistic intensity, controllability, and diversity.
PCIE_EgoHandPose Solution for EgoExo4D Hand Pose Challenge
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:This report presents our team's 'PCIE_EgoHandPose' solution for the EgoExo4D Hand Pose Challenge at CVPR2024. The main goal of the challenge is to accurately estimate hand poses, which involve 21 3D joints, using an RGB egocentric video image provided for the task. This task is particularly challenging due to the subtle movements and occlusions. To handle the complexity of the task, we propose the Hand Pose Vision Transformer (HP-ViT). The HP-ViT comprises a ViT backbone and transformer head to estimate joint positions in 3D, utilizing MPJPE and RLE loss function. Our approach achieved the 1st position in the Hand Pose challenge with 25.51 MPJPE and 8.49 PA-MPJPE. Code is available at https://github.com/KanokphanL/PCIE_EgoHandPose
ACTrack: Adding Spatio-Temporal Condition for Visual Object Tracking
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Efficiently modeling spatio-temporal relations of objects is a key challenge in visual object tracking (VOT). Existing methods track by appearance-based similarity or long-term relation modeling, resulting in rich temporal contexts between consecutive frames being easily overlooked. Moreover, training trackers from scratch or fine-tuning large pre-trained models needs more time and memory consumption. In this paper, we present ACTrack, a new tracking framework with additive spatio-temporal conditions. It preserves the quality and capabilities of the pre-trained Transformer backbone by freezing its parameters, and makes a trainable lightweight additive net to model spatio-temporal relations in tracking. We design an additive siamese convolutional network to ensure the integrity of spatial features and perform temporal sequence modeling to simplify the tracking pipeline. Experimental results on several benchmarks prove that ACTrack could balance training efficiency and tracking performance.
Technical Report for Argoverse Challenges on Unified Sensor-based Detection, Tracking, and Forecasting
Nov 27, 2023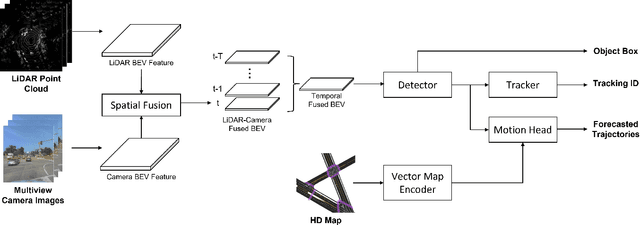
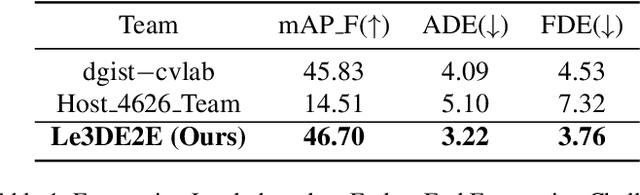
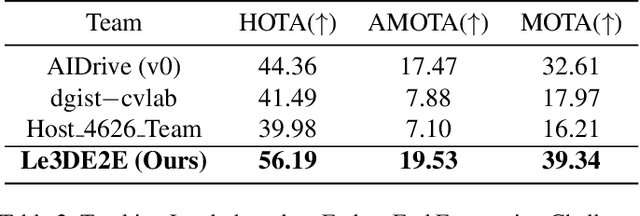
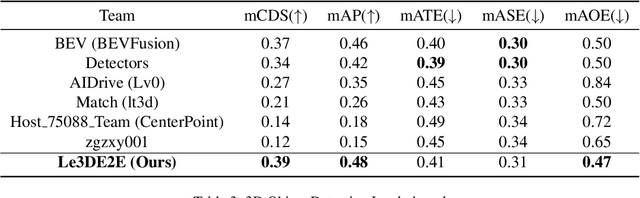
Abstract:This report presents our Le3DE2E solution for unified sensor-based detection, tracking, and forecasting in Argoverse Challenges at CVPR 2023 Workshop on Autonomous Driving (WAD). We propose a unified network that incorporates three tasks, including detection, tracking, and forecasting. This solution adopts a strong Bird's Eye View (BEV) encoder with spatial and temporal fusion and generates unified representations for multi-tasks. The solution was tested in the Argoverse 2 sensor dataset to evaluate the detection, tracking, and forecasting of 26 object categories. We achieved 1st place in Detection, Tracking, and Forecasting on the E2E Forecasting track in Argoverse Challenges at CVPR 2023 WAD.
The 2nd Workshop on Maritime Computer Vision 2024
Nov 23, 2023



Abstract:The 2nd Workshop on Maritime Computer Vision (MaCVi) 2024 addresses maritime computer vision for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) and Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USV). Three challenges categories are considered: (i) UAV-based Maritime Object Tracking with Re-identification, (ii) USV-based Maritime Obstacle Segmentation and Detection, (iii) USV-based Maritime Boat Tracking. The USV-based Maritime Obstacle Segmentation and Detection features three sub-challenges, including a new embedded challenge addressing efficicent inference on real-world embedded devices. This report offers a comprehensive overview of the findings from the challenges. We provide both statistical and qualitative analyses, evaluating trends from over 195 submissions. All datasets, evaluation code, and the leaderboard are available to the public at https://macvi.org/workshop/macvi24.
ReIDTracker Sea: the technical report of BoaTrack and SeaDronesSee-MOT challenge at MaCVi of WACV24
Nov 12, 2023


Abstract:Multi-Object Tracking is one of the most important technologies in maritime computer vision. Our solution tries to explore Multi-Object Tracking in maritime Unmanned Aerial vehicles (UAVs) and Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) usage scenarios. Most of the current Multi-Object Tracking algorithms require complex association strategies and association information (2D location and motion, 3D motion, 3D depth, 2D appearance) to achieve better performance, which makes the entire tracking system extremely complex and heavy. At the same time, most of the current Multi-Object Tracking algorithms still require video annotation data which is costly to obtain for training. Our solution tries to explore Multi-Object Tracking in a completely unsupervised way. The scheme accomplishes instance representation learning by using self-supervision on ImageNet. Then, by cooperating with high-quality detectors, the multi-target tracking task can be completed simply and efficiently. The scheme achieved top 3 performance on both UAV-based Multi-Object Tracking with Reidentification and USV-based Multi-Object Tracking benchmarks and the solution won the championship in many multiple Multi-Object Tracking competitions. such as BDD100K MOT,MOTS, Waymo 2D MOT
1st Place Solution for CVPR2023 BURST Long Tail and Open World Challenges
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Currently, Video Instance Segmentation (VIS) aims at segmenting and categorizing objects in videos from a closed set of training categories that contain only a few dozen of categories, lacking the ability to handle diverse objects in real-world videos. As TAO and BURST datasets release, we have the opportunity to research VIS in long-tailed and open-world scenarios. Traditional VIS methods are evaluated on benchmarks limited to a small number of common classes, But practical applications require trackers that go beyond these common classes, detecting and tracking rare and even never-before-seen objects. Inspired by the latest MOT paper for the long tail task (Tracking Every Thing in the Wild, Siyuan Li et), for the BURST long tail challenge, we train our model on a combination of LVISv0.5 and the COCO dataset using repeat factor sampling. First, train the detector with segmentation and CEM on LVISv0.5 + COCO dataset. And then, train the instance appearance similarity head on the TAO dataset. at last, our method (LeTracker) gets 14.9 HOTAall in the BURST test set, ranking 1st in the benchmark. for the open-world challenges, we only use 64 classes (Intersection classes of BURST Train subset and COCO dataset, without LVIS dataset) annotations data training, and testing on BURST test set data and get 61.4 OWTAall, ranking 1st in the benchmark. Our code will be released to facilitate future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge