Jianwei Shuai
XBound-Former: Toward Cross-scale Boundary Modeling in Transformers
Jun 02, 2022



Abstract:Skin lesion segmentation from dermoscopy images is of great significance in the quantitative analysis of skin cancers, which is yet challenging even for dermatologists due to the inherent issues, i.e., considerable size, shape and color variation, and ambiguous boundaries. Recent vision transformers have shown promising performance in handling the variation through global context modeling. Still, they have not thoroughly solved the problem of ambiguous boundaries as they ignore the complementary usage of the boundary knowledge and global contexts. In this paper, we propose a novel cross-scale boundary-aware transformer, \textbf{XBound-Former}, to simultaneously address the variation and boundary problems of skin lesion segmentation. XBound-Former is a purely attention-based network and catches boundary knowledge via three specially designed learners. We evaluate the model on two skin lesion datasets, ISIC-2016\&PH$^2$ and ISIC-2018, where our model consistently outperforms other convolution- and transformer-based models, especially on the boundary-wise metrics. We extensively verify the generalization ability of polyp lesion segmentation that has similar characteristics, and our model can also yield significant improvement compared to the latest models.
Lane detection with Position Embedding
Mar 23, 2022
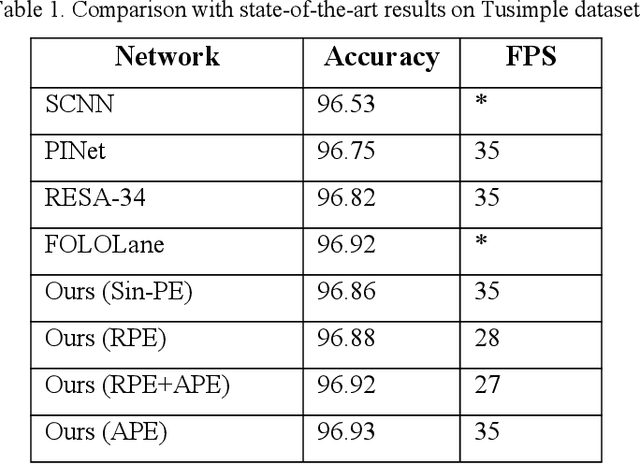

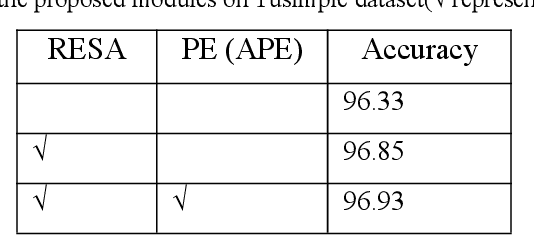
Abstract:Recently, lane detection has made great progress in autonomous driving. RESA (REcurrent Feature-Shift Aggregator) is based on image segmentation. It presents a novel module to enrich lane feature after preliminary feature extraction with an ordinary CNN. For Tusimple dataset, there is not too complicated scene and lane has more prominent spatial features. On the basis of RESA, we introduce the method of position embedding to enhance the spatial features. The experimental results show that this method has achieved the best accuracy 96.93% on Tusimple dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge