Jun Hou
Fed-NDIF: A Noise-Embedded Federated Diffusion Model For Low-Count Whole-Body PET Denoising
Mar 20, 2025



Abstract:Low-count positron emission tomography (LCPET) imaging can reduce patients' exposure to radiation but often suffers from increased image noise and reduced lesion detectability, necessitating effective denoising techniques. Diffusion models have shown promise in LCPET denoising for recovering degraded image quality. However, training such models requires large and diverse datasets, which are challenging to obtain in the medical domain. To address data scarcity and privacy concerns, we combine diffusion models with federated learning -- a decentralized training approach where models are trained individually at different sites, and their parameters are aggregated on a central server over multiple iterations. The variation in scanner types and image noise levels within and across institutions poses additional challenges for federated learning in LCPET denoising. In this study, we propose a novel noise-embedded federated learning diffusion model (Fed-NDIF) to address these challenges, leveraging a multicenter dataset and varying count levels. Our approach incorporates liver normalized standard deviation (NSTD) noise embedding into a 2.5D diffusion model and utilizes the Federated Averaging (FedAvg) algorithm to aggregate locally trained models into a global model, which is subsequently fine-tuned on local datasets to optimize performance and obtain personalized models. Extensive validation on datasets from the University of Bern, Ruijin Hospital in Shanghai, and Yale-New Haven Hospital demonstrates the superior performance of our method in enhancing image quality and improving lesion quantification. The Fed-NDIF model shows significant improvements in PSNR, SSIM, and NMSE of the entire 3D volume, as well as enhanced lesion detectability and quantification, compared to local diffusion models and federated UNet-based models.
Explainable AI for Clinical Outcome Prediction: A Survey of Clinician Perceptions and Preferences
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Explainable AI (XAI) techniques are necessary to help clinicians make sense of AI predictions and integrate predictions into their decision-making workflow. In this work, we conduct a survey study to understand clinician preference among different XAI techniques when they are used to interpret model predictions over text-based EHR data. We implement four XAI techniques (LIME, Attention-based span highlights, exemplar patient retrieval, and free-text rationales generated by LLMs) on an outcome prediction model that uses ICU admission notes to predict a patient's likelihood of experiencing in-hospital mortality. Using these XAI implementations, we design and conduct a survey study of 32 practicing clinicians, collecting their feedback and preferences on the four techniques. We synthesize our findings into a set of recommendations describing when each of the XAI techniques may be more appropriate, their potential limitations, as well as recommendations for improvement.
CFTrack: Enhancing Lightweight Visual Tracking through Contrastive Learning and Feature Matching
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Achieving both efficiency and strong discriminative ability in lightweight visual tracking is a challenge, especially on mobile and edge devices with limited computational resources. Conventional lightweight trackers often struggle with robustness under occlusion and interference, while deep trackers, when compressed to meet resource constraints, suffer from performance degradation. To address these issues, we introduce CFTrack, a lightweight tracker that integrates contrastive learning and feature matching to enhance discriminative feature representations. CFTrack dynamically assesses target similarity during prediction through a novel contrastive feature matching module optimized with an adaptive contrastive loss, thereby improving tracking accuracy. Extensive experiments on LaSOT, OTB100, and UAV123 show that CFTrack surpasses many state-of-the-art lightweight trackers, operating at 136 frames per second on the NVIDIA Jetson NX platform. Results on the HOOT dataset further demonstrate CFTrack's strong discriminative ability under heavy occlusion.
A Comprehensive Survey on the Trustworthiness of Large Language Models in Healthcare
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:The application of large language models (LLMs) in healthcare has the potential to revolutionize clinical decision-making, medical research, and patient care. As LLMs are increasingly integrated into healthcare systems, several critical challenges must be addressed to ensure their reliable and ethical deployment. These challenges include truthfulness, where models generate misleading information; privacy, with risks of unintentional data retention; robustness, requiring defenses against adversarial attacks; fairness, addressing biases in clinical outcomes; explainability, ensuring transparent decision-making; and safety, mitigating risks of misinformation and medical errors. Recently, researchers have begun developing benchmarks and evaluation frameworks to systematically assess the trustworthiness of LLMs. However, the trustworthiness of LLMs in healthcare remains underexplored, lacking a systematic review that provides a comprehensive understanding and future insights into this area. This survey bridges this gap by providing a comprehensive overview of the recent research of existing methodologies and solutions aimed at mitigating the above risks in healthcare. By focusing on key trustworthiness dimensions including truthfulness, privacy and safety, robustness, fairness and bias, and explainability, we present a thorough analysis of how these issues impact the reliability and ethical use of LLMs in healthcare. This paper highlights ongoing efforts and offers insights into future research directions to ensure the safe and trustworthy deployment of LLMs in healthcare.
HMIL: Hierarchical Multi-Instance Learning for Fine-Grained Whole Slide Image Classification
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:Fine-grained classification of whole slide images (WSIs) is essential in precision oncology, enabling precise cancer diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies. The core of this task involves distinguishing subtle morphological variations within the same broad category of gigapixel-resolution images, which presents a significant challenge. While the multi-instance learning (MIL) paradigm alleviates the computational burden of WSIs, existing MIL methods often overlook hierarchical label correlations, treating fine-grained classification as a flat multi-class classification task. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel hierarchical multi-instance learning (HMIL) framework. By facilitating on the hierarchical alignment of inherent relationships between different hierarchy of labels at instance and bag level, our approach provides a more structured and informative learning process. Specifically, HMIL incorporates a class-wise attention mechanism that aligns hierarchical information at both the instance and bag levels. Furthermore, we introduce supervised contrastive learning to enhance the discriminative capability for fine-grained classification and a curriculum-based dynamic weighting module to adaptively balance the hierarchical feature during training. Extensive experiments on our large-scale cytology cervical cancer (CCC) dataset and two public histology datasets, BRACS and PANDA, demonstrate the state-of-the-art class-wise and overall performance of our HMIL framework. Our source code is available at https://github.com/ChengJin-git/HMIL.
2.5D Multi-view Averaging Diffusion Model for 3D Medical Image Translation: Application to Low-count PET Reconstruction with CT-less Attenuation Correction
Jun 12, 2024
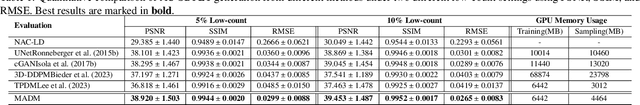

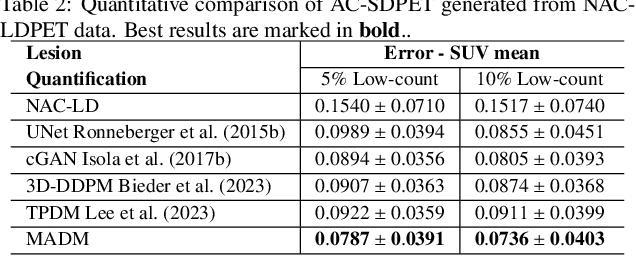
Abstract:Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is an important clinical imaging tool but inevitably introduces radiation hazards to patients and healthcare providers. Reducing the tracer injection dose and eliminating the CT acquisition for attenuation correction can reduce the overall radiation dose, but often results in PET with high noise and bias. Thus, it is desirable to develop 3D methods to translate the non-attenuation-corrected low-dose PET (NAC-LDPET) into attenuation-corrected standard-dose PET (AC-SDPET). Recently, diffusion models have emerged as a new state-of-the-art deep learning method for image-to-image translation, better than traditional CNN-based methods. However, due to the high computation cost and memory burden, it is largely limited to 2D applications. To address these challenges, we developed a novel 2.5D Multi-view Averaging Diffusion Model (MADM) for 3D image-to-image translation with application on NAC-LDPET to AC-SDPET translation. Specifically, MADM employs separate diffusion models for axial, coronal, and sagittal views, whose outputs are averaged in each sampling step to ensure the 3D generation quality from multiple views. To accelerate the 3D sampling process, we also proposed a strategy to use the CNN-based 3D generation as a prior for the diffusion model. Our experimental results on human patient studies suggested that MADM can generate high-quality 3D translation images, outperforming previous CNN-based and Diffusion-based baseline methods.
SceneX:Procedural Controllable Large-scale Scene Generation via Large-language Models
Mar 23, 2024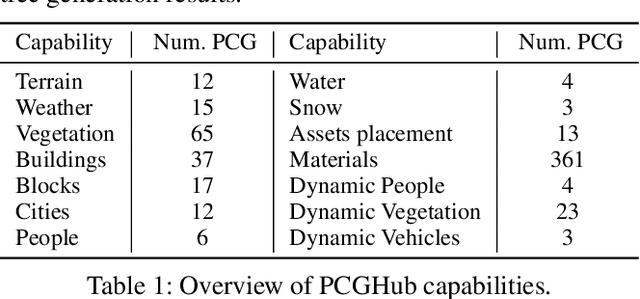

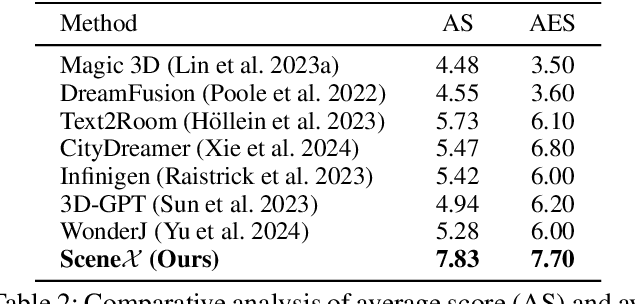
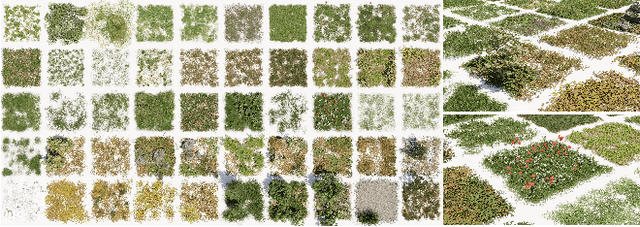
Abstract:Due to its great application potential, large-scale scene generation has drawn extensive attention in academia and industry. Recent research employs powerful generative models to create desired scenes and achieves promising results. However, most of these methods represent the scene using 3D primitives (e.g. point cloud or radiance field) incompatible with the industrial pipeline, which leads to a substantial gap between academic research and industrial deployment. Procedural Controllable Generation (PCG) is an efficient technique for creating scalable and high-quality assets, but it is unfriendly for ordinary users as it demands profound domain expertise. To address these issues, we resort to using the large language model (LLM) to drive the procedural modeling. In this paper, we introduce a large-scale scene generation framework, SceneX, which can automatically produce high-quality procedural models according to designers' textual descriptions.Specifically, the proposed method comprises two components, PCGBench and PCGPlanner. The former encompasses an extensive collection of accessible procedural assets and thousands of hand-craft API documents. The latter aims to generate executable actions for Blender to produce controllable and precise 3D assets guided by the user's instructions. Our SceneX can generate a city spanning 2.5 km times 2.5 km with delicate layout and geometric structures, drastically reducing the time cost from several weeks for professional PCG engineers to just a few hours for an ordinary user. Extensive experiments demonstrated the capability of our method in controllable large-scale scene generation and editing, including asset placement and season translation.
DiPrompT: Disentangled Prompt Tuning for Multiple Latent Domain Generalization in Federated Learning
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for learning from decentralized data, and federated domain generalization further considers the test dataset (target domain) is absent from the decentralized training data (source domains). However, most existing FL methods assume that domain labels are provided during training, and their evaluation imposes explicit constraints on the number of domains, which must strictly match the number of clients. Because of the underutilization of numerous edge devices and additional cross-client domain annotations in the real world, such restrictions may be impractical and involve potential privacy leaks. In this paper, we propose an efficient and novel approach, called Disentangled Prompt Tuning (DiPrompT), a method that tackles the above restrictions by learning adaptive prompts for domain generalization in a distributed manner. Specifically, we first design two types of prompts, i.e., global prompt to capture general knowledge across all clients and domain prompts to capture domain-specific knowledge. They eliminate the restriction on the one-to-one mapping between source domains and local clients. Furthermore, a dynamic query metric is introduced to automatically search the suitable domain label for each sample, which includes two-substep text-image alignments based on prompt tuning without labor-intensive annotation. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that our DiPrompT achieves superior domain generalization performance over state-of-the-art FL methods when domain labels are not provided, and even outperforms many centralized learning methods using domain labels.
POUR-Net: A Population-Prior-Aided Over-Under-Representation Network for Low-Count PET Attenuation Map Generation
Jan 25, 2024



Abstract:Low-dose PET offers a valuable means of minimizing radiation exposure in PET imaging. However, the prevalent practice of employing additional CT scans for generating attenuation maps (u-map) for PET attenuation correction significantly elevates radiation doses. To address this concern and further mitigate radiation exposure in low-dose PET exams, we propose POUR-Net - an innovative population-prior-aided over-under-representation network that aims for high-quality attenuation map generation from low-dose PET. First, POUR-Net incorporates an over-under-representation network (OUR-Net) to facilitate efficient feature extraction, encompassing both low-resolution abstracted and fine-detail features, for assisting deep generation on the full-resolution level. Second, complementing OUR-Net, a population prior generation machine (PPGM) utilizing a comprehensive CT-derived u-map dataset, provides additional prior information to aid OUR-Net generation. The integration of OUR-Net and PPGM within a cascade framework enables iterative refinement of $\mu$-map generation, resulting in the production of high-quality $\mu$-maps. Experimental results underscore the effectiveness of POUR-Net, showing it as a promising solution for accurate CT-free low-count PET attenuation correction, which also surpasses the performance of previous baseline methods.
Combating Data Imbalances in Federated Semi-supervised Learning with Dual Regulators
Jul 16, 2023



Abstract:Federated learning has become a popular method to learn from decentralized heterogeneous data. Federated semi-supervised learning (FSSL) emerges to train models from a small fraction of labeled data due to label scarcity on decentralized clients. Existing FSSL methods assume independent and identically distributed (IID) labeled data across clients and consistent class distribution between labeled and unlabeled data within a client. This work studies a more practical and challenging scenario of FSSL, where data distribution is different not only across clients but also within a client between labeled and unlabeled data. To address this challenge, we propose a novel FSSL framework with dual regulators, FedDure.} FedDure lifts the previous assumption with a coarse-grained regulator (C-reg) and a fine-grained regulator (F-reg): C-reg regularizes the updating of the local model by tracking the learning effect on labeled data distribution; F-reg learns an adaptive weighting scheme tailored for unlabeled instances in each client. We further formulate the client model training as bi-level optimization that adaptively optimizes the model in the client with two regulators. Theoretically, we show the convergence guarantee of the dual regulators. Empirically, we demonstrate that FedDure is superior to the existing methods across a wide range of settings, notably by more than 11% on CIFAR-10 and CINIC-10 datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge