Sindhura Kommu
A Comprehensive Survey on the Trustworthiness of Large Language Models in Healthcare
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:The application of large language models (LLMs) in healthcare has the potential to revolutionize clinical decision-making, medical research, and patient care. As LLMs are increasingly integrated into healthcare systems, several critical challenges must be addressed to ensure their reliable and ethical deployment. These challenges include truthfulness, where models generate misleading information; privacy, with risks of unintentional data retention; robustness, requiring defenses against adversarial attacks; fairness, addressing biases in clinical outcomes; explainability, ensuring transparent decision-making; and safety, mitigating risks of misinformation and medical errors. Recently, researchers have begun developing benchmarks and evaluation frameworks to systematically assess the trustworthiness of LLMs. However, the trustworthiness of LLMs in healthcare remains underexplored, lacking a systematic review that provides a comprehensive understanding and future insights into this area. This survey bridges this gap by providing a comprehensive overview of the recent research of existing methodologies and solutions aimed at mitigating the above risks in healthcare. By focusing on key trustworthiness dimensions including truthfulness, privacy and safety, robustness, fairness and bias, and explainability, we present a thorough analysis of how these issues impact the reliability and ethical use of LLMs in healthcare. This paper highlights ongoing efforts and offers insights into future research directions to ensure the safe and trustworthy deployment of LLMs in healthcare.
Gene Regulatory Network Inference from Pre-trained Single-Cell Transcriptomics Transformer with Joint Graph Learning
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:Inferring gene regulatory networks (GRNs) from single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data is a complex challenge that requires capturing the intricate relationships between genes and their regulatory interactions. In this study, we tackle this challenge by leveraging the single-cell BERT-based pre-trained transformer model (scBERT), trained on extensive unlabeled scRNA-seq data, to augment structured biological knowledge from existing GRNs. We introduce a novel joint graph learning approach that combines the rich contextual representations learned by pre-trained single-cell language models with the structured knowledge encoded in GRNs using graph neural networks (GNNs). By integrating these two modalities, our approach effectively reasons over boththe gene expression level constraints provided by the scRNA-seq data and the structured biological knowledge inherent in GRNs. We evaluate our method on human cell benchmark datasets from the BEELINE study with cell type-specific ground truth networks. The results demonstrate superior performance over current state-of-the-art baselines, offering a deeper understanding of cellular regulatory mechanisms.
AI for Biomedicine in the Era of Large Language Models
Mar 23, 2024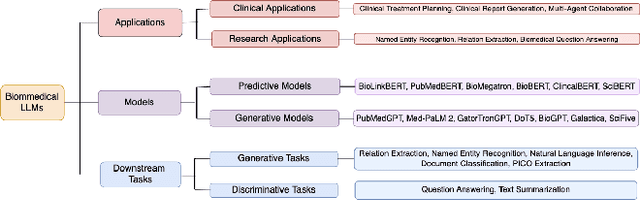
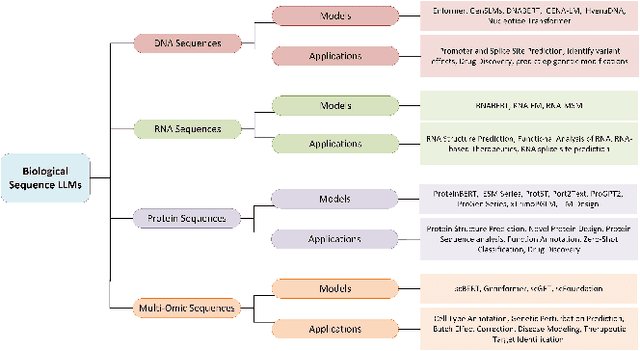
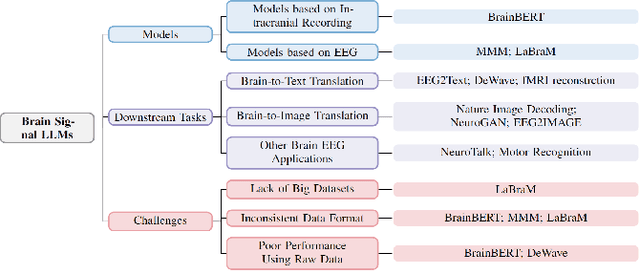
Abstract:The capabilities of AI for biomedicine span a wide spectrum, from the atomic level, where it solves partial differential equations for quantum systems, to the molecular level, predicting chemical or protein structures, and further extending to societal predictions like infectious disease outbreaks. Recent advancements in large language models, exemplified by models like ChatGPT, have showcased significant prowess in natural language tasks, such as translating languages, constructing chatbots, and answering questions. When we consider biomedical data, we observe a resemblance to natural language in terms of sequences: biomedical literature and health records presented as text, biological sequences or sequencing data arranged in sequences, or sensor data like brain signals as time series. The question arises: Can we harness the potential of recent large language models to drive biomedical knowledge discoveries? In this survey, we will explore the application of large language models to three crucial categories of biomedical data: 1) textual data, 2) biological sequences, and 3) brain signals. Furthermore, we will delve into large language model challenges in biomedical research, including ensuring trustworthiness, achieving personalization, and adapting to multi-modal data representation
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge