Huiyuan Fu
MUSE: Multi-Subject Unified Synthesis via Explicit Layout Semantic Expansion
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Existing text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating high-quality images guided by textual prompts. However, achieving multi-subject compositional synthesis with precise spatial control remains a significant challenge. In this work, we address the task of layout-controllable multi-subject synthesis (LMS), which requires both faithful reconstruction of reference subjects and their accurate placement in specified regions within a unified image. While recent advancements have separately improved layout control and subject synthesis, existing approaches struggle to simultaneously satisfy the dual requirements of spatial precision and identity preservation in this composite task. To bridge this gap, we propose MUSE, a unified synthesis framework that employs concatenated cross-attention (CCA) to seamlessly integrate layout specifications with textual guidance through explicit semantic space expansion. The proposed CCA mechanism enables bidirectional modality alignment between spatial constraints and textual descriptions without interference. Furthermore, we design a progressive two-stage training strategy that decomposes the LMS task into learnable sub-objectives for effective optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MUSE achieves zero-shot end-to-end generation with superior spatial accuracy and identity consistency compared to existing solutions, advancing the frontier of controllable image synthesis. Our code and model are available at https://github.com/pf0607/MUSE.
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Image Super-Resolution ($\times$4): Methods and Results
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:This paper presents the NTIRE 2025 image super-resolution ($\times$4) challenge, one of the associated competitions of the 10th NTIRE Workshop at CVPR 2025. The challenge aims to recover high-resolution (HR) images from low-resolution (LR) counterparts generated through bicubic downsampling with a $\times$4 scaling factor. The objective is to develop effective network designs or solutions that achieve state-of-the-art SR performance. To reflect the dual objectives of image SR research, the challenge includes two sub-tracks: (1) a restoration track, emphasizes pixel-wise accuracy and ranks submissions based on PSNR; (2) a perceptual track, focuses on visual realism and ranks results by a perceptual score. A total of 286 participants registered for the competition, with 25 teams submitting valid entries. This report summarizes the challenge design, datasets, evaluation protocol, the main results, and methods of each team. The challenge serves as a benchmark to advance the state of the art and foster progress in image SR.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Image Denoising Challenge Report
Apr 16, 2025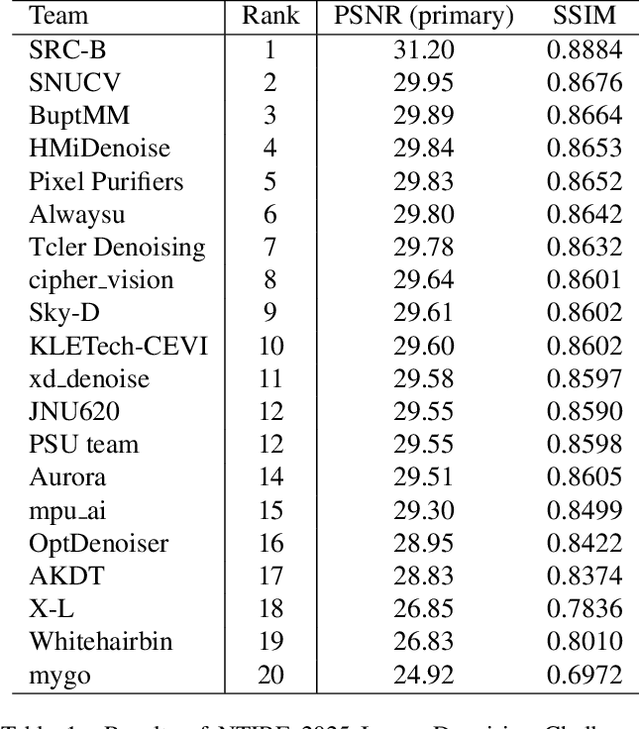


Abstract:This paper presents an overview of the NTIRE 2025 Image Denoising Challenge ({\sigma} = 50), highlighting the proposed methodologies and corresponding results. The primary objective is to develop a network architecture capable of achieving high-quality denoising performance, quantitatively evaluated using PSNR, without constraints on computational complexity or model size. The task assumes independent additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) with a fixed noise level of 50. A total of 290 participants registered for the challenge, with 20 teams successfully submitting valid results, providing insights into the current state-of-the-art in image denoising.
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Event-Based Image Deblurring: Methods and Results
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an overview of NTIRE 2025 the First Challenge on Event-Based Image Deblurring, detailing the proposed methodologies and corresponding results. The primary goal of the challenge is to design an event-based method that achieves high-quality image deblurring, with performance quantitatively assessed using Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR). Notably, there are no restrictions on computational complexity or model size. The task focuses on leveraging both events and images as inputs for single-image deblurring. A total of 199 participants registered, among whom 15 teams successfully submitted valid results, offering valuable insights into the current state of event-based image deblurring. We anticipate that this challenge will drive further advancements in event-based vision research.
XR-VLM: Cross-Relationship Modeling with Multi-part Prompts and Visual Features for Fine-Grained Recognition
Mar 10, 2025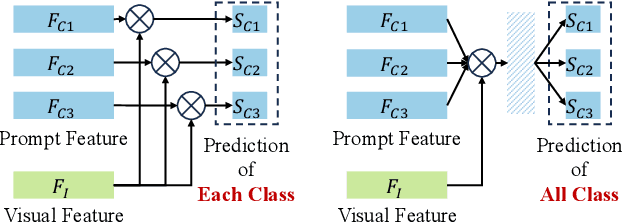
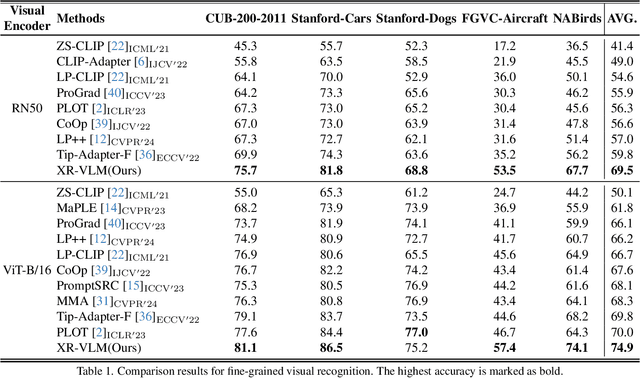
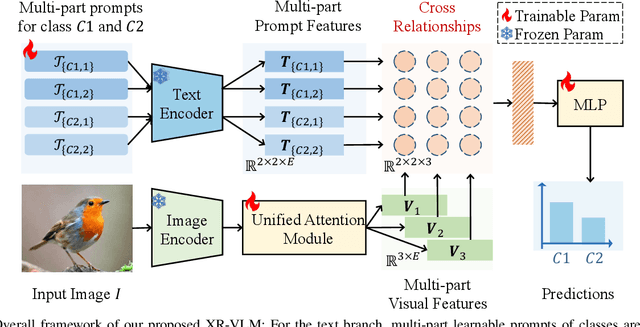
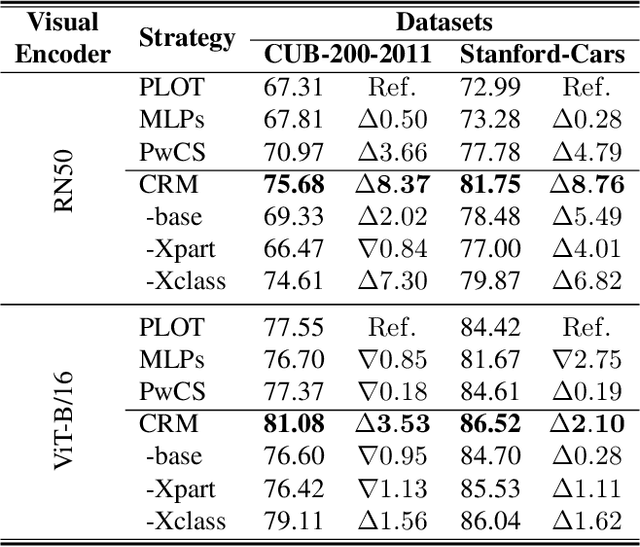
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance on various visual tasks, yet they still require adaptation on downstream tasks to achieve optimal performance. Recently, various adaptation technologies have been proposed, but we observe they often underperform in fine-grained visual recognition, which requires models to capture subtle yet discriminative features to distinguish similar sub-categories. Current adaptation methods typically rely on an alignment-based prediction framework, \ie the visual feature is compared with each class prompt for similarity calculation as the final prediction, which lacks class interaction during the forward pass. Besides, learning single uni-modal feature further restricts the model's expressive capacity. Therefore, we propose a novel mechanism, XR-VLM, to discover subtle differences by modeling cross-relationships, which specifically excels in scenarios involving multiple features. Our method introduces a unified multi-part visual feature extraction module designed to seamlessly integrate with the diverse backbones inherent in VLMs. Additionally, we develop a multi-part prompt learning module to capture multi-perspective descriptions of sub-categories. To further enhance discriminative capability, we propose a cross relationship modeling pattern that combines visual feature with all class prompt features, enabling a deeper exploration of the relationships between these two modalities. Extensive experiments have been conducted on various fine-grained datasets, and the results demonstrate that our method achieves significant improvements compared to current state-of-the-art approaches. Code will be released.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Short-form UGC Video Quality Assessment: Methods and Results
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Shortform UGC Video Quality Assessment (S-UGC VQA), where various excellent solutions are submitted and evaluated on the collected dataset KVQ from popular short-form video platform, i.e., Kuaishou/Kwai Platform. The KVQ database is divided into three parts, including 2926 videos for training, 420 videos for validation, and 854 videos for testing. The purpose is to build new benchmarks and advance the development of S-UGC VQA. The competition had 200 participants and 13 teams submitted valid solutions for the final testing phase. The proposed solutions achieved state-of-the-art performances for S-UGC VQA. The project can be found at https://github.com/lixinustc/KVQChallenge-CVPR-NTIRE2024.
Learning Exposure Correction in Dynamic Scenes
Mar 10, 2024Abstract:Capturing videos with wrong exposure usually produces unsatisfactory visual effects. While image exposure correction is a popular topic, the video counterpart is less explored in the literature. Directly applying prior image-based methods to input videos often results in temporal incoherence with low visual quality. Existing research in this area is also limited by the lack of high-quality benchmark datasets. To address these issues, we construct the first real-world paired video dataset, including both underexposure and overexposure dynamic scenes. To achieve spatial alignment, we utilize two DSLR cameras and a beam splitter to simultaneously capture improper and normal exposure videos. In addition, we propose a Video Exposure Correction Network (VECNet) based on Retinex theory, which incorporates a two-stream illumination learning mechanism to enhance the overexposure and underexposure factors, respectively. The estimated multi-frame reflectance and dual-path illumination components are fused at both feature and image levels, leading to visually appealing results. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing image exposure correction and underexposed video enhancement methods. The code and dataset will be available soon.
Region-Aware Exposure Consistency Network for Mixed Exposure Correction
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:Exposure correction aims to enhance images suffering from improper exposure to achieve satisfactory visual effects. Despite recent progress, existing methods generally mitigate either overexposure or underexposure in input images, and they still struggle to handle images with mixed exposure, i.e., one image incorporates both overexposed and underexposed regions. The mixed exposure distribution is non-uniform and leads to varying representation, which makes it challenging to address in a unified process. In this paper, we introduce an effective Region-aware Exposure Correction Network (RECNet) that can handle mixed exposure by adaptively learning and bridging different regional exposure representations. Specifically, to address the challenge posed by mixed exposure disparities, we develop a region-aware de-exposure module that effectively translates regional features of mixed exposure scenarios into an exposure-invariant feature space. Simultaneously, as de-exposure operation inevitably reduces discriminative information, we introduce a mixed-scale restoration unit that integrates exposure-invariant features and unprocessed features to recover local information. To further achieve a uniform exposure distribution in the global image, we propose an exposure contrastive regularization strategy under the constraints of intra-regional exposure consistency and inter-regional exposure continuity. Extensive experiments are conducted on various datasets, and the experimental results demonstrate the superiority and generalization of our proposed method. The code is released at: https://github.com/kravrolens/RECNet.
Mutual Distillation Learning For Person Re-Identification
Jan 12, 2024Abstract:With the rapid advancements in deep learning technologies, person re-identification (ReID) has witnessed remarkable performance improvements. However, the majority of prior works have traditionally focused on solving the problem via extracting features solely from a single perspective, such as uniform partitioning, hard attention mechanisms, or semantic masks. While these approaches have demonstrated efficacy within specific contexts, they fall short in diverse situations. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, Mutual Distillation Learning For Person Re-identification (termed as MDPR), which addresses the challenging problem from multiple perspectives within a single unified model, leveraging the power of mutual distillation to enhance the feature representations collectively. Specifically, our approach encompasses two branches: a hard content branch to extract local features via a uniform horizontal partitioning strategy and a Soft Content Branch to dynamically distinguish between foreground and background and facilitate the extraction of multi-granularity features via a carefully designed attention mechanism. To facilitate knowledge exchange between these two branches, a mutual distillation and fusion process is employed, promoting the capability of the outputs of each branch. Extensive experiments are conducted on widely used person ReID datasets to validate the effectiveness and superiority of our approach. Notably, our method achieves an impressive $88.7\%/94.4\%$ in mAP/Rank-1 on the DukeMTMC-reID dataset, surpassing the current state-of-the-art results. Our source code is available at https://github.com/KuilongCui/MDPR.
An Empirical Study and Analysis of Learning Generalizable Manipulation Skill in the SAPIEN Simulator
Aug 31, 2022
Abstract:This paper provides a brief overview of our submission to the no interaction track of SAPIEN ManiSkill Challenge 2021. Our approach follows an end-to-end pipeline which mainly consists of two steps: we first extract the point cloud features of multiple objects; then we adopt these features to predict the action score of the robot simulators through a deep and wide transformer-based network. More specially, %to give guidance for future work, to open up avenues for exploitation of learning manipulation skill, we present an empirical study that includes a bag of tricks and abortive attempts. Finally, our method achieves a promising ranking on the leaderboard. All code of our solution is available at https://github.com/liu666666/bigfish\_codes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge