Henming Mao
XR-VLM: Cross-Relationship Modeling with Multi-part Prompts and Visual Features for Fine-Grained Recognition
Mar 10, 2025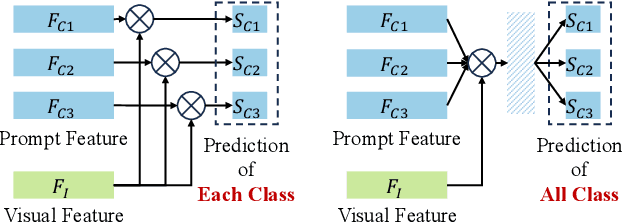
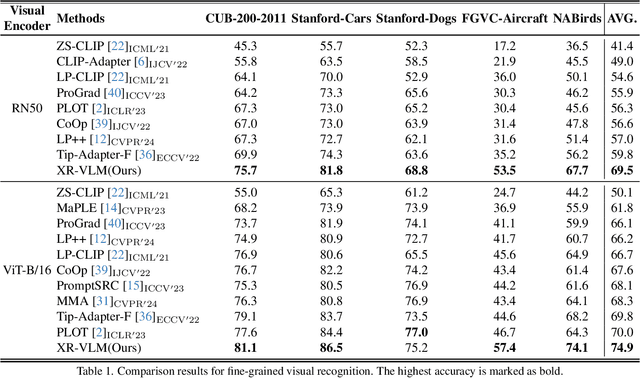
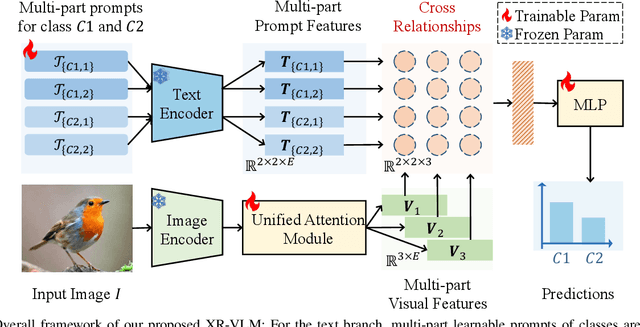
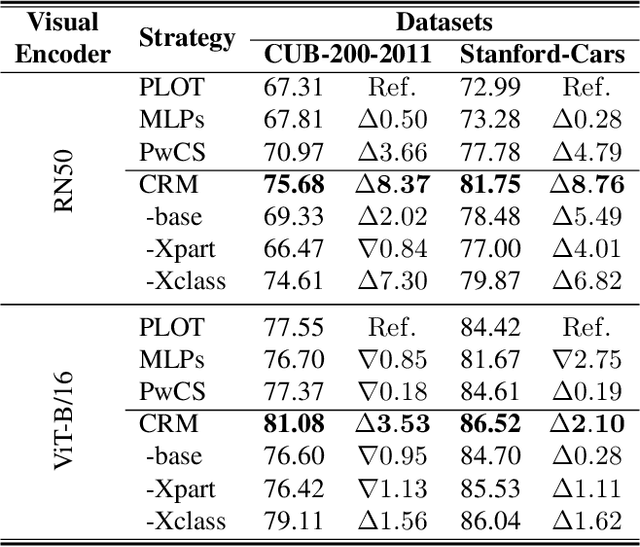
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance on various visual tasks, yet they still require adaptation on downstream tasks to achieve optimal performance. Recently, various adaptation technologies have been proposed, but we observe they often underperform in fine-grained visual recognition, which requires models to capture subtle yet discriminative features to distinguish similar sub-categories. Current adaptation methods typically rely on an alignment-based prediction framework, \ie the visual feature is compared with each class prompt for similarity calculation as the final prediction, which lacks class interaction during the forward pass. Besides, learning single uni-modal feature further restricts the model's expressive capacity. Therefore, we propose a novel mechanism, XR-VLM, to discover subtle differences by modeling cross-relationships, which specifically excels in scenarios involving multiple features. Our method introduces a unified multi-part visual feature extraction module designed to seamlessly integrate with the diverse backbones inherent in VLMs. Additionally, we develop a multi-part prompt learning module to capture multi-perspective descriptions of sub-categories. To further enhance discriminative capability, we propose a cross relationship modeling pattern that combines visual feature with all class prompt features, enabling a deeper exploration of the relationships between these two modalities. Extensive experiments have been conducted on various fine-grained datasets, and the results demonstrate that our method achieves significant improvements compared to current state-of-the-art approaches. Code will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge