Hendrik P. A. Lensch
MatSpray: Fusing 2D Material World Knowledge on 3D Geometry
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Manual modeling of material parameters and 3D geometry is a time consuming yet essential task in the gaming and film industries. While recent advances in 3D reconstruction have enabled accurate approximations of scene geometry and appearance, these methods often fall short in relighting scenarios due to the lack of precise, spatially varying material parameters. At the same time, diffusion models operating on 2D images have shown strong performance in predicting physically based rendering (PBR) properties such as albedo, roughness, and metallicity. However, transferring these 2D material maps onto reconstructed 3D geometry remains a significant challenge. We propose a framework for fusing 2D material data into 3D geometry using a combination of novel learning-based and projection-based approaches. We begin by reconstructing scene geometry via Gaussian Splatting. From the input images, a diffusion model generates 2D maps for albedo, roughness, and metallic parameters. Any existing diffusion model that can convert images or videos to PBR materials can be applied. The predictions are further integrated into the 3D representation either by optimizing an image-based loss or by directly projecting the material parameters onto the Gaussians using Gaussian ray tracing. To enhance fine-scale accuracy and multi-view consistency, we further introduce a light-weight neural refinement step (Neural Merger), which takes ray-traced material features as input and produces detailed adjustments. Our results demonstrate that the proposed methods outperform existing techniques in both quantitative metrics and perceived visual realism. This enables more accurate, relightable, and photorealistic renderings from reconstructed scenes, significantly improving the realism and efficiency of asset creation workflows in content production pipelines.
3D-RE-GEN: 3D Reconstruction of Indoor Scenes with a Generative Framework
Dec 19, 2025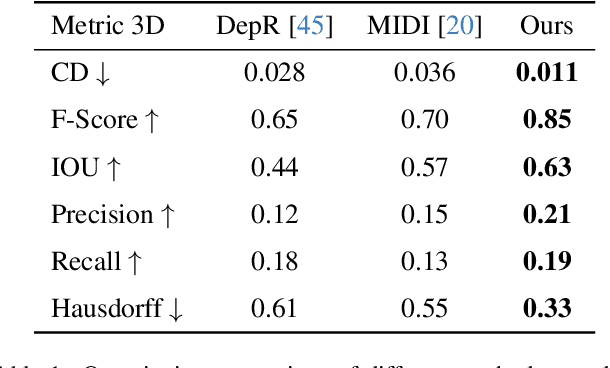
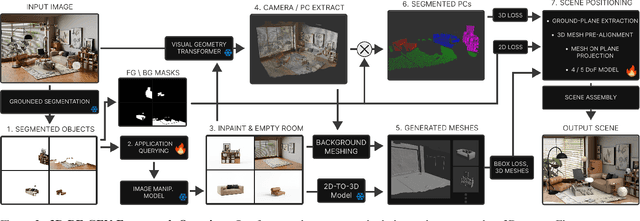
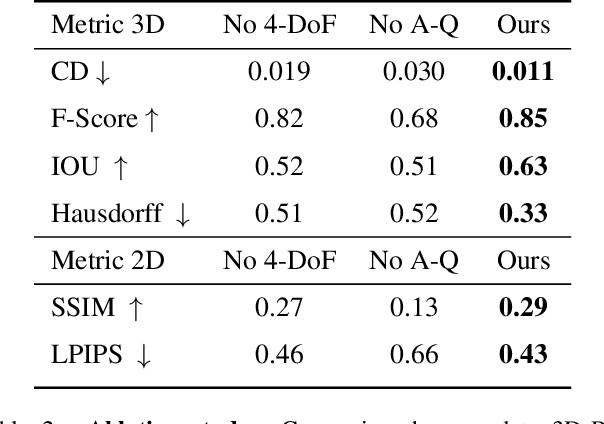
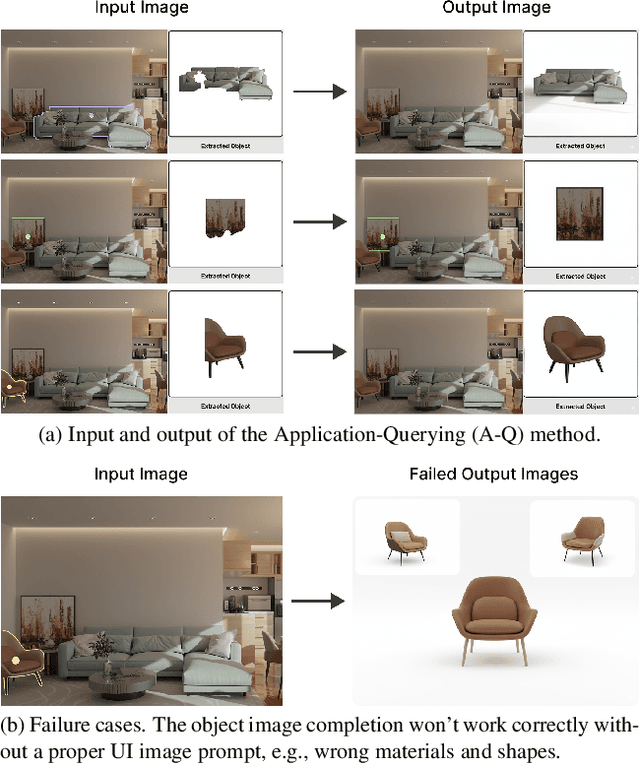
Abstract:Recent advances in 3D scene generation produce visually appealing output, but current representations hinder artists' workflows that require modifiable 3D textured mesh scenes for visual effects and game development. Despite significant advances, current textured mesh scene reconstruction methods are far from artist ready, suffering from incorrect object decomposition, inaccurate spatial relationships, and missing backgrounds. We present 3D-RE-GEN, a compositional framework that reconstructs a single image into textured 3D objects and a background. We show that combining state of the art models from specific domains achieves state of the art scene reconstruction performance, addressing artists' requirements. Our reconstruction pipeline integrates models for asset detection, reconstruction, and placement, pushing certain models beyond their originally intended domains. Obtaining occluded objects is treated as an image editing task with generative models to infer and reconstruct with scene level reasoning under consistent lighting and geometry. Unlike current methods, 3D-RE-GEN generates a comprehensive background that spatially constrains objects during optimization and provides a foundation for realistic lighting and simulation tasks in visual effects and games. To obtain physically realistic layouts, we employ a novel 4-DoF differentiable optimization that aligns reconstructed objects with the estimated ground plane. 3D-RE-GEN~achieves state of the art performance in single image 3D scene reconstruction, producing coherent, modifiable scenes through compositional generation guided by precise camera recovery and spatial optimization.
Memory-Enhanced SAM3 for Occlusion-Robust Surgical Instrument Segmentation
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Accurate surgical instrument segmentation in endoscopic videos is crucial for computer-assisted interventions, yet remains challenging due to frequent occlusions, rapid motion, specular artefacts, and long-term instrument re-entry. While SAM3 provides a powerful spatio-temporal framework for video object segmentation, its performance in surgical scenes is limited by indiscriminate memory updates, fixed memory capacity, and weak identity recovery after occlusions. We propose ReMeDI-SAM3, a training-free memory-enhanced extension of SAM3, that addresses these limitations through three components: (i) relevance-aware memory filtering with a dedicated occlusion-aware memory for storing pre-occlusion frames, (ii) a piecewise interpolation scheme that expands the effective memory capacity, and (iii) a feature-based re-identification module with temporal voting for reliable post-occlusion identity disambiguation. Together, these components mitigate error accumulation and enable reliable recovery after occlusions. Evaluations on EndoVis17 and EndoVis18 under a zero-shot setting show absolute mcIoU improvements of around 7% and 16%, respectively, over vanilla SAM3, outperforming even prior training-based approaches. Project page: https://valaybundele.github.io/remedi-sam3/.
FrameDiffuser: G-Buffer-Conditioned Diffusion for Neural Forward Frame Rendering
Dec 18, 2025



Abstract:Neural rendering for interactive applications requires translating geometric and material properties (G-buffer) to photorealistic images with realistic lighting on a frame-by-frame basis. While recent diffusion-based approaches show promise for G-buffer-conditioned image synthesis, they face critical limitations: single-image models like RGBX generate frames independently without temporal consistency, while video models like DiffusionRenderer are too computationally expensive for most consumer gaming sets ups and require complete sequences upfront, making them unsuitable for interactive applications where future frames depend on user input. We introduce FrameDiffuser, an autoregressive neural rendering framework that generates temporally consistent, photorealistic frames by conditioning on G-buffer data and the models own previous output. After an initial frame, FrameDiffuser operates purely on incoming G-buffer data, comprising geometry, materials, and surface properties, while using its previously generated frame for temporal guidance, maintaining stable, temporal consistent generation over hundreds to thousands of frames. Our dual-conditioning architecture combines ControlNet for structural guidance with ControlLoRA for temporal coherence. A three-stage training strategy enables stable autoregressive generation. We specialize our model to individual environments, prioritizing consistency and inference speed over broad generalization, demonstrating that environment-specific training achieves superior photorealistic quality with accurate lighting, shadows, and reflections compared to generalized approaches.
HistDiST: Histopathological Diffusion-based Stain Transfer
May 11, 2025



Abstract:Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining is the cornerstone of histopathology but lacks molecular specificity. While Immunohistochemistry (IHC) provides molecular insights, it is costly and complex, motivating H&E-to-IHC translation as a cost-effective alternative. Existing translation methods are mainly GAN-based, often struggling with training instability and limited structural fidelity, while diffusion-based approaches remain underexplored. We propose HistDiST, a Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) based framework for high-fidelity H&E-to-IHC translation. HistDiST introduces a dual-conditioning strategy, utilizing Phikon-extracted morphological embeddings alongside VAE-encoded H&E representations to ensure pathology-relevant context and structural consistency. To overcome brightness biases, we incorporate a rescaled noise schedule, v-prediction, and trailing timesteps, enforcing a zero-SNR condition at the final timestep. During inference, DDIM inversion preserves the morphological structure, while an eta-cosine noise schedule introduces controlled stochasticity, balancing structural consistency and molecular fidelity. Moreover, we propose Molecular Retrieval Accuracy (MRA), a novel pathology-aware metric leveraging GigaPath embeddings to assess molecular relevance. Extensive evaluations on MIST and BCI datasets demonstrate that HistDiST significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving a 28% improvement in MRA on the H&E-to-Ki67 translation task, highlighting its effectiveness in capturing true IHC semantics.
EMPERROR: A Flexible Generative Perception Error Model for Probing Self-Driving Planners
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:To handle the complexities of real-world traffic, learning planners for self-driving from data is a promising direction. While recent approaches have shown great progress, they typically assume a setting in which the ground-truth world state is available as input. However, when deployed, planning needs to be robust to the long-tail of errors incurred by a noisy perception system, which is often neglected in evaluation. To address this, previous work has proposed drawing adversarial samples from a perception error model (PEM) mimicking the noise characteristics of a target object detector. However, these methods use simple PEMs that fail to accurately capture all failure modes of detection. In this paper, we present EMPERROR, a novel transformer-based generative PEM, apply it to stress-test an imitation learning (IL)-based planner and show that it imitates modern detectors more faithfully than previous work. Furthermore, it is able to produce realistic noisy inputs that increase the planner's collision rate by up to 85%, demonstrating its utility as a valuable tool for a more complete evaluation of self-driving planners.
Is deeper always better? Replacing linear mappings with deep learning networks in the Discriminative Lexicon Model
Oct 05, 2024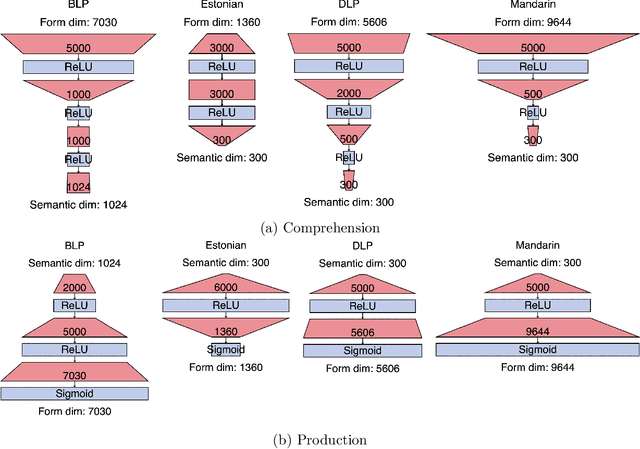
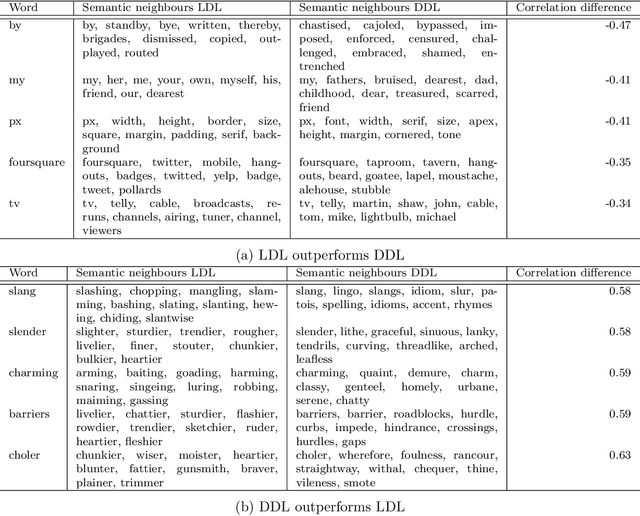
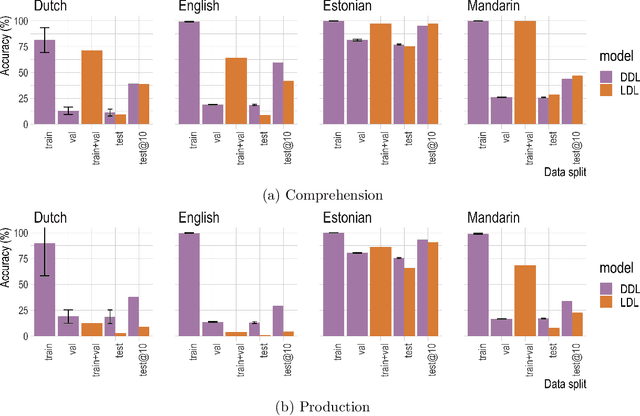
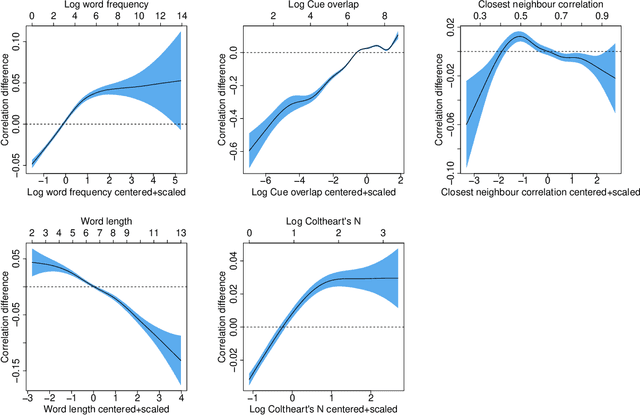
Abstract:Recently, deep learning models have increasingly been used in cognitive modelling of language. This study asks whether deep learning can help us to better understand the learning problem that needs to be solved by speakers, above and beyond linear methods. We utilise the Discriminative Lexicon Model (DLM, Baayen et al., 2019), which models comprehension and production with mappings between numeric form and meaning vectors. While so far, these mappings have been linear (Linear Discriminative Learning, LDL), in the present study we replace them with deep dense neural networks (Deep Discriminative Learning, DDL). We find that DDL affords more accurate mappings for large and diverse datasets from English and Dutch, but not necessarily for Estonian and Taiwan Mandarin. DDL outperforms LDL in particular for words with pseudo-morphological structure such as slend+er. Applied to average reaction times, we find that DDL is outperformed by frequency-informed linear mappings (FIL). However, DDL trained in a frequency-informed way ('frequency-informed' deep learning, FIDDL) substantially outperforms FIL. Finally, while linear mappings can very effectively be updated from trial-to-trial to model incremental lexical learning (Heitmeier et al., 2023), deep mappings cannot do so as effectively. At present, both linear and deep mappings are informative for understanding language.
RISE-SDF: a Relightable Information-Shared Signed Distance Field for Glossy Object Inverse Rendering
Sep 30, 2024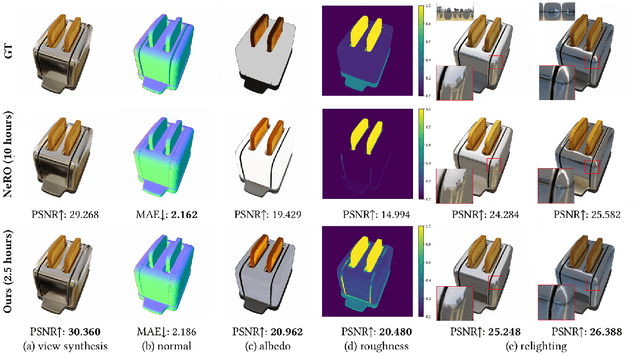
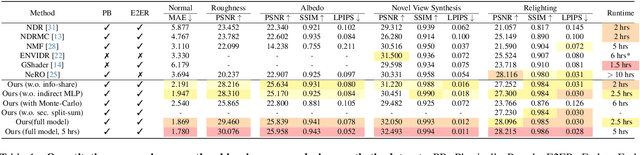
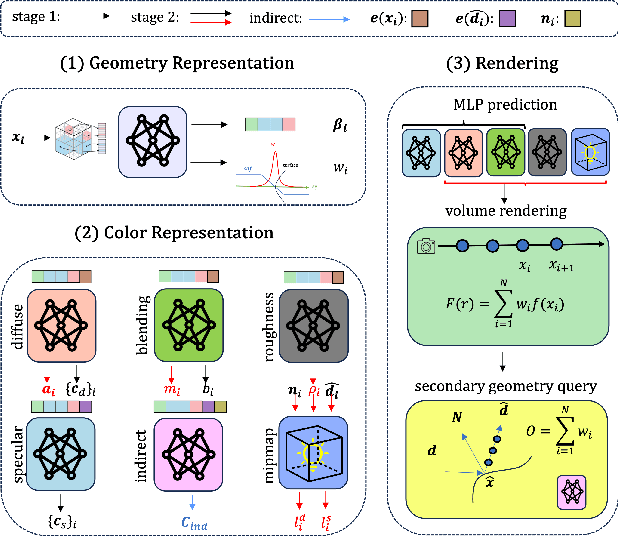

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end relightable neural inverse rendering system that achieves high-quality reconstruction of geometry and material properties, thus enabling high-quality relighting. The cornerstone of our method is a two-stage approach for learning a better factorization of scene parameters. In the first stage, we develop a reflection-aware radiance field using a neural signed distance field (SDF) as the geometry representation and deploy an MLP (multilayer perceptron) to estimate indirect illumination. In the second stage, we introduce a novel information-sharing network structure to jointly learn the radiance field and the physically based factorization of the scene. For the physically based factorization, to reduce the noise caused by Monte Carlo sampling, we apply a split-sum approximation with a simplified Disney BRDF and cube mipmap as the environment light representation. In the relighting phase, to enhance the quality of indirect illumination, we propose a second split-sum algorithm to trace secondary rays under the split-sum rendering framework.Furthermore, there is no dataset or protocol available to quantitatively evaluate the inverse rendering performance for glossy objects. To assess the quality of material reconstruction and relighting, we have created a new dataset with ground truth BRDF parameters and relighting results. Our experiments demonstrate that our algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance in inverse rendering and relighting, with particularly strong results in the reconstruction of highly reflective objects.
Subsurface Scattering for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Aug 22, 2024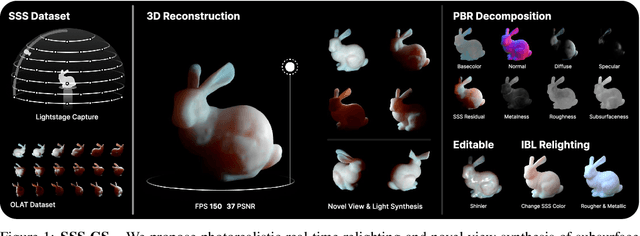
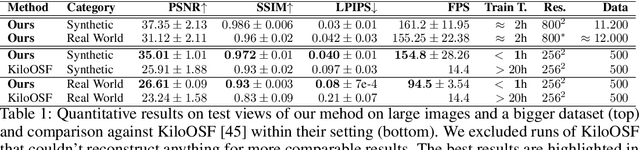
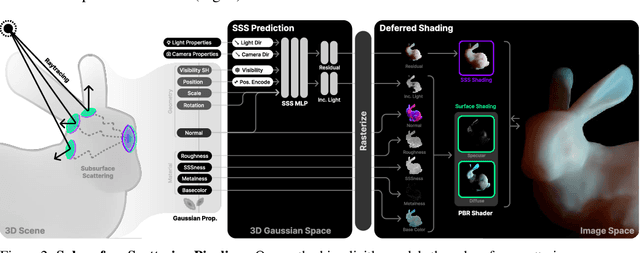
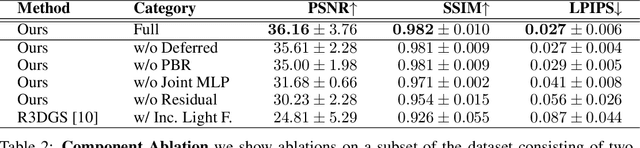
Abstract:3D reconstruction and relighting of objects made from scattering materials present a significant challenge due to the complex light transport beneath the surface. 3D Gaussian Splatting introduced high-quality novel view synthesis at real-time speeds. While 3D Gaussians efficiently approximate an object's surface, they fail to capture the volumetric properties of subsurface scattering. We propose a framework for optimizing an object's shape together with the radiance transfer field given multi-view OLAT (one light at a time) data. Our method decomposes the scene into an explicit surface represented as 3D Gaussians, with a spatially varying BRDF, and an implicit volumetric representation of the scattering component. A learned incident light field accounts for shadowing. We optimize all parameters jointly via ray-traced differentiable rendering. Our approach enables material editing, relighting and novel view synthesis at interactive rates. We show successful application on synthetic data and introduce a newly acquired multi-view multi-light dataset of objects in a light-stage setup. Compared to previous work we achieve comparable or better results at a fraction of optimization and rendering time while enabling detailed control over material attributes. Project page https://sss.jdihlmann.com/
DualAD: Disentangling the Dynamic and Static World for End-to-End Driving
Jun 10, 2024Abstract:State-of-the-art approaches for autonomous driving integrate multiple sub-tasks of the overall driving task into a single pipeline that can be trained in an end-to-end fashion by passing latent representations between the different modules. In contrast to previous approaches that rely on a unified grid to represent the belief state of the scene, we propose dedicated representations to disentangle dynamic agents and static scene elements. This allows us to explicitly compensate for the effect of both ego and object motion between consecutive time steps and to flexibly propagate the belief state through time. Furthermore, dynamic objects can not only attend to the input camera images, but also directly benefit from the inferred static scene structure via a novel dynamic-static cross-attention. Extensive experiments on the challenging nuScenes benchmark demonstrate the benefits of the proposed dual-stream design, especially for modelling highly dynamic agents in the scene, and highlight the improved temporal consistency of our approach. Our method titled DualAD not only outperforms independently trained single-task networks, but also improves over previous state-of-the-art end-to-end models by a large margin on all tasks along the functional chain of driving.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge