Hanyi Zhang
Self-Controlled Dynamic Expansion Model for Continual Learning
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Continual Learning (CL) epitomizes an advanced training paradigm wherein prior data samples remain inaccessible during the acquisition of new tasks. Numerous investigations have delved into leveraging a pre-trained Vision Transformer (ViT) to enhance model efficacy in continual learning. Nonetheless, these approaches typically utilize a singular, static backbone, which inadequately adapts to novel tasks, particularly when engaging with diverse data domains, due to a substantial number of inactive parameters. This paper addresses this limitation by introducing an innovative Self-Controlled Dynamic Expansion Model (SCDEM), which orchestrates multiple distinct trainable pre-trained ViT backbones to furnish diverse and semantically enriched representations. Specifically, by employing the multi-backbone architecture as a shared module, the proposed SCDEM dynamically generates a new expert with minimal parameters to accommodate a new task. A novel Collaborative Optimization Mechanism (COM) is introduced to synergistically optimize multiple backbones by harnessing prediction signals from historical experts, thereby facilitating new task learning without erasing previously acquired knowledge. Additionally, a novel Feature Distribution Consistency (FDC) approach is proposed to align semantic similarity between previously and currently learned representations through an optimal transport distance-based mechanism, effectively mitigating negative knowledge transfer effects. Furthermore, to alleviate over-regularization challenges, this paper presents a novel Dynamic Layer-Wise Feature Attention Mechanism (DLWFAM) to autonomously determine the penalization intensity on each trainable representation layer. An extensive series of experiments have been conducted to evaluate the proposed methodology's efficacy, with empirical results corroborating that the approach attains state-of-the-art performance.
Hybrid Deep Reinforcement Learning for Radio Tracer Localisation in Robotic-assisted Radioguided Surgery
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:Radioguided surgery, such as sentinel lymph node biopsy, relies on the precise localization of radioactive targets by non-imaging gamma/beta detectors. Manual radioactive target detection based on visual display or audible indication of gamma level is highly dependent on the ability of the surgeon to track and interpret the spatial information. This paper presents a learning-based method to realize the autonomous radiotracer detection in robot-assisted surgeries by navigating the probe to the radioactive target. We proposed novel hybrid approach that combines deep reinforcement learning (DRL) with adaptive robotic scanning. The adaptive grid-based scanning could provide initial direction estimation while the DRL-based agent could efficiently navigate to the target utilising historical data. Simulation experiments demonstrate a 95% success rate, and improved efficiency and robustness compared to conventional techniques. Real-world evaluation on the da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK) further confirms the feasibility of the approach, achieving an 80% success rate in radiotracer detection. This method has the potential to enhance consistency, reduce operator dependency, and improve procedural accuracy in radioguided surgeries.
X-IL: Exploring the Design Space of Imitation Learning Policies
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Designing modern imitation learning (IL) policies requires making numerous decisions, including the selection of feature encoding, architecture, policy representation, and more. As the field rapidly advances, the range of available options continues to grow, creating a vast and largely unexplored design space for IL policies. In this work, we present X-IL, an accessible open-source framework designed to systematically explore this design space. The framework's modular design enables seamless swapping of policy components, such as backbones (e.g., Transformer, Mamba, xLSTM) and policy optimization techniques (e.g., Score-matching, Flow-matching). This flexibility facilitates comprehensive experimentation and has led to the discovery of novel policy configurations that outperform existing methods on recent robot learning benchmarks. Our experiments demonstrate not only significant performance gains but also provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of various design choices. This study serves as both a practical reference for practitioners and a foundation for guiding future research in imitation learning.
Towards Fusing Point Cloud and Visual Representations for Imitation Learning
Feb 19, 2025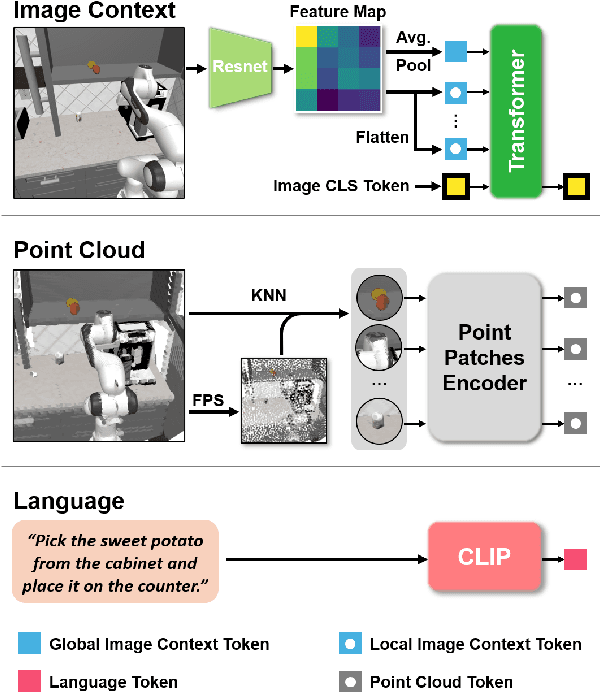
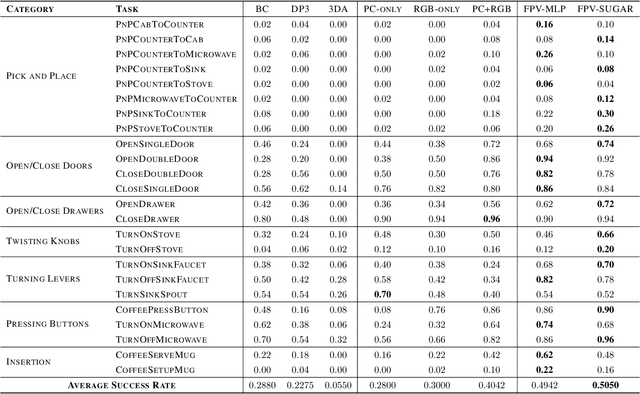
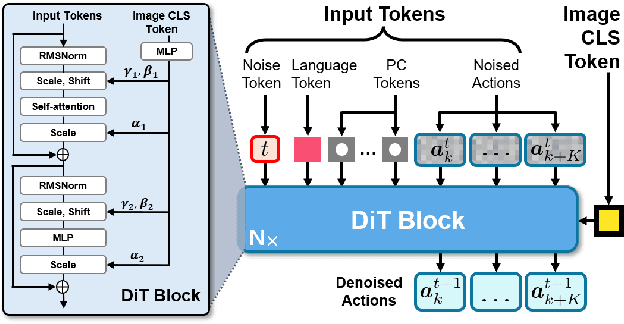
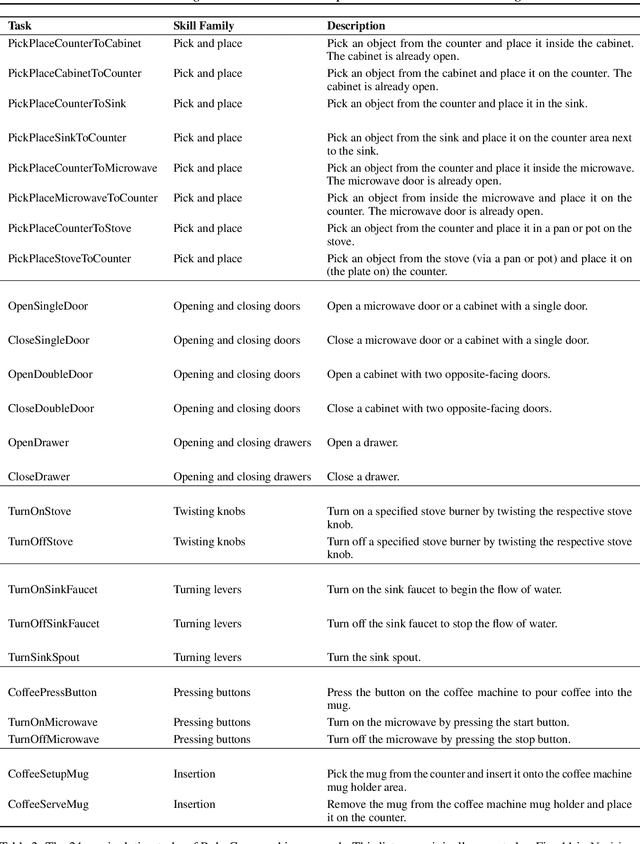
Abstract:Learning for manipulation requires using policies that have access to rich sensory information such as point clouds or RGB images. Point clouds efficiently capture geometric structures, making them essential for manipulation tasks in imitation learning. In contrast, RGB images provide rich texture and semantic information that can be crucial for certain tasks. Existing approaches for fusing both modalities assign 2D image features to point clouds. However, such approaches often lose global contextual information from the original images. In this work, we propose FPV-Net, a novel imitation learning method that effectively combines the strengths of both point cloud and RGB modalities. Our method conditions the point-cloud encoder on global and local image tokens using adaptive layer norm conditioning, leveraging the beneficial properties of both modalities. Through extensive experiments on the challenging RoboCasa benchmark, we demonstrate the limitations of relying on either modality alone and show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across all tasks.
Fast Context-Based Low-Light Image Enhancement via Neural Implicit Representations
Jul 17, 2024
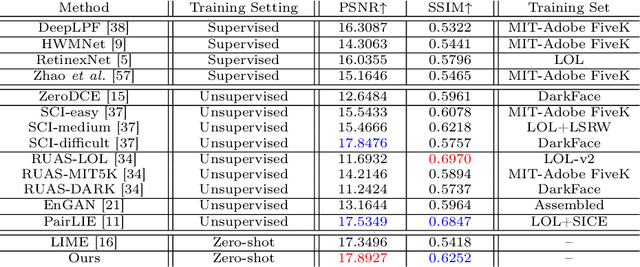
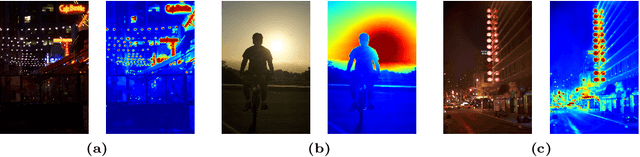
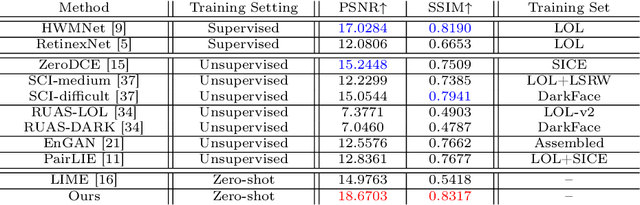
Abstract:Current deep learning-based low-light image enhancement methods often struggle with high-resolution images, and fail to meet the practical demands of visual perception across diverse and unseen scenarios. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach termed CoLIE, which redefines the enhancement process through mapping the 2D coordinates of an underexposed image to its illumination component, conditioned on local context. We propose a reconstruction of enhanced-light images within the HSV space utilizing an implicit neural function combined with an embedded guided filter, thereby significantly reducing computational overhead. Moreover, we introduce a single image-based training loss function to enhance the model's adaptability to various scenes, further enhancing its practical applicability. Through rigorous evaluations, we analyze the properties of our proposed framework, demonstrating its superiority in both image quality and scene adaptability. Furthermore, our evaluation extends to applications in downstream tasks within low-light scenarios, underscoring the practical utility of CoLIE. The source code is available at https://github.com/ctom2/colie.
Generating Multi-Modal and Multi-Attribute Single-Cell Counts with CFGen
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:Generative modeling of single-cell RNA-seq data has shown invaluable potential in community-driven tasks such as trajectory inference, batch effect removal and gene expression generation. However, most recent deep models generating synthetic single cells from noise operate on pre-processed continuous gene expression approximations, ignoring the inherently discrete and over-dispersed nature of single-cell data, which limits downstream applications and hinders the incorporation of robust noise models. Moreover, crucial aspects of deep-learning-based synthetic single-cell generation remain underexplored, such as controllable multi-modal and multi-label generation and its role in the performance enhancement of downstream tasks. This work presents Cell Flow for Generation (CFGen), a flow-based conditional generative model for multi-modal single-cell counts, which explicitly accounts for the discrete nature of the data. Our results suggest improved recovery of crucial biological data characteristics while accounting for novel generative tasks such as conditioning on multiple attributes and boosting rare cell type classification via data augmentation. By showcasing CFGen on a diverse set of biological datasets and settings, we provide evidence of its value to the fields of computational biology and deep generative models.
Cross-modal Audio-visual Co-learning for Text-independent Speaker Verification
Feb 22, 2023



Abstract:Visual speech (i.e., lip motion) is highly related to auditory speech due to the co-occurrence and synchronization in speech production. This paper investigates this correlation and proposes a cross-modal speech co-learning paradigm. The primary motivation of our cross-modal co-learning method is modeling one modality aided by exploiting knowledge from another modality. Specifically, two cross-modal boosters are introduced based on an audio-visual pseudo-siamese structure to learn the modality-transformed correlation. Inside each booster, a max-feature-map embedded Transformer variant is proposed for modality alignment and enhanced feature generation. The network is co-learned both from scratch and with pretrained models. Experimental results on the LRSLip3, GridLip, LomGridLip, and VoxLip datasets demonstrate that our proposed method achieves 60% and 20% average relative performance improvement over independently trained audio-only/visual-only and baseline fusion systems, respectively.
Diversifying Agent's Behaviors in Interactive Decision Models
Mar 06, 2022
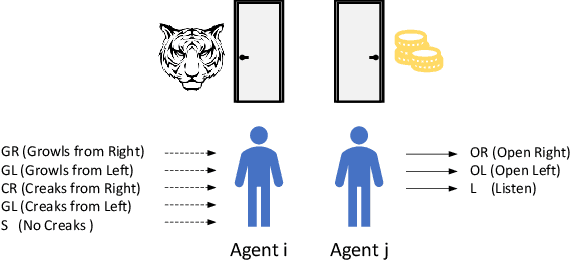
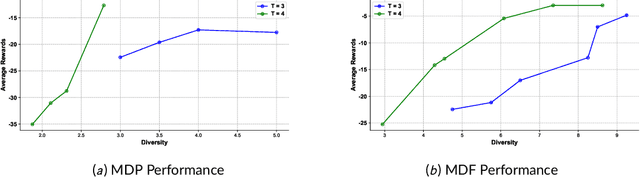
Abstract:Modelling other agents' behaviors plays an important role in decision models for interactions among multiple agents. To optimise its own decisions, a subject agent needs to model what other agents act simultaneously in an uncertain environment. However, modelling insufficiency occurs when the agents are competitive and the subject agent can not get full knowledge about other agents. Even when the agents are collaborative, they may not share their true behaviors due to their privacy concerns. In this article, we investigate into diversifying behaviors of other agents in the subject agent's decision model prior to their interactions. Starting with prior knowledge about other agents' behaviors, we use a linear reduction technique to extract representative behavioral features from the known behaviors. We subsequently generate their new behaviors by expanding the features and propose two diversity measurements to select top-K behaviors. We demonstrate the performance of the new techniques in two well-studied problem domains. This research will contribute to intelligent systems dealing with unknown unknowns in an open artificial intelligence world.
Exploring Deep Learning for Joint Audio-Visual Lip Biometrics
Apr 17, 2021



Abstract:Audio-visual (AV) lip biometrics is a promising authentication technique that leverages the benefits of both the audio and visual modalities in speech communication. Previous works have demonstrated the usefulness of AV lip biometrics. However, the lack of a sizeable AV database hinders the exploration of deep-learning-based audio-visual lip biometrics. To address this problem, we compile a moderate-size database using existing public databases. Meanwhile, we establish the DeepLip AV lip biometrics system realized with a convolutional neural network (CNN) based video module, a time-delay neural network (TDNN) based audio module, and a multimodal fusion module. Our experiments show that DeepLip outperforms traditional speaker recognition models in context modeling and achieves over 50% relative improvements compared with our best single modality baseline, with an equal error rate of 0.75% and 1.11% on the test datasets, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge