Zhong Ming
M3SR: Multi-Scale Multi-Perceptual Mamba for Efficient Spectral Reconstruction
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:The Mamba architecture has been widely applied to various low-level vision tasks due to its exceptional adaptability and strong performance. Although the Mamba architecture has been adopted for spectral reconstruction, it still faces the following two challenges: (1) Single spatial perception limits the ability to fully understand and analyze hyperspectral images; (2) Single-scale feature extraction struggles to capture the complex structures and fine details present in hyperspectral images. To address these issues, we propose a multi-scale, multi-perceptual Mamba architecture for the spectral reconstruction task, called M3SR. Specifically, we design a multi-perceptual fusion block to enhance the ability of the model to comprehensively understand and analyze the input features. By integrating the multi-perceptual fusion block into a U-Net structure, M3SR can effectively extract and fuse global, intermediate, and local features, thereby enabling accurate reconstruction of hyperspectral images at multiple scales. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that the proposed M3SR outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods while incurring a lower computational cost.
Towards Multi-Behavior Multi-Task Recommendation via Behavior-informed Graph Embedding Learning
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Multi-behavior recommendation (MBR) aims to improve the performance w.r.t. the target behavior (i.e., purchase) by leveraging auxiliary behaviors (e.g., click, favourite). However, in real-world scenarios, a recommendation method often needs to process different types of behaviors and generate personalized lists for each task (i.e., each behavior type). Such a new recommendation problem is referred to as multi-behavior multi-task recommendation (MMR). So far, the most powerful MBR methods usually model multi-behavior interactions using a cascading graph paradigm. Although significant progress has been made in optimizing the performance of the target behavior, it often neglects the performance of auxiliary behaviors. To compensate for the deficiencies of the cascading paradigm, we propose a novel solution for MMR, i.e., behavior-informed graph embedding learning (BiGEL). Specifically, we first obtain a set of behavior-aware embeddings by using a cascading graph paradigm. Subsequently, we introduce three key modules to improve the performance of the model. The cascading gated feedback (CGF) module enables a feedback-driven optimization process by integrating feedback from the target behavior to refine the auxiliary behaviors preferences. The global context enhancement (GCE) module integrates the global context to maintain the user's overall preferences, preventing the loss of key preferences due to individual behavior graph modeling. Finally, the contrastive preference alignment (CPA) module addresses the potential changes in user preferences during the cascading process by aligning the preferences of the target behaviors with the global preferences through contrastive learning. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our BiGEL compared with ten very competitive methods.
Automated Information Flow Selection for Multi-scenario Multi-task Recommendation
Dec 15, 2025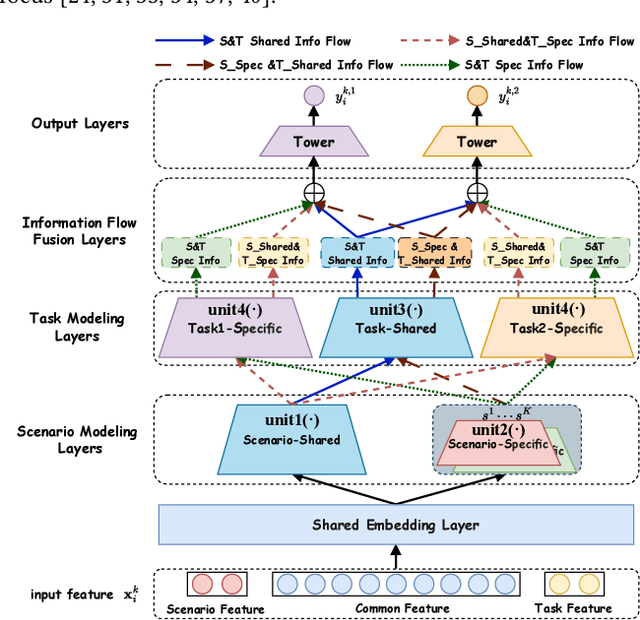
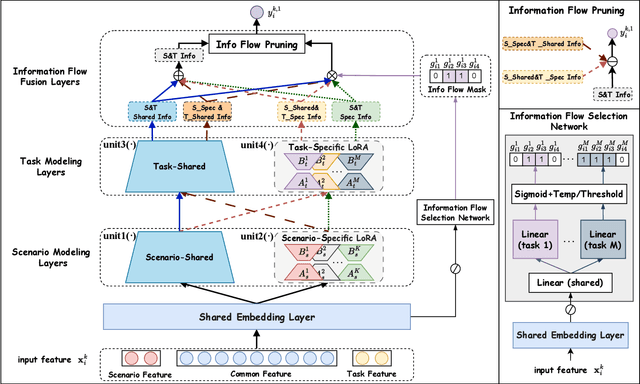
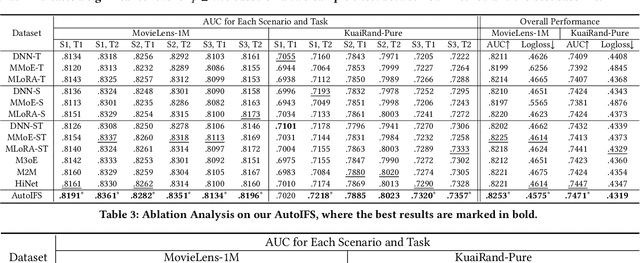
Abstract:Multi-scenario multi-task recommendation (MSMTR) systems must address recommendation demands across diverse scenarios while simultaneously optimizing multiple objectives, such as click-through rate and conversion rate. Existing MSMTR models typically consist of four information units: scenario-shared, scenario-specific, task-shared, and task-specific networks. These units interact to generate four types of relationship information flows, directed from scenario-shared or scenario-specific networks to task-shared or task-specific networks. However, these models face two main limitations: 1) They often rely on complex architectures, such as mixture-of-experts (MoE) networks, which increase the complexity of information fusion, model size, and training cost. 2) They extract all available information flows without filtering out irrelevant or even harmful content, introducing potential noise. Regarding these challenges, we propose a lightweight Automated Information Flow Selection (AutoIFS) framework for MSMTR. To tackle the first issue, AutoIFS incorporates low-rank adaptation (LoRA) to decouple the four information units, enabling more flexible and efficient information fusion with minimal parameter overhead. To address the second issue, AutoIFS introduces an information flow selection network that automatically filters out invalid scenario-task information flows based on model performance feedback. It employs a simple yet effective pruning function to eliminate useless information flows, thereby enhancing the impact of key relationships and improving model performance. Finally, we evaluate AutoIFS and confirm its effectiveness through extensive experiments on two public benchmark datasets and an online A/B test.
VisNumBench: Evaluating Number Sense of Multimodal Large Language Models
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Can Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) develop an intuitive number sense similar to humans? Targeting this problem, we introduce Visual Number Benchmark (VisNumBench) to evaluate the number sense abilities of MLLMs across a wide range of visual numerical tasks. VisNumBench consists of about 1,900 multiple-choice question-answer pairs derived from both synthetic and real-world visual data, covering seven visual numerical attributes and four types of visual numerical estimation tasks. Our experiments on VisNumBench led to the following key findings: (i) The 17 MLLMs we tested, including open-source models such as Qwen2.5-VL and InternVL2.5, as well as proprietary models like GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash, perform significantly below human levels in number sense-related tasks. (ii) Multimodal mathematical models and multimodal chain-of-thought (CoT) models did not exhibit significant improvements in number sense abilities. (iii) Stronger MLLMs with larger parameter sizes and broader general abilities demonstrate modest gains in number sense abilities. We believe VisNumBench will serve as a valuable resource for the research community, encouraging further advancements in enhancing MLLMs' number sense abilities. All benchmark resources, including code and datasets, will be publicly available at https://wwwtttjjj.github.io/VisNumBench/.
A Survey on Sequential Recommendation
Dec 17, 2024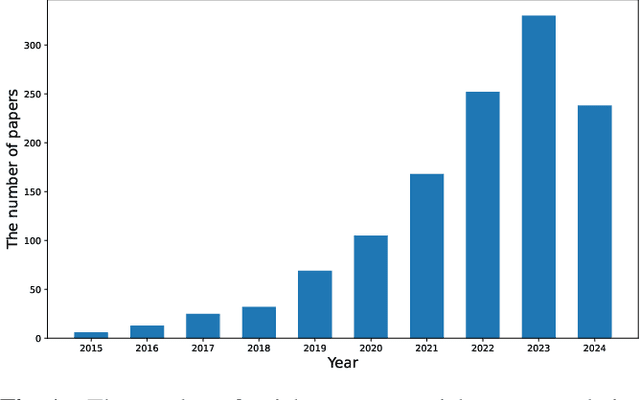
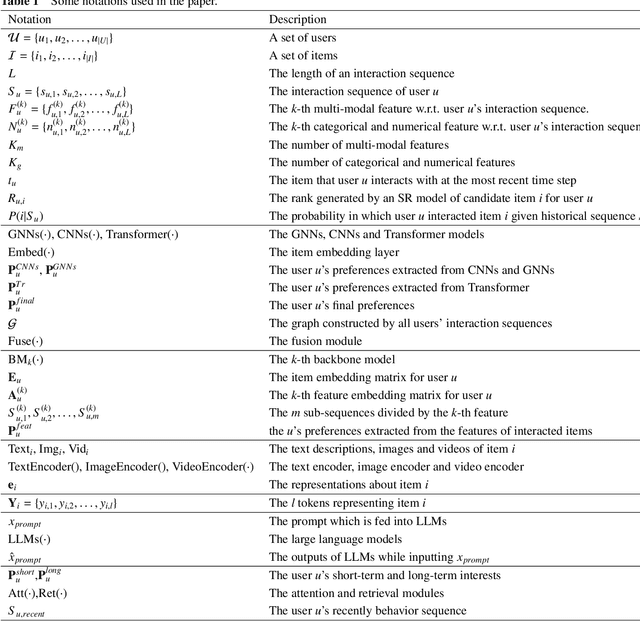
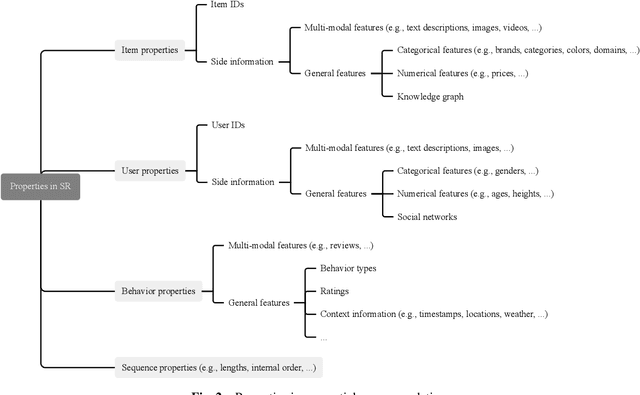
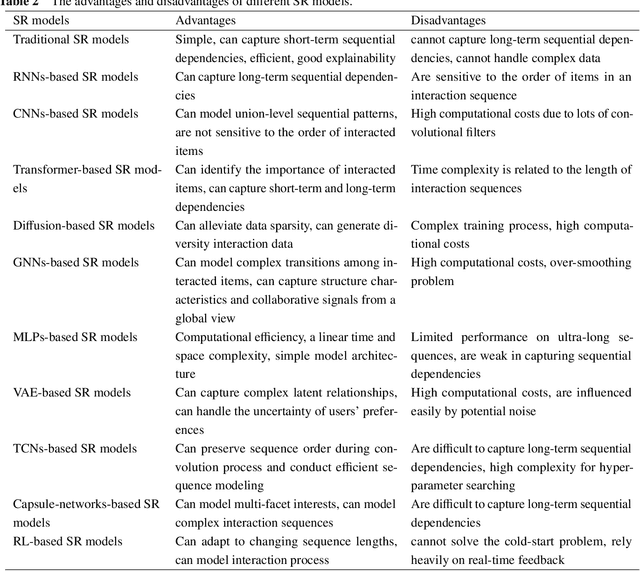
Abstract:Different from most conventional recommendation problems, sequential recommendation focuses on learning users' preferences by exploiting the internal order and dependency among the interacted items, which has received significant attention from both researchers and practitioners. In recent years, we have witnessed great progress and achievements in this field, necessitating a new survey. In this survey, we study the SR problem from a new perspective (i.e., the construction of an item's properties), and summarize the most recent techniques used in sequential recommendation such as pure ID-based SR, SR with side information, multi-modal SR, generative SR, LLM-powered SR, ultra-long SR and data-augmented SR. Moreover, we introduce some frontier research topics in sequential recommendation, e.g., open-domain SR, data-centric SR, could-edge collaborative SR, continuous SR, SR for good, and explainable SR. We believe that our survey could be served as a valuable roadmap for readers in this field.
Lossless and Privacy-Preserving Graph Convolution Network for Federated Item Recommendation
Dec 02, 2024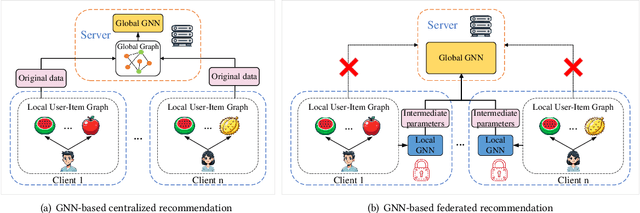

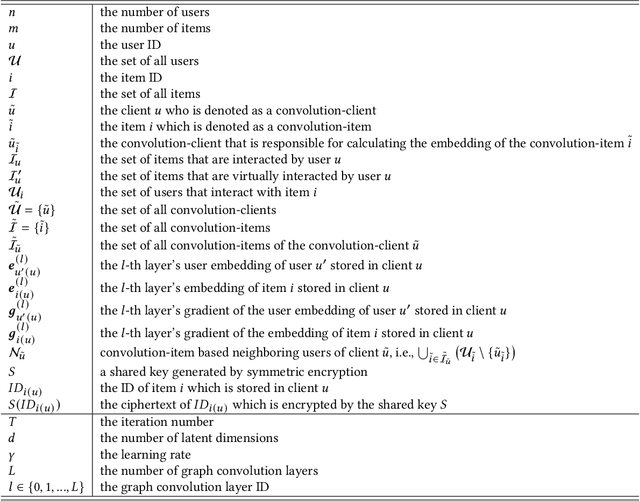
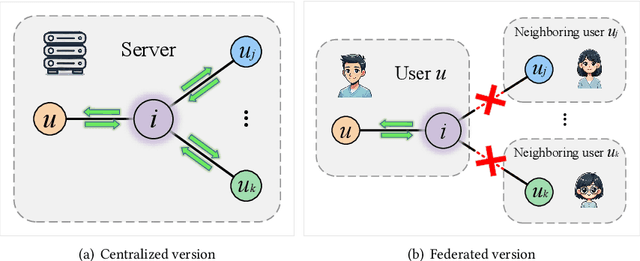
Abstract:Graph neural network (GNN) has emerged as a state-of-the-art solution for item recommendation. However, existing GNN-based recommendation methods rely on a centralized storage of fragmented user-item interaction sub-graphs and training on an aggregated global graph, which will lead to privacy concerns. As a response, some recent works develop GNN-based federated recommendation methods by exploiting decentralized and fragmented user-item sub-graphs in order to preserve user privacy. However, due to privacy constraints, the graph convolution process in existing federated recommendation methods is incomplete compared with the centralized counterpart, causing a degradation of the recommendation performance. In this paper, we propose a novel lossless and privacy-preserving graph convolution network (LP-GCN), which fully completes the graph convolution process with decentralized user-item interaction sub-graphs while ensuring privacy. It is worth mentioning that its performance is equivalent to that of the non-federated (i.e., centralized) counterpart. Moreover, we validate its effectiveness through both theoretical analysis and empirical studies. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets show that our LP-GCN outperforms the existing federated recommendation methods. The code will be publicly available once the paper is accepted.
Sample Enrichment via Temporary Operations on Subsequences for Sequential Recommendation
Jul 25, 2024



Abstract:Sequential recommendation leverages interaction sequences to predict forthcoming user behaviors, crucial for crafting personalized recommendations. However, the true preferences of a user are inherently complex and high-dimensional, while the observed data is merely a simplified and low-dimensional projection of the rich preferences, which often leads to prevalent issues like data sparsity and inaccurate model training. To learn true preferences from the sparse data, most existing works endeavor to introduce some extra information or design some ingenious models. Although they have shown to be effective, extra information usually increases the cost of data collection, and complex models may result in difficulty in deployment. Innovatively, we avoid the use of extra information or alterations to the model; instead, we fill the transformation space between the observed data and the underlying preferences with randomness. Specifically, we propose a novel model-agnostic and highly generic framework for sequential recommendation called sample enrichment via temporary operations on subsequences (SETO), which temporarily and separately enriches the transformation space via sequence enhancement operations with rationality constraints in training. The transformation space not only exists in the process from input samples to preferences but also in preferences to target samples. We highlight our SETO's effectiveness and versatility over multiple representative and state-of-the-art sequential recommendation models (including six single-domain sequential models and two cross-domain sequential models) across multiple real-world datasets (including three single-domain datasets, three cross-domain datasets and a large-scale industry dataset).
Benchmarking for Deep Uplift Modeling in Online Marketing
Jun 01, 2024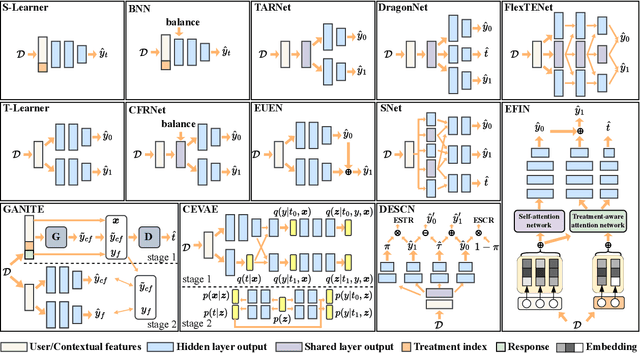



Abstract:Online marketing is critical for many industrial platforms and business applications, aiming to increase user engagement and platform revenue by identifying corresponding delivery-sensitive groups for specific incentives, such as coupons and bonuses. As the scale and complexity of features in industrial scenarios increase, deep uplift modeling (DUM) as a promising technique has attracted increased research from academia and industry, resulting in various predictive models. However, current DUM still lacks some standardized benchmarks and unified evaluation protocols, which limit the reproducibility of experimental results in existing studies and the practical value and potential impact in this direction. In this paper, we provide an open benchmark for DUM and present comparison results of existing models in a reproducible and uniform manner. To this end, we conduct extensive experiments on two representative industrial datasets with different preprocessing settings to re-evaluate 13 existing models. Surprisingly, our experimental results show that the most recent work differs less than expected from traditional work in many cases. In addition, our experiments also reveal the limitations of DUM in generalization, especially for different preprocessing and test distributions. Our benchmarking work allows researchers to evaluate the performance of new models quickly but also reasonably demonstrates fair comparison results with existing models. It also gives practitioners valuable insights into often overlooked considerations when deploying DUM. We will make this benchmarking library, evaluation protocol, and experimental setup available on GitHub.
A Practice-Friendly Two-Stage LLM-Enhanced Paradigm in Sequential Recommendation
Jun 01, 2024Abstract:The training paradigm integrating large language models (LLM) is gradually reshaping sequential recommender systems (SRS) and has shown promising results. However, most existing LLM-enhanced methods rely on rich textual information on the item side and instance-level supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to inject collaborative information into LLM, which is inefficient and limited in many applications. To alleviate these problems, this paper proposes a novel practice-friendly two-stage LLM-enhanced paradigm (TSLRec) for SRS. Specifically, in the information reconstruction stage, we design a new user-level SFT task for collaborative information injection with the assistance of a pre-trained SRS model, which is more efficient and compatible with limited text information. We aim to let LLM try to infer the latent category of each item and reconstruct the corresponding user's preference distribution for all categories from the user's interaction sequence. In the information augmentation stage, we feed each item into LLM to obtain a set of enhanced embeddings that combine collaborative information and LLM inference capabilities. These embeddings can then be used to help train various future SRS models. Finally, we verify the effectiveness and efficiency of our TSLRec on three SRS benchmark datasets.
BMLP: Behavior-aware MLP for Heterogeneous Sequential Recommendation
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:In real recommendation scenarios, users often have different types of behaviors, such as clicking and buying. Existing research methods show that it is possible to capture the heterogeneous interests of users through different types of behaviors. However, most multi-behavior approaches have limitations in learning the relationship between different behaviors. In this paper, we propose a novel multilayer perceptron (MLP)-based heterogeneous sequential recommendation method, namely behavior-aware multilayer perceptron (BMLP). Specifically, it has two main modules, including a heterogeneous interest perception (HIP) module, which models behaviors at multiple granularities through behavior types and transition relationships, and a purchase intent perception (PIP) module, which adaptively fuses subsequences of auxiliary behaviors to capture users' purchase intent. Compared with mainstream sequence models, MLP is competitive in terms of accuracy and has unique advantages in simplicity and efficiency. Extensive experiments show that BMLP achieves significant improvement over state-of-the-art algorithms on four public datasets. In addition, its pure MLP architecture leads to a linear time complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge