Denis Blessing
Trust Region Constrained Measure Transport in Path Space for Stochastic Optimal Control and Inference
Aug 17, 2025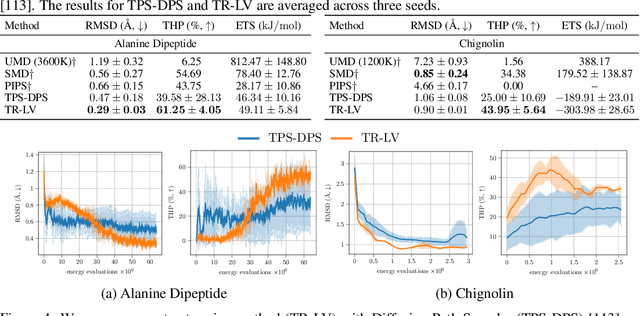
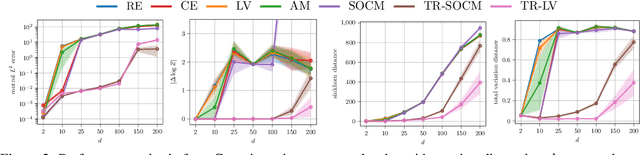
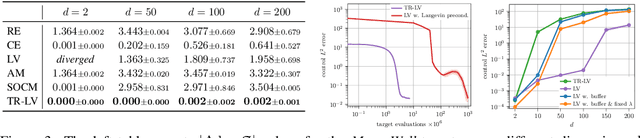
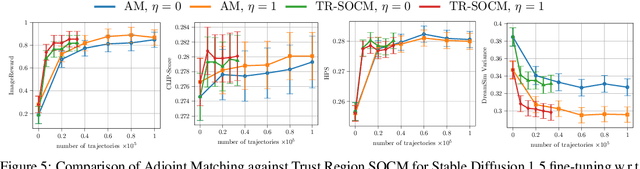
Abstract:Solving stochastic optimal control problems with quadratic control costs can be viewed as approximating a target path space measure, e.g. via gradient-based optimization. In practice, however, this optimization is challenging in particular if the target measure differs substantially from the prior. In this work, we therefore approach the problem by iteratively solving constrained problems incorporating trust regions that aim for approaching the target measure gradually in a systematic way. It turns out that this trust region based strategy can be understood as a geometric annealing from the prior to the target measure, where, however, the incorporated trust regions lead to a principled and educated way of choosing the time steps in the annealing path. We demonstrate in multiple optimal control applications that our novel method can improve performance significantly, including tasks in diffusion-based sampling, transition path sampling, and fine-tuning of diffusion models.
Scaffolding Dexterous Manipulation with Vision-Language Models
Jun 24, 2025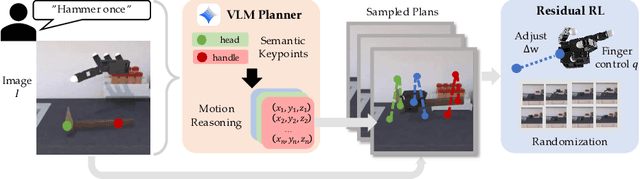
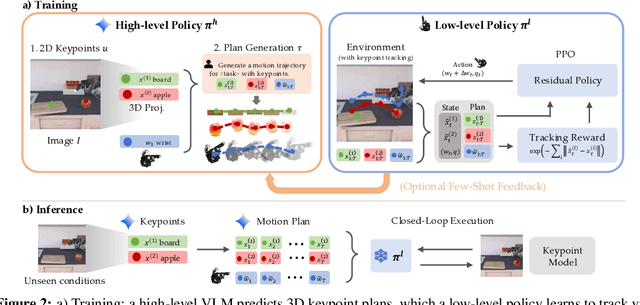
Abstract:Dexterous robotic hands are essential for performing complex manipulation tasks, yet remain difficult to train due to the challenges of demonstration collection and high-dimensional control. While reinforcement learning (RL) can alleviate the data bottleneck by generating experience in simulation, it typically relies on carefully designed, task-specific reward functions, which hinder scalability and generalization. Thus, contemporary works in dexterous manipulation have often bootstrapped from reference trajectories. These trajectories specify target hand poses that guide the exploration of RL policies and object poses that enable dense, task-agnostic rewards. However, sourcing suitable trajectories - particularly for dexterous hands - remains a significant challenge. Yet, the precise details in explicit reference trajectories are often unnecessary, as RL ultimately refines the motion. Our key insight is that modern vision-language models (VLMs) already encode the commonsense spatial and semantic knowledge needed to specify tasks and guide exploration effectively. Given a task description (e.g., "open the cabinet") and a visual scene, our method uses an off-the-shelf VLM to first identify task-relevant keypoints (e.g., handles, buttons) and then synthesize 3D trajectories for hand motion and object motion. Subsequently, we train a low-level residual RL policy in simulation to track these coarse trajectories or "scaffolds" with high fidelity. Across a number of simulated tasks involving articulated objects and semantic understanding, we demonstrate that our method is able to learn robust dexterous manipulation policies. Moreover, we showcase that our method transfers to real-world robotic hands without any human demonstrations or handcrafted rewards.
Underdamped Diffusion Bridges with Applications to Sampling
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:We provide a general framework for learning diffusion bridges that transport prior to target distributions. It includes existing diffusion models for generative modeling, but also underdamped versions with degenerate diffusion matrices, where the noise only acts in certain dimensions. Extending previous findings, our framework allows to rigorously show that score matching in the underdamped case is indeed equivalent to maximizing a lower bound on the likelihood. Motivated by superior convergence properties and compatibility with sophisticated numerical integration schemes of underdamped stochastic processes, we propose \emph{underdamped diffusion bridges}, where a general density evolution is learned rather than prescribed by a fixed noising process. We apply our method to the challenging task of sampling from unnormalized densities without access to samples from the target distribution. Across a diverse range of sampling problems, our approach demonstrates state-of-the-art performance, notably outperforming alternative methods, while requiring significantly fewer discretization steps and no hyperparameter tuning.
Towards Fusing Point Cloud and Visual Representations for Imitation Learning
Feb 19, 2025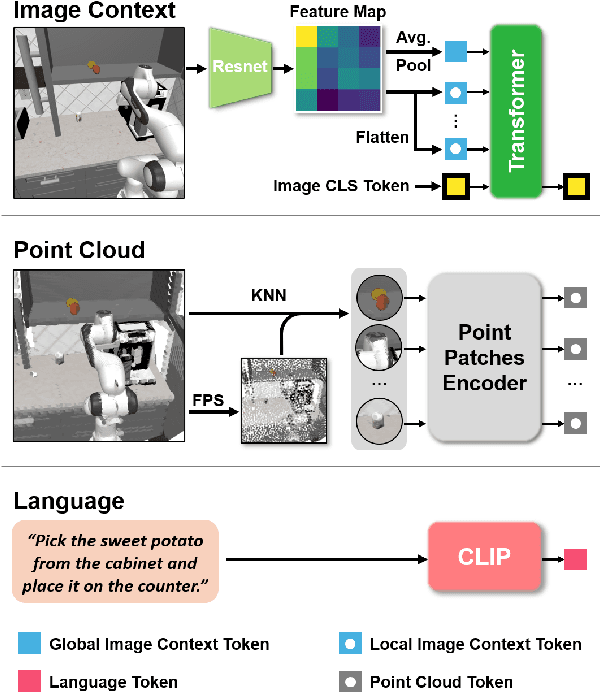
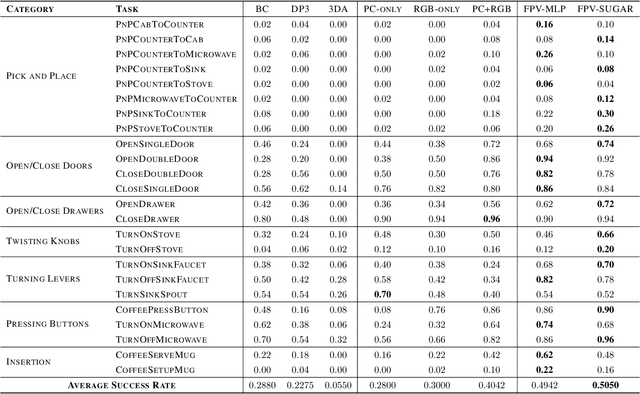
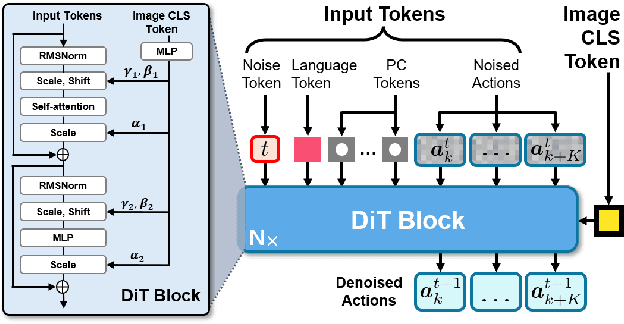
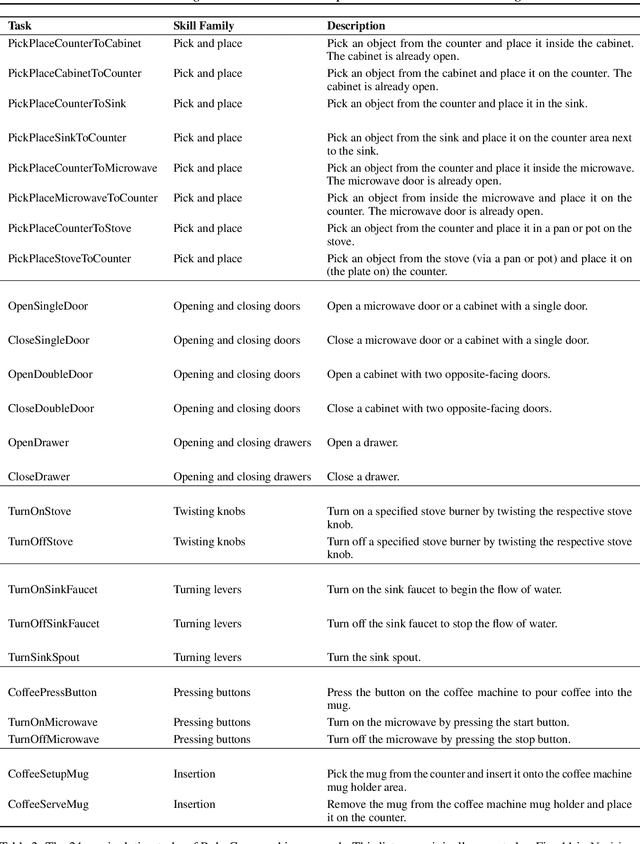
Abstract:Learning for manipulation requires using policies that have access to rich sensory information such as point clouds or RGB images. Point clouds efficiently capture geometric structures, making them essential for manipulation tasks in imitation learning. In contrast, RGB images provide rich texture and semantic information that can be crucial for certain tasks. Existing approaches for fusing both modalities assign 2D image features to point clouds. However, such approaches often lose global contextual information from the original images. In this work, we propose FPV-Net, a novel imitation learning method that effectively combines the strengths of both point cloud and RGB modalities. Our method conditions the point-cloud encoder on global and local image tokens using adaptive layer norm conditioning, leveraging the beneficial properties of both modalities. Through extensive experiments on the challenging RoboCasa benchmark, we demonstrate the limitations of relying on either modality alone and show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across all tasks.
X-IL: Exploring the Design Space of Imitation Learning Policies
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Designing modern imitation learning (IL) policies requires making numerous decisions, including the selection of feature encoding, architecture, policy representation, and more. As the field rapidly advances, the range of available options continues to grow, creating a vast and largely unexplored design space for IL policies. In this work, we present X-IL, an accessible open-source framework designed to systematically explore this design space. The framework's modular design enables seamless swapping of policy components, such as backbones (e.g., Transformer, Mamba, xLSTM) and policy optimization techniques (e.g., Score-matching, Flow-matching). This flexibility facilitates comprehensive experimentation and has led to the discovery of novel policy configurations that outperform existing methods on recent robot learning benchmarks. Our experiments demonstrate not only significant performance gains but also provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of various design choices. This study serves as both a practical reference for practitioners and a foundation for guiding future research in imitation learning.
DIME:Diffusion-Based Maximum Entropy Reinforcement Learning
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:Maximum entropy reinforcement learning (MaxEnt-RL) has become the standard approach to RL due to its beneficial exploration properties. Traditionally, policies are parameterized using Gaussian distributions, which significantly limits their representational capacity. Diffusion-based policies offer a more expressive alternative, yet integrating them into MaxEnt-RL poses challenges--primarily due to the intractability of computing their marginal entropy. To overcome this, we propose Diffusion-Based Maximum Entropy RL (DIME). DIME leverages recent advances in approximate inference with diffusion models to derive a lower bound on the maximum entropy objective. Additionally, we propose a policy iteration scheme that provably converges to the optimal diffusion policy. Our method enables the use of expressive diffusion-based policies while retaining the principled exploration benefits of MaxEnt-RL, significantly outperforming other diffusion-based methods on challenging high-dimensional control benchmarks. It is also competitive with state-of-the-art non-diffusion based RL methods while requiring fewer algorithmic design choices and smaller update-to-data ratios, reducing computational complexity.
Sequential Controlled Langevin Diffusions
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:An effective approach for sampling from unnormalized densities is based on the idea of gradually transporting samples from an easy prior to the complicated target distribution. Two popular methods are (1) Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC), where the transport is performed through successive annealed densities via prescribed Markov chains and resampling steps, and (2) recently developed diffusion-based sampling methods, where a learned dynamical transport is used. Despite the common goal, both approaches have different, often complementary, advantages and drawbacks. The resampling steps in SMC allow focusing on promising regions of the space, often leading to robust performance. While the algorithm enjoys asymptotic guarantees, the lack of flexible, learnable transitions can lead to slow convergence. On the other hand, diffusion-based samplers are learned and can potentially better adapt themselves to the target at hand, yet often suffer from training instabilities. In this work, we present a principled framework for combining SMC with diffusion-based samplers by viewing both methods in continuous time and considering measures on path space. This culminates in the new Sequential Controlled Langevin Diffusion (SCLD) sampling method, which is able to utilize the benefits of both methods and reaches improved performance on multiple benchmark problems, in many cases using only 10% of the training budget of previous diffusion-based samplers.
Variational Distillation of Diffusion Policies into Mixture of Experts
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:This work introduces Variational Diffusion Distillation (VDD), a novel method that distills denoising diffusion policies into Mixtures of Experts (MoE) through variational inference. Diffusion Models are the current state-of-the-art in generative modeling due to their exceptional ability to accurately learn and represent complex, multi-modal distributions. This ability allows Diffusion Models to replicate the inherent diversity in human behavior, making them the preferred models in behavior learning such as Learning from Human Demonstrations (LfD). However, diffusion models come with some drawbacks, including the intractability of likelihoods and long inference times due to their iterative sampling process. The inference times, in particular, pose a significant challenge to real-time applications such as robot control. In contrast, MoEs effectively address the aforementioned issues while retaining the ability to represent complex distributions but are notoriously difficult to train. VDD is the first method that distills pre-trained diffusion models into MoE models, and hence, combines the expressiveness of Diffusion Models with the benefits of Mixture Models. Specifically, VDD leverages a decompositional upper bound of the variational objective that allows the training of each expert separately, resulting in a robust optimization scheme for MoEs. VDD demonstrates across nine complex behavior learning tasks, that it is able to: i) accurately distill complex distributions learned by the diffusion model, ii) outperform existing state-of-the-art distillation methods, and iii) surpass conventional methods for training MoE.
MaIL: Improving Imitation Learning with Mamba
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:This work introduces Mamba Imitation Learning (MaIL), a novel imitation learning (IL) architecture that offers a computationally efficient alternative to state-of-the-art (SoTA) Transformer policies. Transformer-based policies have achieved remarkable results due to their ability in handling human-recorded data with inherently non-Markovian behavior. However, their high performance comes with the drawback of large models that complicate effective training. While state space models (SSMs) have been known for their efficiency, they were not able to match the performance of Transformers. Mamba significantly improves the performance of SSMs and rivals against Transformers, positioning it as an appealing alternative for IL policies. MaIL leverages Mamba as a backbone and introduces a formalism that allows using Mamba in the encoder-decoder structure. This formalism makes it a versatile architecture that can be used as a standalone policy or as part of a more advanced architecture, such as a diffuser in the diffusion process. Extensive evaluations on the LIBERO IL benchmark and three real robot experiments show that MaIL: i) outperforms Transformers in all LIBERO tasks, ii) achieves good performance even with small datasets, iii) is able to effectively process multi-modal sensory inputs, iv) is more robust to input noise compared to Transformers.
Beyond ELBOs: A Large-Scale Evaluation of Variational Methods for Sampling
Jun 11, 2024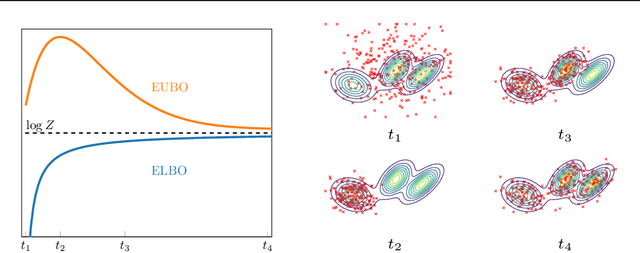
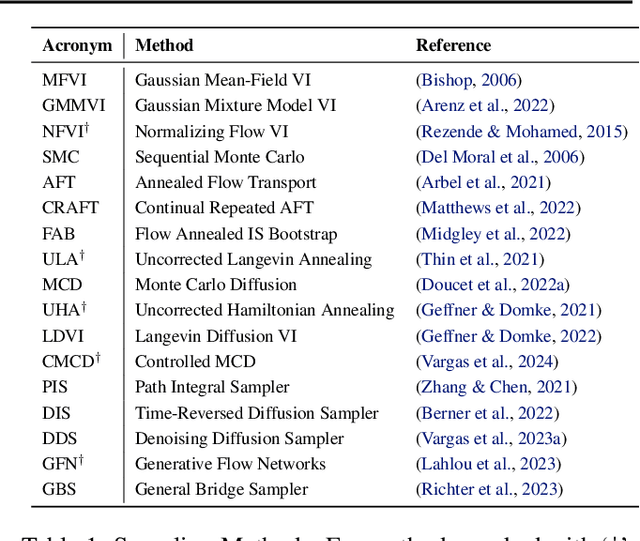
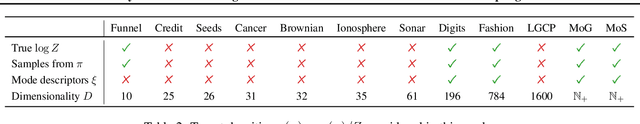
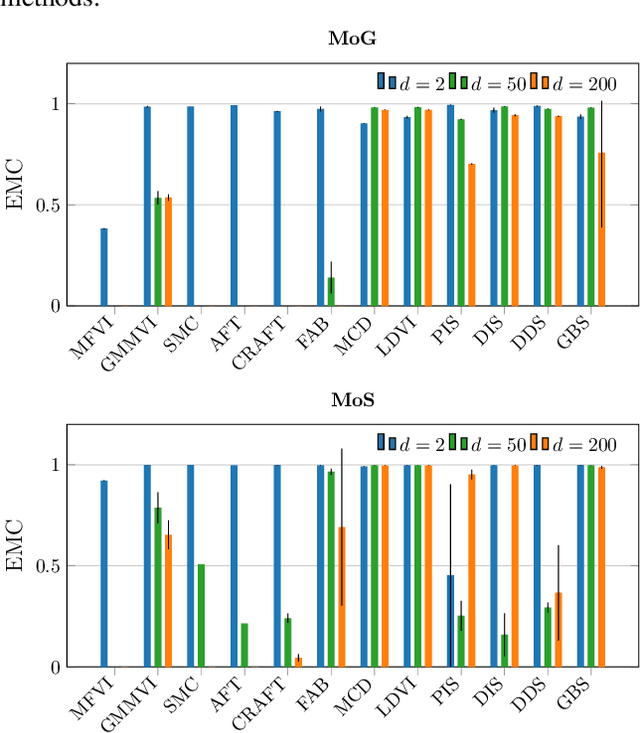
Abstract:Monte Carlo methods, Variational Inference, and their combinations play a pivotal role in sampling from intractable probability distributions. However, current studies lack a unified evaluation framework, relying on disparate performance measures and limited method comparisons across diverse tasks, complicating the assessment of progress and hindering the decision-making of practitioners. In response to these challenges, our work introduces a benchmark that evaluates sampling methods using a standardized task suite and a broad range of performance criteria. Moreover, we study existing metrics for quantifying mode collapse and introduce novel metrics for this purpose. Our findings provide insights into strengths and weaknesses of existing sampling methods, serving as a valuable reference for future developments. The code is publicly available here.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge