Zechu Li
Morphologically Symmetric Reinforcement Learning for Ambidextrous Bimanual Manipulation
May 08, 2025Abstract:Humans naturally exhibit bilateral symmetry in their gross manipulation skills, effortlessly mirroring simple actions between left and right hands. Bimanual robots-which also feature bilateral symmetry-should similarly exploit this property to perform tasks with either hand. Unlike humans, who often favor a dominant hand for fine dexterous skills, robots should ideally execute ambidextrous manipulation with equal proficiency. To this end, we introduce SYMDEX (SYMmetric DEXterity), a reinforcement learning framework for ambidextrous bi-manipulation that leverages the robot's inherent bilateral symmetry as an inductive bias. SYMDEX decomposes complex bimanual manipulation tasks into per-hand subtasks and trains dedicated policies for each. By exploiting bilateral symmetry via equivariant neural networks, experience from one arm is inherently leveraged by the opposite arm. We then distill the subtask policies into a global ambidextrous policy that is independent of the hand-task assignment. We evaluate SYMDEX on six challenging simulated manipulation tasks and demonstrate successful real-world deployment on two of them. Our approach strongly outperforms baselines on complex task in which the left and right hands perform different roles. We further demonstrate SYMDEX's scalability by extending it to a four-arm manipulation setup, where our symmetry-aware policies enable effective multi-arm collaboration and coordination. Our results highlight how structural symmetry as inductive bias in policy learning enhances sample efficiency, robustness, and generalization across diverse dexterous manipulation tasks.
DIME:Diffusion-Based Maximum Entropy Reinforcement Learning
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:Maximum entropy reinforcement learning (MaxEnt-RL) has become the standard approach to RL due to its beneficial exploration properties. Traditionally, policies are parameterized using Gaussian distributions, which significantly limits their representational capacity. Diffusion-based policies offer a more expressive alternative, yet integrating them into MaxEnt-RL poses challenges--primarily due to the intractability of computing their marginal entropy. To overcome this, we propose Diffusion-Based Maximum Entropy RL (DIME). DIME leverages recent advances in approximate inference with diffusion models to derive a lower bound on the maximum entropy objective. Additionally, we propose a policy iteration scheme that provably converges to the optimal diffusion policy. Our method enables the use of expressive diffusion-based policies while retaining the principled exploration benefits of MaxEnt-RL, significantly outperforming other diffusion-based methods on challenging high-dimensional control benchmarks. It is also competitive with state-of-the-art non-diffusion based RL methods while requiring fewer algorithmic design choices and smaller update-to-data ratios, reducing computational complexity.
Learning Multimodal Behaviors from Scratch with Diffusion Policy Gradient
Jun 02, 2024



Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms typically parameterize the policy as a deep network that outputs either a deterministic action or a stochastic one modeled as a Gaussian distribution, hence restricting learning to a single behavioral mode. Meanwhile, diffusion models emerged as a powerful framework for multimodal learning. However, the use of diffusion policies in online RL is hindered by the intractability of policy likelihood approximation, as well as the greedy objective of RL methods that can easily skew the policy to a single mode. This paper presents Deep Diffusion Policy Gradient (DDiffPG), a novel actor-critic algorithm that learns from scratch multimodal policies parameterized as diffusion models while discovering and maintaining versatile behaviors. DDiffPG explores and discovers multiple modes through off-the-shelf unsupervised clustering combined with novelty-based intrinsic motivation. DDiffPG forms a multimodal training batch and utilizes mode-specific Q-learning to mitigate the inherent greediness of the RL objective, ensuring the improvement of the diffusion policy across all modes. Our approach further allows the policy to be conditioned on mode-specific embeddings to explicitly control the learned modes. Empirical studies validate DDiffPG's capability to master multimodal behaviors in complex, high-dimensional continuous control tasks with sparse rewards, also showcasing proof-of-concept dynamic online replanning when navigating mazes with unseen obstacles.
Reconciling Reality through Simulation: A Real-to-Sim-to-Real Approach for Robust Manipulation
Mar 06, 2024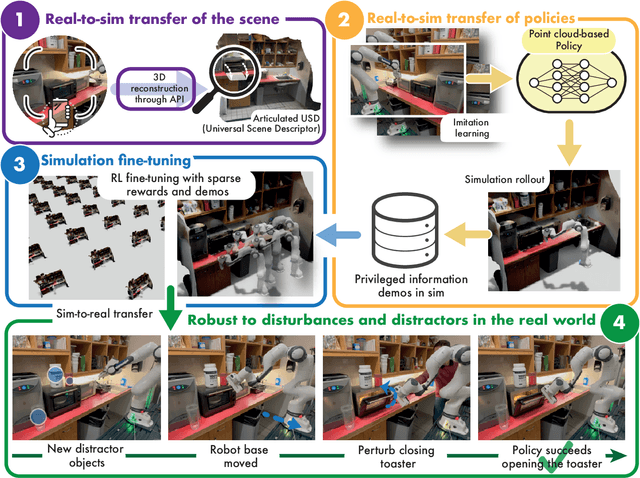
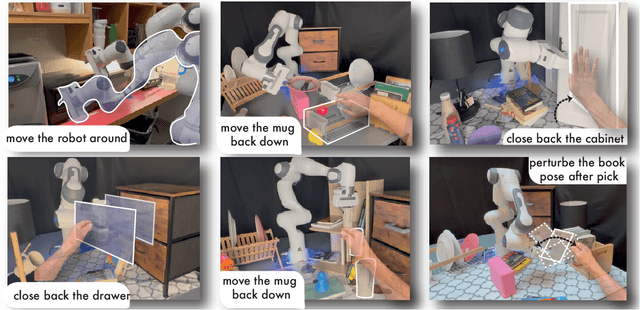
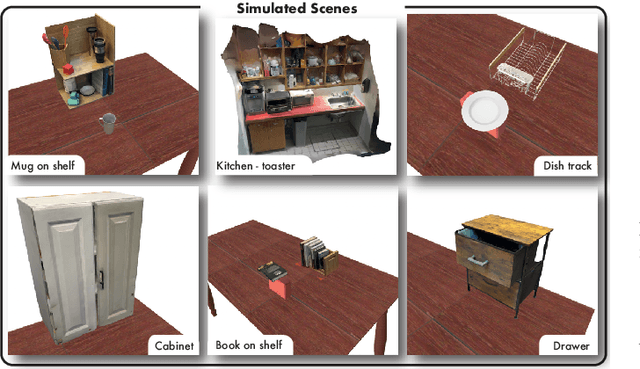

Abstract:Imitation learning methods need significant human supervision to learn policies robust to changes in object poses, physical disturbances, and visual distractors. Reinforcement learning, on the other hand, can explore the environment autonomously to learn robust behaviors but may require impractical amounts of unsafe real-world data collection. To learn performant, robust policies without the burden of unsafe real-world data collection or extensive human supervision, we propose RialTo, a system for robustifying real-world imitation learning policies via reinforcement learning in "digital twin" simulation environments constructed on the fly from small amounts of real-world data. To enable this real-to-sim-to-real pipeline, RialTo proposes an easy-to-use interface for quickly scanning and constructing digital twins of real-world environments. We also introduce a novel "inverse distillation" procedure for bringing real-world demonstrations into simulated environments for efficient fine-tuning, with minimal human intervention and engineering required. We evaluate RialTo across a variety of robotic manipulation problems in the real world, such as robustly stacking dishes on a rack, placing books on a shelf, and six other tasks. RialTo increases (over 67%) in policy robustness without requiring extensive human data collection. Project website and videos at https://real-to-sim-to-real.github.io/RialTo/
Parallel $Q$-Learning: Scaling Off-policy Reinforcement Learning under Massively Parallel Simulation
Jul 24, 2023Abstract:Reinforcement learning is time-consuming for complex tasks due to the need for large amounts of training data. Recent advances in GPU-based simulation, such as Isaac Gym, have sped up data collection thousands of times on a commodity GPU. Most prior works used on-policy methods like PPO due to their simplicity and ease of scaling. Off-policy methods are more data efficient but challenging to scale, resulting in a longer wall-clock training time. This paper presents a Parallel $Q$-Learning (PQL) scheme that outperforms PPO in wall-clock time while maintaining superior sample efficiency of off-policy learning. PQL achieves this by parallelizing data collection, policy learning, and value learning. Different from prior works on distributed off-policy learning, such as Apex, our scheme is designed specifically for massively parallel GPU-based simulation and optimized to work on a single workstation. In experiments, we demonstrate that $Q$-learning can be scaled to \textit{tens of thousands of parallel environments} and investigate important factors affecting learning speed. The code is available at https://github.com/Improbable-AI/pql.
ElegantRL-Podracer: Scalable and Elastic Library for Cloud-Native Deep Reinforcement Learning
Dec 11, 2021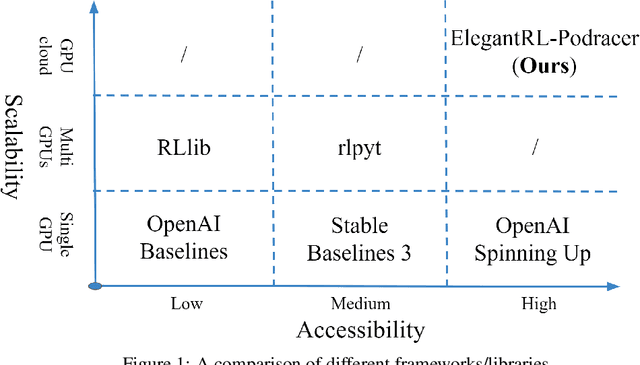
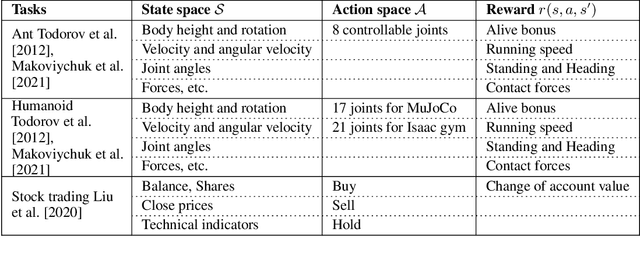
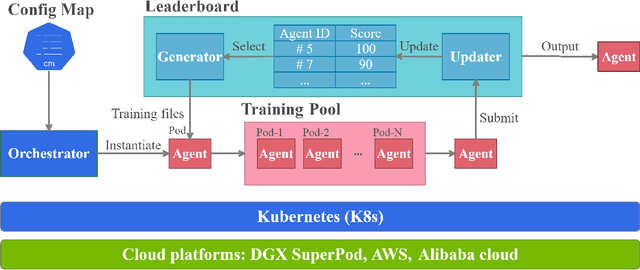
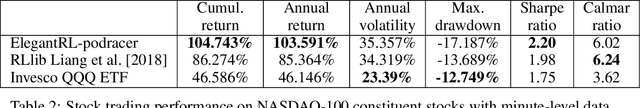
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has revolutionized learning and actuation in applications such as game playing and robotic control. The cost of data collection, i.e., generating transitions from agent-environment interactions, remains a major challenge for wider DRL adoption in complex real-world problems. Following a cloud-native paradigm to train DRL agents on a GPU cloud platform is a promising solution. In this paper, we present a scalable and elastic library ElegantRL-podracer for cloud-native deep reinforcement learning, which efficiently supports millions of GPU cores to carry out massively parallel training at multiple levels. At a high-level, ElegantRL-podracer employs a tournament-based ensemble scheme to orchestrate the training process on hundreds or even thousands of GPUs, scheduling the interactions between a leaderboard and a training pool with hundreds of pods. At a low-level, each pod simulates agent-environment interactions in parallel by fully utilizing nearly 7,000 GPU CUDA cores in a single GPU. Our ElegantRL-podracer library features high scalability, elasticity and accessibility by following the development principles of containerization, microservices and MLOps. Using an NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD cloud, we conduct extensive experiments on various tasks in locomotion and stock trading and show that ElegantRL-podracer substantially outperforms RLlib. Our codes are available on GitHub.
* 9 pages, 7 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge