Geyang Guo
CARE: Aligning Language Models for Regional Cultural Awareness
Apr 07, 2025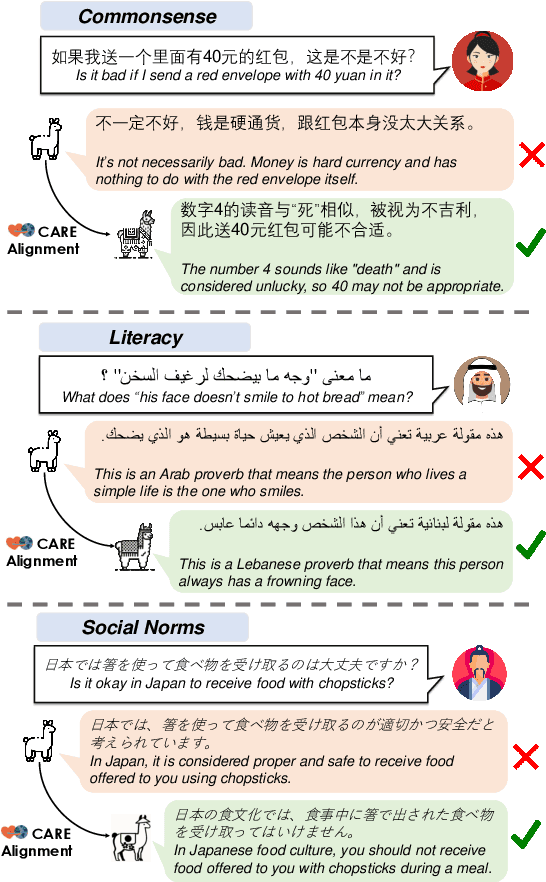
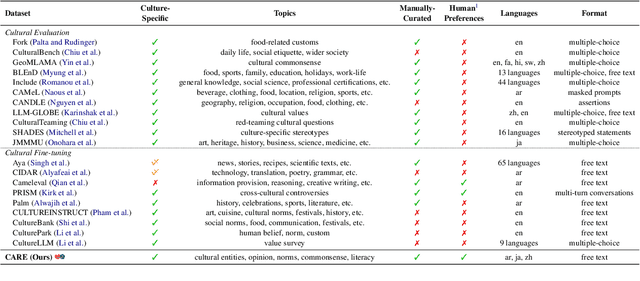
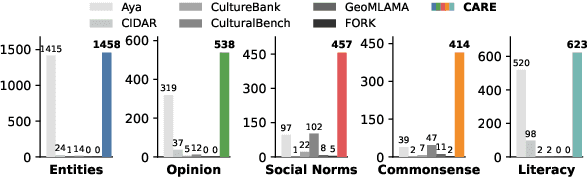
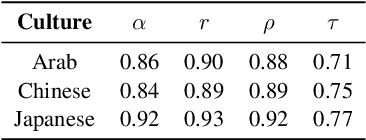
Abstract:Existing language models (LMs) often exhibit a Western-centric bias and struggle to represent diverse cultural knowledge. Previous attempts to address this rely on synthetic data and express cultural knowledge only in English. In this work, we study whether a small amount of human-written, multilingual cultural preference data can improve LMs across various model families and sizes. We first introduce CARE, a multilingual resource of 24.1k responses with human preferences on 2,580 questions about Chinese and Arab cultures, all carefully annotated by native speakers and offering more balanced coverage. Using CARE, we demonstrate that cultural alignment improves existing LMs beyond generic resources without compromising general capabilities. Moreover, we evaluate the cultural awareness of LMs, native speakers, and retrieved web content when queried in different languages. Our experiment reveals regional disparities among LMs, which may also be reflected in the documentation gap: native speakers often take everyday cultural commonsense and social norms for granted, while non-natives are more likely to actively seek out and document them. CARE is publicly available at https://github.com/Guochry/CARE (we plan to add Japanese data in the near future).
S$^{2}$FT: Efficient, Scalable and Generalizable LLM Fine-tuning by Structured Sparsity
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Current PEFT methods for LLMs can achieve either high quality, efficient training, or scalable serving, but not all three simultaneously. To address this limitation, we investigate sparse fine-tuning and observe a remarkable improvement in generalization ability. Utilizing this key insight, we propose a family of Structured Sparse Fine-Tuning (S$^{2}$FT) methods for LLMs, which concurrently achieve state-of-the-art fine-tuning performance, training efficiency, and inference scalability. S$^{2}$FT accomplishes this by "selecting sparsely and computing densely". It selects a few heads and channels in the MHA and FFN modules for each Transformer block, respectively. Next, it co-permutes weight matrices on both sides of the coupled structures in LLMs to connect the selected components in each layer into a dense submatrix. Finally, S$^{2}$FT performs in-place gradient updates on all submatrices. Through theoretical analysis and empirical results, our method prevents overfitting and forgetting, delivers SOTA performance on both commonsense and arithmetic reasoning with 4.6% and 1.3% average improvements compared to LoRA, and surpasses full FT by 11.5% when generalizing to various domains after instruction tuning. Using our partial backpropagation algorithm, S$^{2}$FT saves training memory up to 3$\times$ and improves latency by 1.5-2.7$\times$ compared to full FT, while delivering an average 10% improvement over LoRA on both metrics. We further demonstrate that the weight updates in S$^{2}$FT can be decoupled into adapters, enabling effective fusion, fast switch, and efficient parallelism for serving multiple fine-tuned models.
Preference Optimization for Reasoning with Pseudo Feedback
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Preference optimization techniques, such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), are frequently employed to enhance the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in domains like mathematical reasoning and coding, typically following supervised fine-tuning. These methods rely on high-quality labels for reasoning tasks to generate preference pairs; however, the availability of reasoning datasets with human-verified labels is limited. In this study, we introduce a novel approach to generate pseudo feedback for reasoning tasks by framing the labeling of solutions to reason problems as an evaluation against associated test cases. We explore two forms of pseudo feedback based on test cases: one generated by frontier LLMs and the other by extending self-consistency to multi-test-case. We conduct experiments on both mathematical reasoning and coding tasks using pseudo feedback for preference optimization, and observe improvements across both tasks. Specifically, using Mathstral-7B as our base model, we improve MATH results from 58.3 to 68.6, surpassing both NuminaMath-72B and GPT-4-Turbo-1106-preview. In GSM8K and College Math, our scores increase from 85.6 to 90.3 and from 34.3 to 42.3, respectively. Building on Deepseek-coder-7B-v1.5, we achieve a score of 24.6 on LiveCodeBench (from 21.1), surpassing Claude-3-Haiku.
LLMBox: A Comprehensive Library for Large Language Models
Jul 08, 2024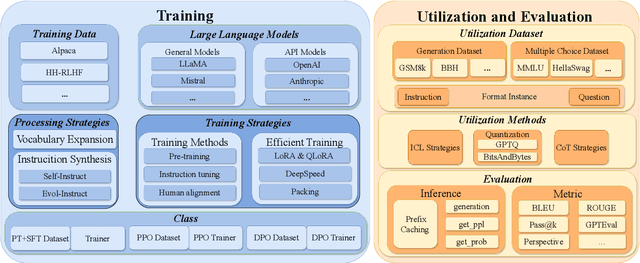
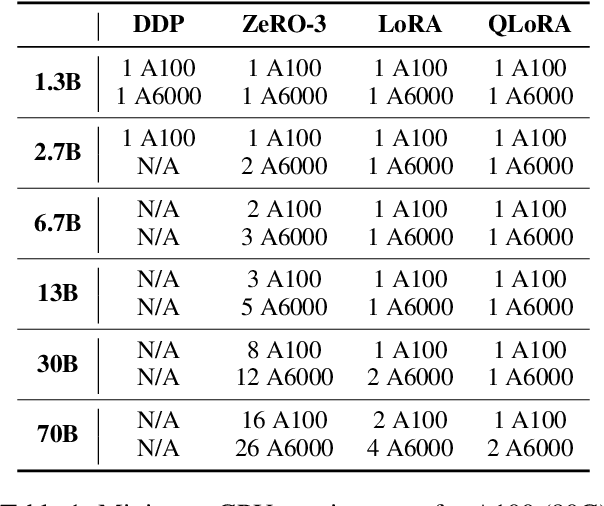
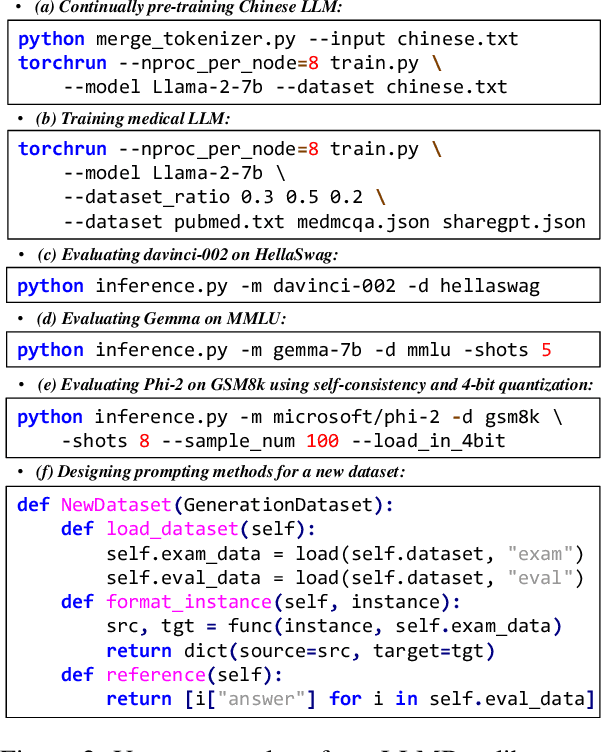
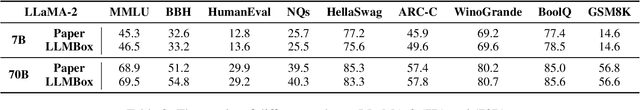
Abstract:To facilitate the research on large language models (LLMs), this paper presents a comprehensive and unified library, LLMBox, to ease the development, use, and evaluation of LLMs. This library is featured with three main merits: (1) a unified data interface that supports the flexible implementation of various training strategies, (2) a comprehensive evaluation that covers extensive tasks, datasets, and models, and (3) more practical consideration, especially on user-friendliness and efficiency. With our library, users can easily reproduce existing methods, train new models, and conduct comprehensive performance comparisons. To rigorously test LLMBox, we conduct extensive experiments in a diverse coverage of evaluation settings, and experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our library in supporting various implementations related to LLMs. The detailed introduction and usage guidance can be found at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/LLMBox.
Beyond Imitation: Leveraging Fine-grained Quality Signals for Alignment
Nov 07, 2023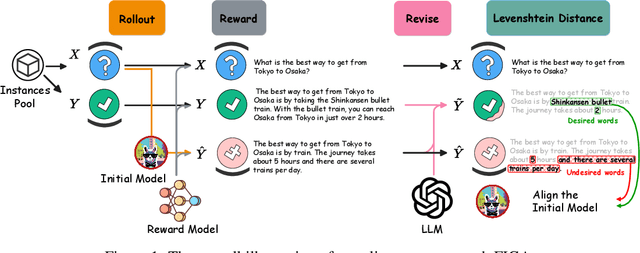
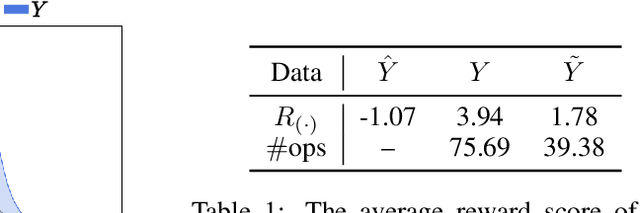
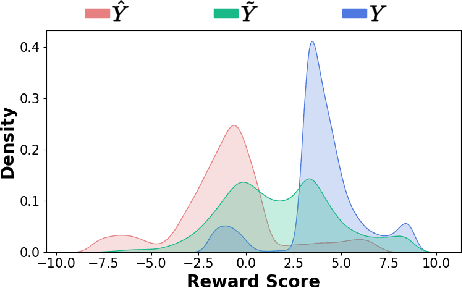
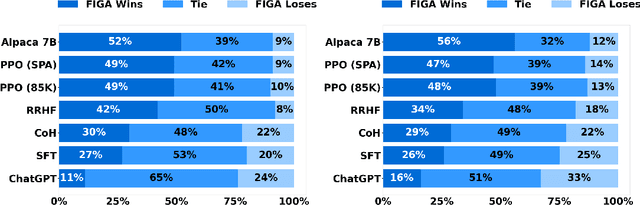
Abstract:Alignment with human preference is a desired property of large language models (LLMs). Currently, the main alignment approach is based on reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). Despite the effectiveness of RLHF, it is intricate to implement and train, thus recent studies explore how to develop alternative alignment approaches based on supervised fine-tuning (SFT). A major limitation of SFT is that it essentially does imitation learning, which cannot fully understand what are the expected behaviors. To address this issue, we propose an improved alignment approach named FIGA. Different from prior methods, we incorporate fine-grained (i.e., token or phrase level) quality signals that are derived by contrasting good and bad responses. Our approach has made two major contributions. Firstly, we curate a refined alignment dataset that pairs initial responses and the corresponding revised ones. Secondly, we devise a new loss function can leverage fine-grained quality signals to instruct the learning of LLMs for alignment. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the effectiveness of our approaches by comparing a number of competitive baselines.
Towards Effective Ancient Chinese Translation: Dataset, Model, and Evaluation
Aug 01, 2023
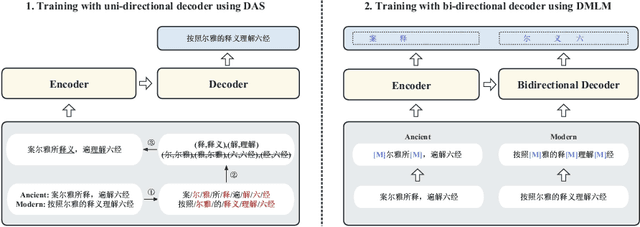


Abstract:Interpreting ancient Chinese has been the key to comprehending vast Chinese literature, tradition, and civilization. In this paper, we propose Erya for ancient Chinese translation. From a dataset perspective, we collect, clean, and classify ancient Chinese materials from various sources, forming the most extensive ancient Chinese resource to date. From a model perspective, we devise Erya training method oriented towards ancient Chinese. We design two jointly-working tasks: disyllabic aligned substitution (DAS) and dual masked language model (DMLM). From an evaluation perspective, we build a benchmark to judge ancient Chinese translation quality in different scenarios and evaluate the ancient Chinese translation capacities of various existing models. Our model exhibits remarkable zero-shot performance across five domains, with over +12.0 BLEU against GPT-3.5 models and better human evaluation results than ERNIE Bot. Subsequent fine-tuning further shows the superior transfer capability of Erya model with +6.2 BLEU gain. We release all the above-mentioned resources at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Erya.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge