Shiyi Xu
DexterCap: An Affordable and Automated System for Capturing Dexterous Hand-Object Manipulation
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Capturing fine-grained hand-object interactions is challenging due to severe self-occlusion from closely spaced fingers and the subtlety of in-hand manipulation motions. Existing optical motion capture systems rely on expensive camera setups and extensive manual post-processing, while low-cost vision-based methods often suffer from reduced accuracy and reliability under occlusion. To address these challenges, we present DexterCap, a low-cost optical capture system for dexterous in-hand manipulation. DexterCap uses dense, character-coded marker patches to achieve robust tracking under severe self-occlusion, together with an automated reconstruction pipeline that requires minimal manual effort. With DexterCap, we introduce DexterHand, a dataset of fine-grained hand-object interactions covering diverse manipulation behaviors and objects, from simple primitives to complex articulated objects such as a Rubik's Cube. We release the dataset and code to support future research on dexterous hand-object interaction.
ICPC-Eval: Probing the Frontiers of LLM Reasoning with Competitive Programming Contests
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:With the significant progress of large reasoning models in complex coding and reasoning tasks, existing benchmarks, like LiveCodeBench and CodeElo, are insufficient to evaluate the coding capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in real competition environments. Moreover, current evaluation metrics such as Pass@K fail to capture the reflective abilities of reasoning models. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{ICPC-Eval}, a top-level competitive coding benchmark designed to probing the frontiers of LLM reasoning. ICPC-Eval includes 118 carefully curated problems from 11 recent ICPC contests held in various regions of the world, offering three key contributions: 1) A challenging realistic ICPC competition scenario, featuring a problem type and difficulty distribution consistent with actual contests. 2) A robust test case generation method and a corresponding local evaluation toolkit, enabling efficient and accurate local evaluation. 3) An effective test-time scaling evaluation metric, Refine@K, which allows iterative repair of solutions based on execution feedback. The results underscore the significant challenge in evaluating complex reasoning abilities: top-tier reasoning models like DeepSeek-R1 often rely on multi-turn code feedback to fully unlock their in-context reasoning potential when compared to non-reasoning counterparts. Furthermore, despite recent advancements in code generation, these models still lag behind top-performing human teams. We release the benchmark at: https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs
LLMBox: A Comprehensive Library for Large Language Models
Jul 08, 2024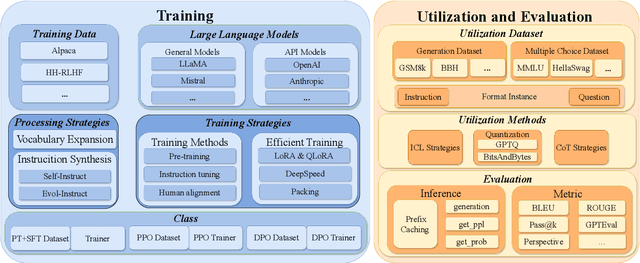
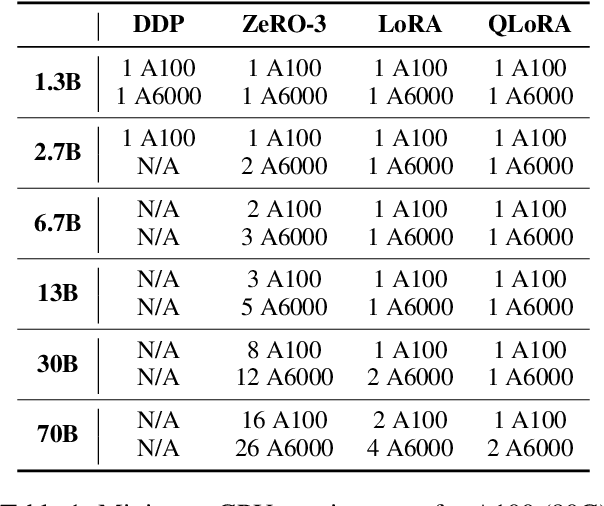
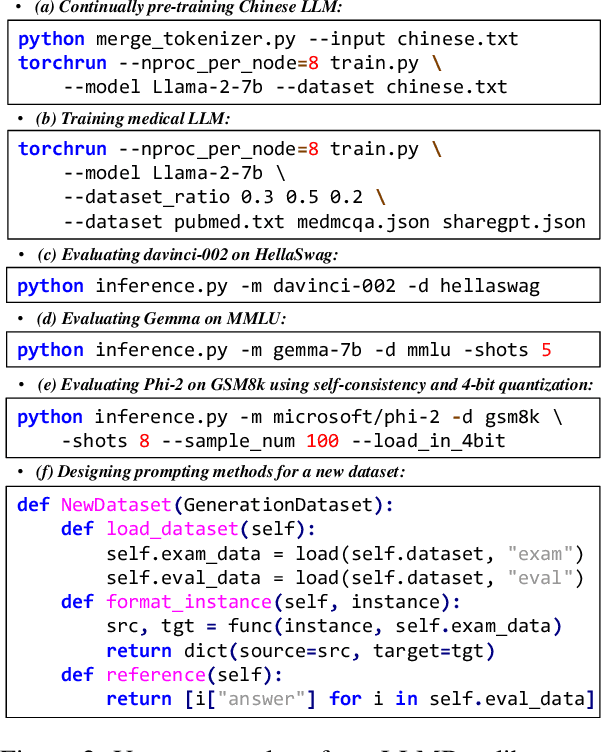
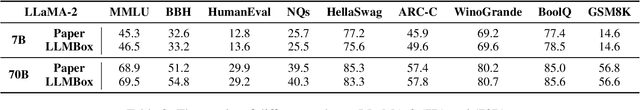
Abstract:To facilitate the research on large language models (LLMs), this paper presents a comprehensive and unified library, LLMBox, to ease the development, use, and evaluation of LLMs. This library is featured with three main merits: (1) a unified data interface that supports the flexible implementation of various training strategies, (2) a comprehensive evaluation that covers extensive tasks, datasets, and models, and (3) more practical consideration, especially on user-friendliness and efficiency. With our library, users can easily reproduce existing methods, train new models, and conduct comprehensive performance comparisons. To rigorously test LLMBox, we conduct extensive experiments in a diverse coverage of evaluation settings, and experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our library in supporting various implementations related to LLMs. The detailed introduction and usage guidance can be found at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/LLMBox.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge