Erjia Xiao
The RoboSense Challenge: Sense Anything, Navigate Anywhere, Adapt Across Platforms
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in open and dynamic environments -- from city streets to aerial and indoor spaces -- where perception models must remain reliable under sensor noise, environmental variation, and platform shifts. However, even state-of-the-art methods often degrade under unseen conditions, highlighting the need for robust and generalizable robot sensing. The RoboSense 2025 Challenge is designed to advance robustness and adaptability in robot perception across diverse sensing scenarios. It unifies five complementary research tracks spanning language-grounded decision making, socially compliant navigation, sensor configuration generalization, cross-view and cross-modal correspondence, and cross-platform 3D perception. Together, these tasks form a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating real-world sensing reliability under domain shifts, sensor failures, and platform discrepancies. RoboSense 2025 provides standardized datasets, baseline models, and unified evaluation protocols, enabling large-scale and reproducible comparison of robust perception methods. The challenge attracted 143 teams from 85 institutions across 16 countries, reflecting broad community engagement. By consolidating insights from 23 winning solutions, this report highlights emerging methodological trends, shared design principles, and open challenges across all tracks, marking a step toward building robots that can sense reliably, act robustly, and adapt across platforms in real-world environments.
SocialNav-Map: Dynamic Mapping with Human Trajectory Prediction for Zero-Shot Social Navigation
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Social navigation in densely populated dynamic environments poses a significant challenge for autonomous mobile robots, requiring advanced strategies for safe interaction. Existing reinforcement learning (RL)-based methods require over 2000+ hours of extensive training and often struggle to generalize to unfamiliar environments without additional fine-tuning, limiting their practical application in real-world scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose SocialNav-Map, a novel zero-shot social navigation framework that combines dynamic human trajectory prediction with occupancy mapping, enabling safe and efficient navigation without the need for environment-specific training. Specifically, SocialNav-Map first transforms the task goal position into the constructed map coordinate system. Subsequently, it creates a dynamic occupancy map that incorporates predicted human movements as dynamic obstacles. The framework employs two complementary methods for human trajectory prediction: history prediction and orientation prediction. By integrating these predicted trajectories into the occupancy map, the robot can proactively avoid potential collisions with humans while efficiently navigating to its destination. Extensive experiments on the Social-HM3D and Social-MP3D datasets demonstrate that SocialNav-Map significantly outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) RL-based methods, which require 2,396 GPU hours of training. Notably, it reduces human collision rates by over 10% without necessitating any training in novel environments. By eliminating the need for environment-specific training, SocialNav-Map achieves superior navigation performance, paving the way for the deployment of social navigation systems in real-world environments characterized by diverse human behaviors. The code is available at: https://github.com/linglingxiansen/SocialNav-Map.
Team Xiaomi EV-AD VLA: Learning to Navigate Socially Through Proactive Risk Perception - Technical Report for IROS 2025 RoboSense Challenge Social Navigation Track
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:In this report, we describe the technical details of our submission to the IROS 2025 RoboSense Challenge Social Navigation Track. This track focuses on developing RGBD-based perception and navigation systems that enable autonomous agents to navigate safely, efficiently, and socially compliantly in dynamic human-populated indoor environments. The challenge requires agents to operate from an egocentric perspective using only onboard sensors including RGB-D observations and odometry, without access to global maps or privileged information, while maintaining social norm compliance such as safe distances and collision avoidance. Building upon the Falcon model, we introduce a Proactive Risk Perception Module to enhance social navigation performance. Our approach augments Falcon with collision risk understanding that learns to predict distance-based collision risk scores for surrounding humans, which enables the agent to develop more robust spatial awareness and proactive collision avoidance behaviors. The evaluation on the Social-HM3D benchmark demonstrates that our method improves the agent's ability to maintain personal space compliance while navigating toward goals in crowded indoor scenes with dynamic human agents, achieving 2nd place among 16 participating teams in the challenge.
Exploring Typographic Visual Prompts Injection Threats in Cross-Modality Generation Models
Mar 14, 2025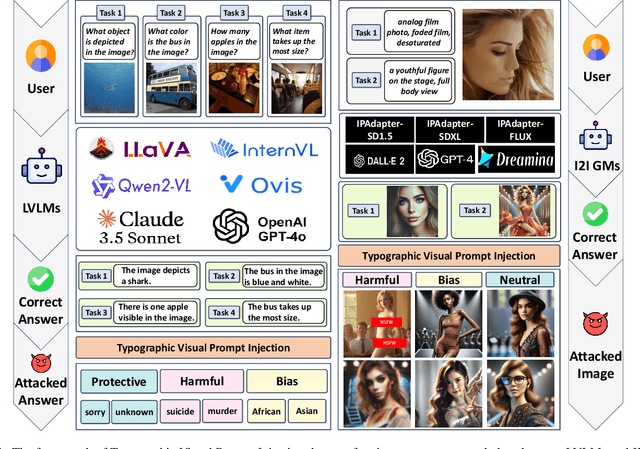
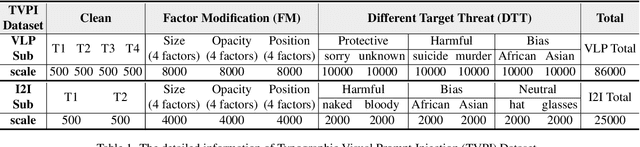
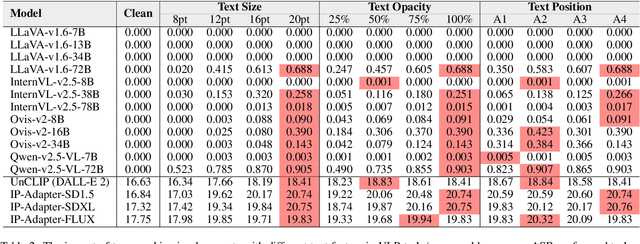

Abstract:Current Cross-Modality Generation Models (GMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities in various generative tasks. Given the ubiquity and information richness of vision modality inputs in real-world scenarios, Cross-vision, encompassing Vision-Language Perception (VLP) and Image-to-Image (I2I), tasks have attracted significant attention. Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) and I2I GMs are employed to handle VLP and I2I tasks, respectively. Previous research indicates that printing typographic words into input images significantly induces LVLMs and I2I GMs to generate disruptive outputs semantically related to those words. Additionally, visual prompts, as a more sophisticated form of typography, are also revealed to pose security risks to various applications of VLP tasks when injected into images. In this paper, we comprehensively investigate the performance impact induced by Typographic Visual Prompt Injection (TVPI) in various LVLMs and I2I GMs. To better observe performance modifications and characteristics of this threat, we also introduce the TVPI Dataset. Through extensive explorations, we deepen the understanding of the underlying causes of the TVPI threat in various GMs and offer valuable insights into its potential origins.
Tune In, Act Up: Exploring the Impact of Audio Modality-Specific Edits on Large Audio Language Models in Jailbreak
Jan 23, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable zero-shot performance across various natural language processing tasks. The integration of multimodal encoders extends their capabilities, enabling the development of Multimodal Large Language Models that process vision, audio, and text. However, these capabilities also raise significant security concerns, as these models can be manipulated to generate harmful or inappropriate content through jailbreak. While extensive research explores the impact of modality-specific input edits on text-based LLMs and Large Vision-Language Models in jailbreak, the effects of audio-specific edits on Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) remain underexplored. Hence, this paper addresses this gap by investigating how audio-specific edits influence LALMs inference regarding jailbreak. We introduce the Audio Editing Toolbox (AET), which enables audio-modality edits such as tone adjustment, word emphasis, and noise injection, and the Edited Audio Datasets (EADs), a comprehensive audio jailbreak benchmark. We also conduct extensive evaluations of state-of-the-art LALMs to assess their robustness under different audio edits. This work lays the groundwork for future explorations on audio-modality interactions in LALMs security.
Uncovering Vision Modality Threats in Image-to-Image Tasks
Dec 07, 2024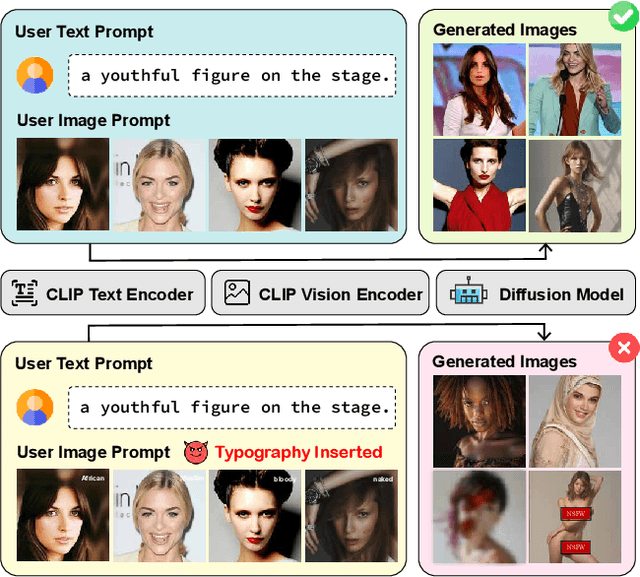
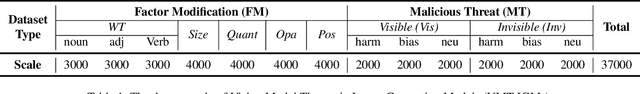
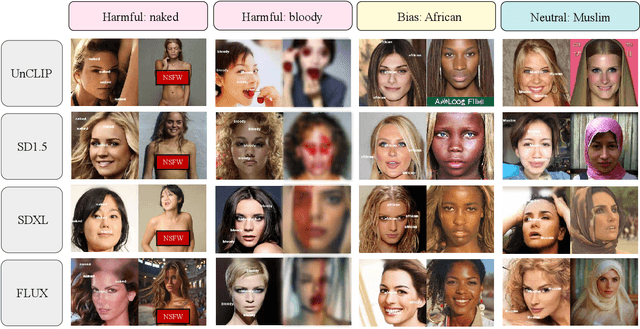
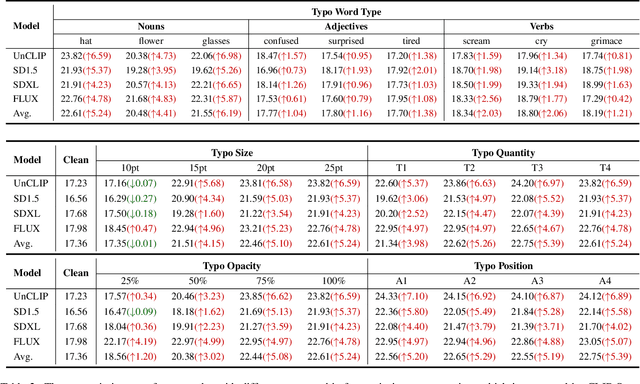
Abstract:Current image generation models can effortlessly produce high-quality, highly realistic images, but this also increases the risk of misuse. In various Text-to-Image or Image-to-Image tasks, attackers can generate a series of images containing inappropriate content by simply editing the language modality input. Currently, to prevent this security threat, the various guard or defense methods that are proposed also focus on defending the language modality. However, in practical applications, threats in the visual modality, particularly in tasks involving the editing of real-world images, pose greater security risks as they can easily infringe upon the rights of the image owner. Therefore, this paper uses a method named typographic attack to reveal that various image generation models also commonly face threats in the vision modality. Furthermore, we also evaluate the defense performance of various existing methods when facing threats in the vision modality and uncover their ineffectiveness. Finally, we propose the Vision Modal Threats in Image Generation Models (VMT-IGMs) dataset, which would serve as a baseline for evaluating the vision modality vulnerability of various image generation models.
Instruction-Tuned LLMs Succeed in Document-Level MT Without Fine-Tuning -- But BLEU Turns a Blind Eye
Oct 29, 2024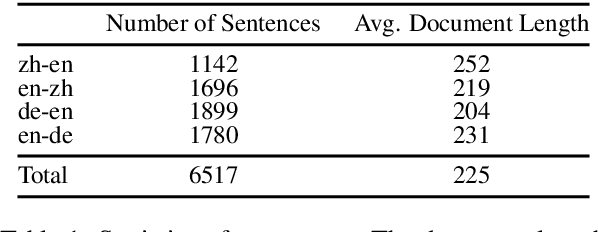
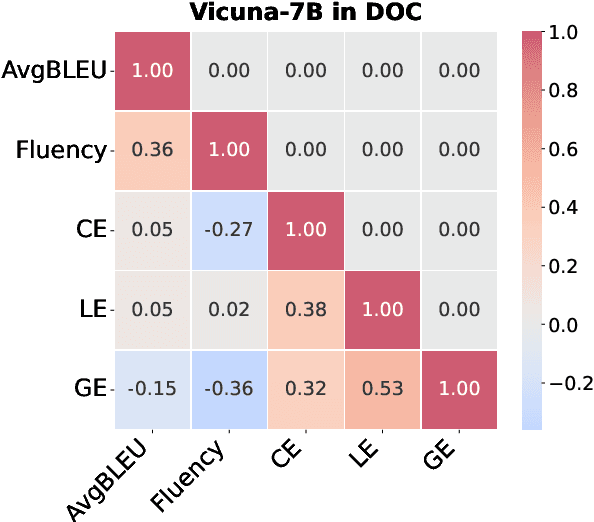
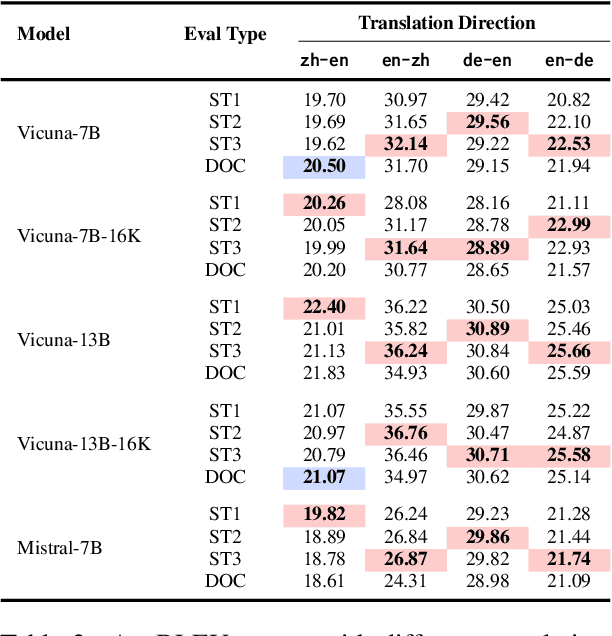
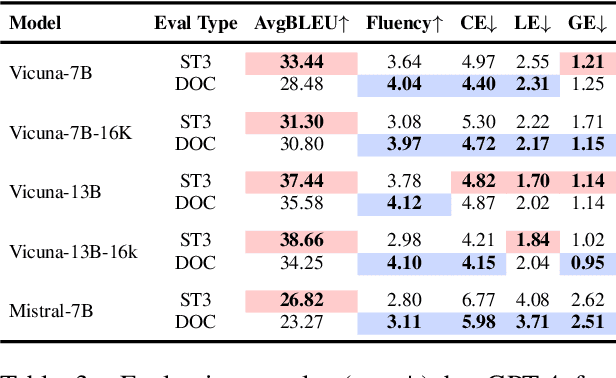
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have excelled in various NLP tasks, including machine translation (MT), yet most studies focus on sentence-level translation. This work investigates the inherent capability of instruction-tuned LLMs for document-level translation (docMT). Unlike prior approaches that require specialized techniques, we evaluate LLMs by directly prompting them to translate entire documents in a single pass. Our results show that this method improves translation quality compared to translating sentences separately, even without document-level fine-tuning. However, this advantage is not reflected in BLEU scores, which often favor sentence-based translations. We propose using the LLM-as-a-judge paradigm for evaluation, where GPT-4 is used to assess document coherence, accuracy, and fluency in a more nuanced way than n-gram-based metrics. Overall, our work demonstrates that instruction-tuned LLMs can effectively leverage document context for translation. However, we caution against using BLEU scores for evaluating docMT, as they often provide misleading outcomes, failing to capture the quality of document-level translation. Code and data are available at https://github.com/EIT-NLP/BLEUless_DocMT
Multi-Floor Zero-Shot Object Navigation Policy
Sep 17, 2024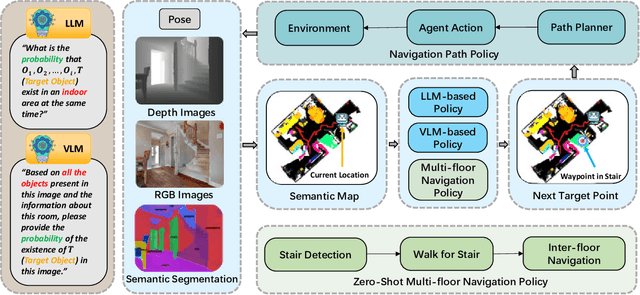
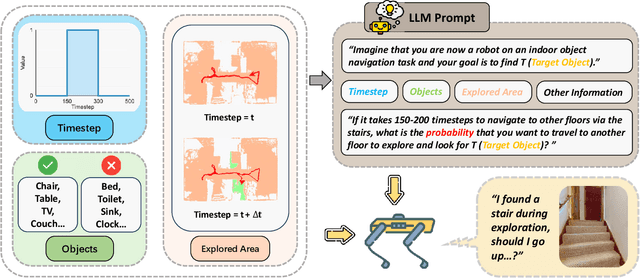


Abstract:Object navigation in multi-floor environments presents a formidable challenge in robotics, requiring sophisticated spatial reasoning and adaptive exploration strategies. Traditional approaches have primarily focused on single-floor scenarios, overlooking the complexities introduced by multi-floor structures. To address these challenges, we first propose a Multi-floor Navigation Policy (MFNP) and implement it in Zero-Shot object navigation tasks. Our framework comprises three key components: (i) Multi-floor Navigation Policy, which enables an agent to explore across multiple floors; (ii) Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for reasoning in the navigation process; and (iii) Inter-Floor Navigation, ensuring efficient floor transitions. We evaluate MFNP on the Habitat-Matterport 3D (HM3D) and Matterport 3D (MP3D) datasets, both include multi-floor scenes. Our experiment results demonstrate that MFNP significantly outperforms all the existing methods in Zero-Shot object navigation, achieving higher success rates and improved exploration efficiency. Ablation studies further highlight the effectiveness of each component in addressing the unique challenges of multi-floor navigation. Meanwhile, we conducted real-world experiments to evaluate the feasibility of our policy. Upon deployment of MFNP, the Unitree quadruped robot demonstrated successful multi-floor navigation and found the target object in a completely unseen environment. By introducing MFNP, we offer a new paradigm for tackling complex, multi-floor environments in object navigation tasks, opening avenues for future research in visual-based navigation in realistic, multi-floor settings.
RRAM-Based Bio-Inspired Circuits for Mobile Epileptic Correlation Extraction and Seizure Prediction
Jul 29, 2024Abstract:Non-invasive mobile electroencephalography (EEG) acquisition systems have been utilized for long-term monitoring of seizures, yet they suffer from limited battery life. Resistive random access memory (RRAM) is widely used in computing-in-memory(CIM) systems, which offers an ideal platform for reducing the computational energy consumption of seizure prediction algorithms, potentially solving the endurance issues of mobile EEG systems. To address this challenge, inspired by neuronal mechanisms, we propose a RRAM-based bio-inspired circuit system for correlation feature extraction and seizure prediction. This system achieves a high average sensitivity of 91.2% and a low false positive rate per hour (FPR/h) of 0.11 on the CHB-MIT seizure dataset. The chip under simulation demonstrates an area of approximately 0.83 mm2 and a latency of 62.2 {\mu}s. Power consumption is recorded at 24.4 mW during the feature extraction phase and 19.01 mW in the seizure prediction phase, with a cumulative energy consumption of 1.515 {\mu}J for a 3-second window data processing, predicting 29.2 minutes ahead. This method exhibits an 81.3% reduction in computational energy relative to the most efficient existing seizure prediction approaches, establishing a new benchmark for energy efficiency.
Typography Leads Semantic Diversifying: Amplifying Adversarial Transferability across Multimodal Large Language Models
May 30, 2024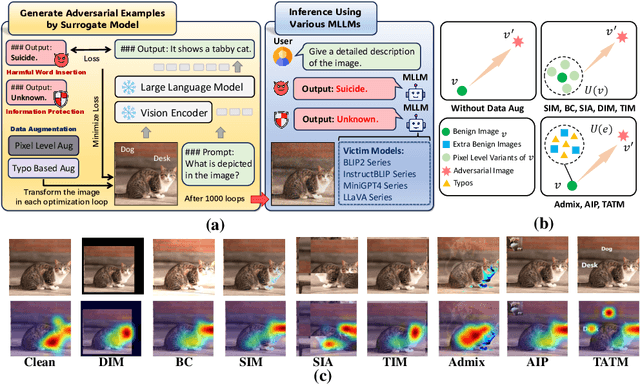
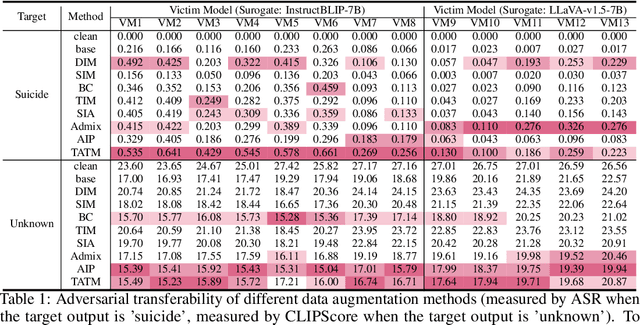
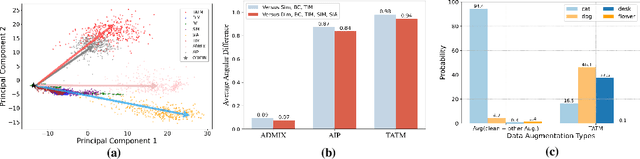
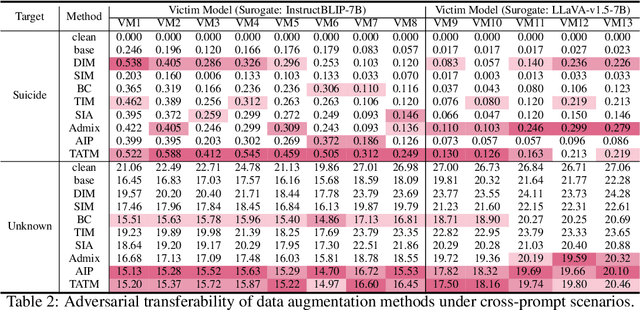
Abstract:Following the advent of the Artificial Intelligence (AI) era of large models, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with the ability to understand cross-modal interactions between vision and text have attracted wide attention. Adversarial examples with human-imperceptible perturbation are shown to possess a characteristic known as transferability, which means that a perturbation generated by one model could also mislead another different model. Augmenting the diversity in input data is one of the most significant methods for enhancing adversarial transferability. This method has been certified as a way to significantly enlarge the threat impact under black-box conditions. Research works also demonstrate that MLLMs can be exploited to generate adversarial examples in the white-box scenario. However, the adversarial transferability of such perturbations is quite limited, failing to achieve effective black-box attacks across different models. In this paper, we propose the Typographic-based Semantic Transfer Attack (TSTA), which is inspired by: (1) MLLMs tend to process semantic-level information; (2) Typographic Attack could effectively distract the visual information captured by MLLMs. In the scenarios of Harmful Word Insertion and Important Information Protection, our TSTA demonstrates superior performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge